General Manuel Belgrano Railway
| Belgrano Railway | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Freight train at Ingeniero Maury, Salta Province | |||
| Overview | |||
| Status | Active | ||
| Owner | Government of Argentina | ||
| Locale | Argentina | ||
| Termini | |||
| Stations | |||
| Service | |||
| Type | Commuter rail Regional rail | ||
| Operator(s) | Ferrovías (Norte line) Trenes Argentinos (Sur line and regional services) Belgrano Cargas (Freight) | ||
| History | |||
| Opened | 1948 | ||
| Technical | |||
| Track gauge | 1,000 mm (3 ft 3+3⁄8 in) metre gauge | ||
| |||
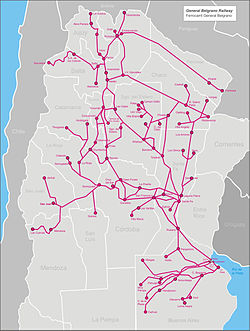
The General Manuel Belgrano Railway (FCGMB) (Spanish: Ferrocarril General Manuel Belgrano), named after the Argentine politician and military leader Manuel Belgrano, is a 1,000 mm (3 ft 3+3⁄8 in) metre gauge railway and the longest of the Argentine system. It was one of the six State-owned Argentine railway companies formed after President Juan Perón's nationalisation of the railway network in 1948.
Retiro station is the railway's terminus in Buenos Aires, from which the railway runs to many provinces in the Centre and North of Argentina, such as Santa Fe, Córdoba, Tucumán, La Rioja, Catamarca, Chaco, Santiago del Estero, Salta and Jujuy.[1]
In the metropolitan section of the city of Buenos Aires, Ferrocarril Belgrano is divided into two lines, Belgrano Norte and Belgrano Sur, currently operated by Private company Ferrovías and state-owned company Trenes Argentinos Operaciones respectively.
Passenger trains of Norte Line are only run to Villa Rosa in Pilar Partido. From then on, freight services run to the rest of the network, operated by State-owned company Belgrano Cargas. Some short-distance passenger services are also operated by another State company, Trenes Argentinos Operadora Ferroviaria, in Chaco Province.[2][3][4][5]
Ferrocarril Belgrano ran passenger services to La Quiaca and even to Bolivia although those branches were closed in the 1980s or early 1990s. There are projects to run passenger services between La Quiaca and San Salvador de Jujuy, both cities in Jujuy Province.
The main lines departed from Retiro station in Buenos Aires to the north through the provinces of Buenos Aires, Santa Fe, Córdoba, Santiago del Estero, Tucumán, Chaco, Formosa, Salta, Jujuy, San Luis, Mendoza, San Juan, La Rioja and Catamarca.
History
[edit]Background
[edit]


















In 1876, Ferrocarril Central Norte started services from Córdoba to Tucumán. It was the first metre gauge in Argentina, mainly due to economic reasons. It had been built by the Argentine State to expand Central Argentine Railway network (Rosario-Córdoba), a British-owned company by then.
By the beginning of the 20th century, the national government had built several metre gauge railway lines, most of them in the North of Argentina. The Argentine State Railway owned a 3,490 km length network. The most important were the Central Norte and Argentino del Norte, as part of other lines in Patagonia and Littoral regions.
In 1905 the Congress of Argentina authorised the construction of a line from Cerrillos to Rosario de Lerma in Salta Province as a railway projected to get access to the Puna de Atacama. One year after other project proposed to get access through Quebrada de Humahuaca was suggested, but works were not carried out.
Projects were revived several times but it was not until 1921 when the Argentine State Railway company started the construction of a line. Works -directed by American engineer Richard Maury- continued until 1930 when the overthrow of Hipólito Yrigoyen caused their interruption with only a few kilometers built, while Maury was fired by the de facto government. Works resumed in 1936, reaching the cities of Olacapato (1941), Unquillal (1944) and Tolar Grande (1945). President Juan Perón encouraged works to continue after he became president that same year.
