Benzodioxan
Appearance
(Redirected from Benzodioxane)

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,3-Dihydro-1,4-benzodioxine | |
| Other names
Dihydrobenzodioxin; 1,4-Benzodioxane; Benzo-1,4-dioxane; Ethylene o-phenylene dioxide; Pyrocatechol ethylene ether
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H8O2 | |
| Molar mass | 136.150 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
The benzodioxans are a group of isomeric chemical compounds with the molecular formula C8H8O2.[1] There are three isomers of benzodioxan, as the second atom of oxygen of the dioxane can be in a second, third or fourth position: 1,2-dioxane, 1,3-dioxane and 1,4-dioxane, which respectively give 1,2-benzodioxan, 1,3-benzodioxan and 1,4-benzodioxan.[2][3]
Derivatives
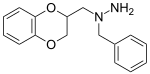
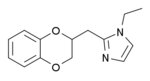
[edit]Some derivatives of 1,4-benzodioxan are used as pharmaceuticals including:[4][5][6][7]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "1,4-Benzodioxane". PubChem. National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 2022-09-05. Retrieved 2022-09-05.
- ^ "TECHNICAL FACT SHEET – 1,4-DIOXANE" (PDF). Technical Fact Sheet. 51 (6): 9. 2017. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-08-13. Retrieved 2022-09-05 – via United States Environmental Protection Agency.
- ^ Jablonski, Stanley (1967). Russian drug index. Public Health Service publication. U.S. Dept. of Health, Education, and Welfare, Public Health Service: United States Department of Health.
- ^ Sun, Juan; Cao, Ning; Zhang, Xiao-Min; Yang, Yu-Shun; Zhang, Yan-Bin; Wang, Xiao-Ming; Zhu, Hai-Liang (2011-08-15). "Oxadiazole derivatives containing 1,4-benzodioxan as potential immunosuppressive agents against RAW264.7 cells". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 19 (16): 4895–4902. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2011.06.061. ISSN 1464-3391. PMID 21782456.
- ^ "1,4-benzodioxan derivatives their preparation and pharmaceutical compositions containing them - Patent IL-43272-A - PubChem". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2022-09-05.
- ^ Sun, Juan; Wang, Su; Sheng, Gui-Hua; Lian, Zhi-Min; Liu, Han-Yu; Zhu, Hai-Liang (2016-11-01). "Synthesis of phenylpiperazine derivatives of 1,4-benzodioxan as selective COX-2 inhibitors and anti-inflammatory agents". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 24 (21): 5626–5632. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2016.09.023. ISSN 1464-3391. PMID 27658794.
- ^ Matos, M. Agostinha R.; Sousa, Clara C. S.; Morais, Victor M. F. (2008-08-28). "Experimental and computational thermochemistry of 1,4-benzodioxan and its 6-R derivatives". The Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 112 (34): 7961–7968. Bibcode:2008JPCA..112.7961M. doi:10.1021/jp803579y. ISSN 1520-5215. PMID 18683910.
External links
[edit] Media related to Benzodioxan at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Benzodioxan at Wikimedia Commons