(+)-Benzo(a)pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide
![(+)-Benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/0e/%28%2B%29-Benzo%28a%29pyrene-7%2C8-dihydrodiol-9%2C10-epoxide.png/220px-%28%2B%29-Benzo%28a%29pyrene-7%2C8-dihydrodiol-9%2C10-epoxide.png)
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(7R,8S,8aS,9aR)-7,8,8a,9a-Tetrahydrobenzo[1,12]tetrapheno[10,11-b]oxirene-7,8-diol | |
| Other names
(+)-Benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide
(+)-7,8,9,10-Tetrahydrobenzo[a]pyrene-7,8-diol-9,10-epoxide (7R,8S,8aR,9aS)-7,8,8a,9a-Tetrahydrobenzo[1,12]tetrapheno[10,11-b]oxirene-7,8-diol 7,8,8a,9a-Tetrahydro-(7R,8S,8aR,9aS)-benzo[10,11]chryseno[3,4-b]oxirene-7,8-diol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H14O3 | |
| Molar mass | 302.329 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.6 ± 0.1 g cm−3 |
| Boiling point | 594.2 ± 50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Dimethyl sulfoxide, dichloromethane, methanol | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
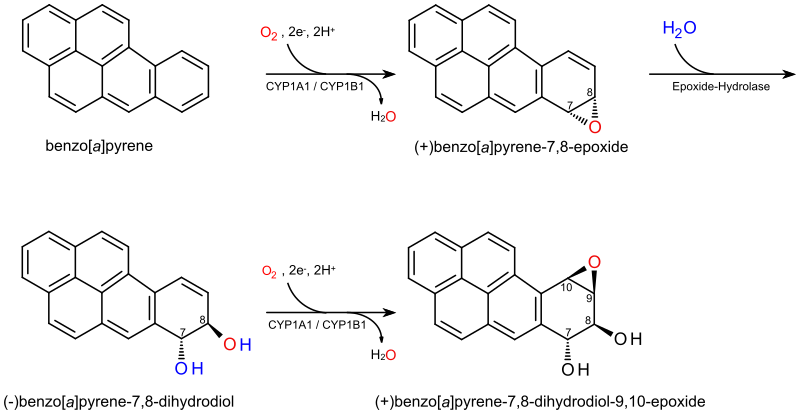
(+)-Benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide is an organic compound with molecular formula C20H14O3. It is a metabolite and derivative of benzo[a]pyrene (found in tobacco smoke[1]) as a result of oxidation to include hydroxyl and epoxide functionalities. (+)-Benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide binds to the N2 atom of a guanine nucleobase in DNA,[2][3] distorting the double helix structure[4] by intercalation of the pyrene moiety between base pairs through π-stacking.[5] The carcinogenic properties of tobacco smoking are attributed in part to this compound binding and inactivating the tumor suppression ability of certain genes, leading to genetic mutations and potentially to cancer.[6]
Structure
[edit]
Pyrene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon consisting of four benzene rings fused together in a planar aromatic arrangement which approximates a rhombus in shape. Benzo[a]pyrene is a derivative in which a fifth benzene ring has been fused to the pyrene system, and is a component of tobacco smoke which is a procarcinogen partly responsible for the carcinogenic and mutagenic effects of smoking.[1] Benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide is a metabolite of benzo[a]pyrene formed by the introduction of vicinal hydroxyl and epoxide functional groups to the fifth benzene ring.[7] These oxidations are stereoselective, producing the pair of enantiomers with the hydroxyl groups on opposite sides of the pyrene plane and with the epoxide on the same side as its adjacent hydroxyl group. (+)-Benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide is specifically the (7R,8S,8aR,9aS) stereoisomer.