In January 1948 works were finished at last and the line was opened, joining Argentina and Chile in Socompa. Trains ran along 29 bridges, 21 tunnels, 13 viaducts, 2 zig-zags and 2 spirals. In 1972 the line started to operate as a touristic service, under the commercial name "Tren a las Nubes" (Train to the Clouds)
Nationalisation
[edit]After the World War II finished, British and French-owned railway companies in Argentina began proceedings with the purpose of selling their railways due to financial problems to operate those services. Finally on March 1, 1948, all the foreign railway companies in Argentina were nationalised under the Juan Perón's administration, creating the State-owned company "Empresa de Ferrocarriles del Estado Argentino (EFEA)", then renamed to Ferrocarriles Argentinos, taking over all the railway lines of Argentina, including passenger and freight services.
From then on, a restructuring of the entire Argentine rail network was carried out, given the lines local heroes' names. As a result, several former British and French companies, such as Compañía Gral. de Buenos Aires, Central Norte, Argentino del Norte, Mildland and Provincial de Santa Fe became part of the same network, renamed "Ferrocarril General Manuel Belgrano" to honor Manuel Belgrano, hero of the War of independence and the creator of the flag of Argentina.
The Patagonian railway owned by state became part of General Roca Railway and the Littoral lines were added to General Urquiza Railway. On the other side, the Provincial de Buenos Aires railway remained managed in an autonomous way until 1953 when it was also added to Ferrocarril Belgrano.
The six companies were managed by Ferrocarriles Argentinos which was later broken up during the process of railway privatisation beginning in 1991 during Carlos Menem's presidency.
The following metre gauge railway companies were added to Ferrocarril Belgrano network after the 1948 nationalisation:
Ferrocarril General Belgrano
| |
| Former company | Provinces |
|---|---|
| Central Northern (1) | La Rioja, Catamarca, Córdoba, Tucumán, Formosa, Chaco, Santiago del Estero, Salta, Jujuy |
| Córdoba North Western | Córdoba |
| Provincial de Buenos Aires | Buenos Aires |
| Provincial de Santa Fe | Santa Fe, Chaco, Córdoba |
| Midland | Buenos Aires |
| Compañía General de Buenos Aires | Buenos Aires, Santa Fe |
| Córdoba Central | Santa Fe, Córdoba, Santiago del Estero |
| Transandine | Mendoza |
Note:
- (1) The Central Northern had previously taken over North Argentine Railway in 1909.
Eastern Bolivian line
[edit]In 1937, while the Chaco War happened, governments of Argentina and Brazil had competed to extend their railway lines to Bolivia. The branch projected would run from Yacuiba to Santa Cruz de la Sierra but part of the path was being occupied by the Paraguayan Army. On February 25, 1938, governments of Bolivia and Brazil signed an agreement to build a railway line from Santa Cruz to Brazilian city Corumbá, which would allow Bolivia to have access to Atlantic Ocean. That same year, Juan Rivero Torres was appointed chief of the Bolivian delegation to help organize the Mixed Bolivian-Brazilian Railway Commission; until 1951, he served as delegate engineer of Bolivia in the construction of the Santa Cruz-Corumbá Railway, thereby forming a rail corridor to connect South America's Atlantic ports with its Pacific ones.[6] As for Brazil, the railway would facilitate an access to the oil-rich Eastern Bolivia region. On March 15 Bolivia ratified that agreement, declaring null the other contract signed with Argentina in November 1937. Indigenous Chiquitano forced laborers built parts of the Santa Cruz–Corumbá Railway.[7]
Nevertheless, the Congresses of Argentina and Bolivia ratified the agreement. On the other hand, Brazil started to work in Bolivia in 1948, having finished the 625-km length Santa Cruz - Corumbá railway line in 1955.
In 1949 Argentina financed and built the railway to Santa Cruz, crossing Eastern Bolivia. That line connected Amazonas and de la Plata drainage basins as a natural extension of the Yacuiba branch. That also joined Argentine railways other railroad lines of the regions, such as Brazil, Chilean and Bolivian networks. The Yacuiba - Santa Cruz de la Sierra branch was opened in 1958.
Rosario railways
[edit]Once the metre gauge railways became part of Ferrocarril Belgrano, the government ordered the closure of Córdoba Central Railway, Provincial de Santa Fe and Compañía Gral. de Buenos Aires terminal stations in the city of Rosario for passenger services. In the case of the CGBA (that joined Buenos Aires Province with Rosario through a branch from Pergamino) the closure was definite and the building would be later occupied by the National Gendarmerie. Passenger services were moved to Rosario Oeste station.
Likewise, the Ferrocarril Provincial de Santa Fe terminus was remodeled and re-opened in the late 1950s as a bus terminus, renaming it "Coronel Juan D. Perón" to honor former President of Argentina. The station was renamed later as "Mariano Moreno".
Tucumán railways
[edit]Belgrano Railway operated two stations from Córdoba Central, the original built by the Argentine North Western Railway (ANWR, also named El Provincial due to its line extended within Tucumán Province and acquired in 1899) and the other station built by the CC itself, Tucumán Belgrano railway station. The Provincial station operated passenger and freight services until the late 1960s, when the passenger traffic was moved to Central Northern Railway station, also known as "El Bajo".
After the entire railway network was nationalised during Juan Perón's administration, the Córdoba Central station started to be operated by recently formed Ferrocarriles Argentinos. The station remained active as an intermediate stop for trains run by Belgrano Railway to La Quiaca in Jujuy Province.[8] The ANWR station would be finally closed in 1978.[9]
In the early 1990s, when the Carlos Menem's administration privatised all the railway services, the Belgrano Railway freight service remained under the control of the state due to lack of interest from private inversors. On the other hand, all the long-distance passenger services were closed in March 1993 so the station has remained active for freight trains exclusively since then. The Córdoba Central is currently operated by state-owned Trenes Argentinos Cargas y Logística.
Ex-Midland evolution
[edit]This railway extended along Buenos Aires Province from its terminus of Puente Alsina in Lanús Partido to Carhué, an important tourist centre by then.
After the nationalisation several improvements were carried out in the line, such as the addition of a rail track between Aldo Bonzi and Libertad to increase frequency of the services. The modernisation included the purchase of brand-new diesel locomotives by American company Whitcomb in 1951 (with the addition of 15 new ones by Werkspoor in 1955) and the construction of a junction in the Tapiales and Aldo Bonzi stations that allowed ex-Midland connecting its line with Ferrocarril Sarmiento railway near Haedo in Greater Buenos Aires.
By December 1955 the Ferrocarril Belgrano ran more than 40 services per day in the Puente Alsina−Aldo Bonzi section.
Railcars acquired from the Birmingham Railway Carriage and Wagon Company in 1939 that were still running passenger services on the line were put out of service in 1971, replacing them with the Ganz Works previously used by the Argentine State Railway since 1936. The Ganz railcars ran services until 1977 when the line was definitely closed.
When the Libertad−Plomer section was closed, Buenos Aires station of ex-CGBA was set as terminus. Trains ran without passengers from Puenta Alsina to Aldo Bonzi, running back to Tapiales junction where they departed to Buenos Aires station. Passengers waited and took the train in Buenos Aires, being carried to Carhué via Plomer. The lack of maintenance caused a progressive deterioration in the rolling stock and stations of the line, therefore the line was closed in September 1977. Workshops at Libertad were demolished. Nevertheless, the closure of the region did not make a negative impact in the economy of the Province due to rail tracks crossed along low-populated regions. Besides, most of that regions were already served by other railway lines with better access to the city of Buenos Aires.