Biosynthesis
[edit]The metabolism of the tobacco smoke procarcinogen benzo[a]pyrene involves three distinct steps – the introduction of an epoxide group in the 7,8-position, its hydration to a vicinal diol and the introduction of an epoxide in the 9,10-position.[8][9] In the first step, a cytochrome P450 1A1 (CYP1A1) catalysed oxidation produces several products including (+)-benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-epoxide.[7] The enzyme epoxide hydrolase, then hydrates the epoxide ring to yield the vicinal diol (−)-benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol, which is then oxidised by cytochrome P450 oxidase again forming the mutagen and carcinogen (+)-benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide. This diol epoxide covalently binds to DNA by a ring-opening to alkylate the nucleobase forming a distorted structure, as shown at right, with intercalation of a pyrene polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon moiety between the base pairs favouring π-stacking;[5] these distortions have been confirmed by X-ray crystallographic and nuclear magnetic resonance structure studies.[2] Aflatoxin has a similar mechanism of action, though its binding is through the N7, rather than the N2,[3] position of guanine.[10] Multiple stereochemical outcomes are possible from these transformations. The anti stereoisomer (shown here) and its enantiomer are the ultimate carcinogens from benzo[a]pyrene, but the syn isomers are also produced.[11]
Biochemistry
[edit]
(+)-Benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide has been shown to bind to an N2 atom of a guanine nucleobase in DNA,[2][3] distorting the double helix structure[4] by intercalation of the pyrene moiety between base pairs through π-stacking.[5]
There are indications that (+)-benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide specifically targets the protective p53 gene;[12] More than 50 percent of human tumors contain a mutation or deletion of the p53 gene.[13] This gene is a transcription factor that regulates the cell cycle and hence functions as a tumor suppressor. The anti-benzo[a]pyrene diol epoxides induce guanine to thymine transversions in related areas of p53, thereby inactivating its tumor suppression ability in certain cells, leading to genetic mutations and potentially to cancer.[6]
Induction of CYP1A1 by benzo[a]pyrene occurs via binding to the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in the cytosol, leading the transformed receptor to translocate to the nucleus where it dimerises with aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator and then binds xenobiotic response elements in DNA located upstream of certain genes. This process increases transcription of genes including CYP1A1, resulting in increased CYP1A1 protein production.[14] This process is similar to induction of CYP1A1 by certain polychlorinated biphenyls and dioxins. Seemingly, CYP1A1 activity in the intestinal mucosa prevents major amounts of ingested benzo[a]pyrene to enter portal blood and systemic circulation.[15] Intestinal, but not hepatic, expression of CYP1A1 depends on TOLL-like receptor 2 (TLR2),[16] which is a eucaryotic receptor for bacterial surface structures such as lipoteichoic acid. Moreover, benzo[a]pyrene has been found to activate a transposon, LINE1, in humans.[17]
References
[edit]- ^ a b Seager, S. L.; Slabaugh, M. R. (2013). "Properties and Uses of Aromatic Compounds". Organic and Biochemistry for Today (8th ed.). Cengage Learning. pp. 65–66. ISBN 9781285605906.
- ^ a b c Pradhan, P.; Tirumala, S.; Liu, X.; Sayer, J. M.; Jerina, D. M.; Yeh, H. J. C. (2001). "Solution Structure of a Trans-Opened (10S)-dA Adduct of (+)-(7S,8R,9S,10R)-7,8-Dihydroxy-9,10-epoxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrobenzo[a]pyrene in a fully Complementary DNA Duplex: Evidence for a Major Syn Conformation". Biochemistry. 40 (20): 5870–5881. doi:10.1021/bi002896q. PMID 11352722.
- ^ a b c Karle, I. L.; Yagi, H.; Sayer, J. M.; Jerina, D. M. (2004). "Crystal and Molecular Structure of a Benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-diol-9,10-epoxide N2-Deoxyguanosine Adduct: Absolute Configuration and Conformation". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 101 (6): 1433–1438. Bibcode:2004PNAS..101.1433K. doi:10.1073/pnas.0307305101. PMC 341736. PMID 14757823.
- ^ a b Volk, D. E.; Thiviyanathan, V.; Rice, J. S.; Luxon, B. A.; Shah, J. H.; Yagi, H.; Sayer, J. M.; Yeh, H. J.; Jerina, D. M.; Gorenstein, D. G. (2003). "Solution structure of a cis-opened (10R)-N6-deoxyadenosine adduct of (9S,10R)-9,10-epoxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrobenzo[a]pyrene in a DNA duplex". Biochemistry. 42 (6): 1410–1420. doi:10.1021/bi026745u. PMID 12578353.
- ^ a b c Hargis, J. C.; Schaefer, H. F.; Houk, K. N.; Wheeler, S. E. (2010). "Noncovalent Interactions of a Benzo[a]pyrene Diol Epoxide with DNA Base Pairs: Insight into the Formation of Adducts of (+)-BaP DE-2 with DNA". Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 114 (4): 2038–2044. Bibcode:2010JPCA..114.2038H. doi:10.1021/jp911376p. PMC 2826197. PMID 20063873.