Ex-Compañía General evolution
[edit]That railway line operated services from Buenos Aires station in Parque Patricios to cities at the East of Buenos Aires Province and ports of La Plata and Rosario. When the company was added to Ferrocarril Belgrano, its network was significantly restructured.
In Rosario, the CGBA terminal station was closed and all its branches put out of service. In Buenos Aires, the CGBA workshops in Riachuelo were closed so all the rolling stock was moved to Libertad workshops of Midland Railway. In La Plata, a joint with ex-Ferrocarril Provincial (FPBA) was built in Etcheverry station, using that line for all the freight trains that served the port in La Plata. The line that belonged to CGBA was abandoned and its rail tracks removed in the most part of the path.
Finally in 1961, branches from Patricios to General Villegas and Victorino de la Plaza and Vedia to Pergamino were closed. Likewise, the milk train (that served the region bringing fresh milk from local dairy farms) was definitely suspended when the government banned the commercialization of bulk products in the city of Buenos Aires.
In August 1977, National Decree N° 2294 stated the closure of the 225-km length line between Patricios and Victorino de la Plaza. Since then, stations and rail tracks had been suffered progressive deterioration, with no plans from the government to re-activate the CGBA lines.
Ex-F.C. Provincial evolution
[edit]The Ferrocarril Provincial was the last to become part of Ferrocarril Belgrano network. As the CGBA rail tracks from Port of La Plata to the crossing with FC Provincial (near Etcheverry) had been removed in the 1950s, therefore a joint was built to allow trains from González Catán to run on ex-FCPBA tracks to La Plata.
In October 1961 the Etcheverry−Mira Pampa and Carlos Beguerie−Azul−Olavarría branches were closed by the national government. Three years later the Olavarría−La Plata section was partially re-opened only for freight services, but this line would be definitely deactivated in 1968.
One year later a joint between former Midland, Provincial and the Port of Buenos Aires was built to reach Avellaneda. In 1974 rail tracks from Carlos Beguerie to Mira Pampa were removed. On July 5, 1977, this line was definitely closed for passenger services, running freight trains until one of the bridges was broken by a truck near Gobernador Monteverde, leaving the line inactive. Years later Avellaneda station (terminus of the line) would be re-opened as a railway museum.
Ex-FC Provincial de Santa Fe evolution
[edit]The Ferrocarril Provincial de Santa Fe had been a French-owned company operating trains in the provinces of Santa Fe, Chaco and Córdoba that became part of the Ferrocarril Belgrano after nationalisation of the entire network in 1948.
In the city of Rosario the terminal stations of former French-owned companies, Córdoba Central, Compañía General de Buenos Aires and Provincial de Santa Fe, were closed for passenger services. From then on, the traffic of passenger would be moved to Rosario Oeste station.
The Rosario terminus of ex-Provincial de Santa Fe was remodeled and re-opened at late 1950s as a bus terminus, renaming it "Coronel Perón" although it would be changed to Mariano Moreno to honor one of the most notable personalities of the 1810 Revolution. After becoming a bus station the warehouses remained active for freight services until they were definitely closed in 1987. The rail tracks were also removed while the Municipality of Rosario made a Convention Center ("Patrio de la Madera") on that place.[10]
FCPSF's Central Station (terminus of the line located in the city of Santa Fe) was demolished in 1962 to build a new bus terminus, which was inaugurated in 1968.
After the privatisation of all the Argentine railways in early 1990 during Carlos Menem's administration, several railway lines were closed and many cities of the region lost their only public transport that connected them with the main cities of Santa Fe and Chaco.
In the case of Chaco, the government of the province created a state-owned company, named "Servicios Ferroviarios del Chaco (SEFECHA)" to operate regional services on the Ferrocarril Belgrano tracks, using small railcars. The national government took over the services in May 2010,[11] and has been operating them since then, through state-owned company Trenes Argentinos.