- ^ a b Eisenstadt, E.; Warren, A. J.; Porter, J.; Atkins, D.; Miller, J. H. (1982). "Carcinogenic Epoxides of Benzo[a]pyrene and Cyclopenta[cd]pyrene Induce Base Substitutions via Specific Transversions". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 79 (6): 1945–1949. Bibcode:1982PNAS...79.1945E. doi:10.1073/pnas.79.6.1945. PMC 346098. PMID 7043469.
- ^ a b Shou, M.; Gonzalez, F. J.; Gelboin, H. V. (1996). "Stereoselective Epoxidation and Hydration at the K-region of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons by cDNA-Expressed Cytochromes P450 1A1, 1A2, and Epoxide Hydrolase". Biochemistry. 35 (49): 15807–15813. doi:10.1021/bi962042z. PMID 8961944.
- ^ Jiang, H.; Gelhaus, S. L.; Mangal, D.; Harvey, R. G.; Blair, I. A.; Penning, T. M. (2007). "Metabolism of Benzo[a]pyrene in Human Bronchoalveolar H358 Cells Using Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry". Chemical Research in Toxicology. 20 (9): 1331–1341. doi:10.1021/tx700107z. PMC 2423818. PMID 17702526.
- ^ Uno, S.; Dalton, T. P.; Dragin, N.; Curran, C. P.; Derkenne, S.; Miller, M. L.; Shertzer, H. G.; Gonzalez, F. J.; Nebert, D. W. (2006). "Oral Benzo[a]pyrene in Cyp1 Knockout Mouse Lines: CYP1A1 Important in Detoxication, CYP1B1 Metabolism Required for Immune Damage Independent of Total-Body Burden and Clearance Rate". Molecular Pharmacology. 69 (4): 1103–1112. doi:10.1124/mol.105.021501. PMID 16377763. S2CID 10834208.
- ^ Eaton, D. L.; Gallagher, E. P. (1994). "Mechanisms of Aflatoxin Carcinogenesis". Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology. 34: 135–172. doi:10.1146/annurev.pa.34.040194.001031. PMID 8042848.
- ^ Kleiböhmer, W. (2001). "Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon (PAH) Metabolites". Environmental Analysis (Volume 3 of Handbook of Analytical Separations). Elsevier. pp. 99–122. ISBN 9780080505763.
- ^ Pfeifer, G. P.; Denissenko, M. F.; Olivier, M.; Tretyakova, N.; Hecht, S. S.; Hainaut, P. (2002). "Tobacco Smoke Carcinogens, DNA Damage and p53 Mutations in Smoking-Associated Cancers". Oncogene. 21 (48): 7435–7451. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205803. PMID 12379884.
- ^ Hollstein, M.; Sidransky, D.; Vogelstein, B.; Harris, C. C. (1991). "p53 Mutations in Human Cancers". Science. 253 (5015): 49–53. Bibcode:1991Sci...253...49H. doi:10.1126/science.1905840. PMID 1905840. S2CID 38527914.
- ^ Whitlock, J. P. (1999). "Induction of Cytochrome P4501A1". Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology. 39: 103–125. doi:10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.39.1.103. PMID 10331078.
- ^ Uno, S.; Dragin, N.; Miller, M. L.; Dalton, T. P.; Gonzalez, F. J.; Nebert, D. W. (2008). "Basal and Inducible CYP1 mRNA Quantitation and Protein Localization throughout the Mouse Gastrointestinal Tract". Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 44 (4): 570–583. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.10.044. PMC 2754765. PMID 17997381.
- ^ Do, K. N.; Fink, L. N.; Jensen, T. E.; Gautier, L.; Parlesak, A. (2012). "TLR2 Controls Intestinal Carcinogen Detoxication by CYP1A1". PLoS ONE. 7 (3): e32309. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...732309D. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0032309. PMC 3307708. PMID 22442665.
- ^ Stribinskis, V.; Ramos, K. S. (2006). "Activation of Human Long Interspersed Nuclear Element 1 Retrotransposition by Benzo[a]pyrene, a Ubiquitous Environmental Carcinogen". Cancer Research. 66 (5): 2616–2620. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-05-3478. PMID 16510580.