Privatisation
[edit]By the beginning of the 1990s Ferrocarriles Argentinos's financial situation was catastrophic so the national government led by Carlos Menem decided to restructure the company. A new company, named "Ferrocarriles Metropolitanos S.A. (FEMESA)" was created to manage and operate passenger services in the urban area of Buenos Aires, leaving FA the operation of long-distance passenger trains and freight services. Nevertheless, passenger trains served by FA would be interrupted by a National Decree on March 10, 1993. Only a few lines (operated by the provincial governments) continued to operate outside Buenos Aires Province.
Under FEMESA administration, the urban services of Ferrocarril Belgrano were divided into two lines, Belgrano Norte (Retiro–Villa Rosa) and Belgrano Sur (Buenos Aires–González Catán–Marinos del Crucero General Belgrano and Puente Alsina–Aldo Bonzi). Both lines had a low passenger traffic compared with other lines such as Sarmiento or Mitre.[citation needed]
Belgrano Sur line that ran trains on ex-Compañía General and Midland railways was granted in concession to Private company Metropolitano (through its TMB division) in 1994. In 1999 the company tried to run a special service with railcars from González Catán to Villars but it was soon abandoned.
The Belgrano Norte line was granted in concession to Ferrovías, a company that owned EMEPA, a hugh railway workshop near Chascomús. By 1994 (first year of the concession) the number of passengers carried had increased to 14,800,000. The company also made investments, acquiring new diesel locomotives and coaches, upgrading infrastructure (renewing rail tracks and signalling and replacing the old bridges) along the entire line. Because of the improvements, the Belgrano Norte Line increased the number of passengers to 36 million.
10,800 of 14,000-km length run by Ferrocarriles Argentinos for freight services were taken over by State company Ferrocarril General Belgrano S.A., established in 1993 because of no one private company had made an offer to operate the line. Belgrano S.A. continued operating until 1997 when it was given to Unión Ferroviaria, the railway syndicate of Argentina. The company transported about 1,500,000 tons (a very low volume compared with the 4,000,000 tons transported in the 1970s). Most of the cargo was oil and fuel, although other products transported included grains, minerals and construction materials.
In November 1999 the company was given in concession to Ferrocarril Belgrano Cargas S.A., formed by the Unión Ferroviaria and local cooperative "Laguna Paiva". The government of Argentina owned 1% with the attribution to choose the Director. In 2004 the company was re-privatised, keeping the national government 1% of the company.
State interventions
[edit]
As part of railway privatization, carried out during the presidency of Carlos Menem, a concession to operate the services was granted to the government of Chaco Province in 1992, so the State-owned company "Servicios Ferroviarios del Chaco" (SEFECHA) was created in August 1999.
Through its intervention, the government of Chaco reestablished many passenger services in the Province, connecting its main cities such as Resistencia or Sáenz Peña with the rest of the region.
In May 2010, the government of Argentina took over services previously operated by SEFECHA, which was dissolved.[12] Nowadays those services, together with those of Tren de las Sierras in Córdoba Province, are the only ex-General Manuel Belgrano Railway passenger services in the interior of the country that are still in operation.
Suburban services
[edit]Belgrano Norte
[edit]
In the metropolitan sector of the City of Buenos Aires there is a diesel commuter line that operates from the Retiro terminus in the city-centre to the town of Villa Rosa in Pilar Partido of Buenos Aires Province. The service is operated by private company Ferrovías since 1994.
The line increased the number of passengers carried notably, from 11,8 million in 1993 to about 30,5 million passengers during 2012.[13]
Belgrano Sur
[edit]
On the southern sector of the City of Buenos Aires two diesel commuter lines operate to the southern suburbs of Buenos Aires. The Buenos Aires station-González Catán line was part of French-owned company Compañía General de Ferrocarriles en la Provincia de Buenos Aires (CGBA) that extended its network to the south-west of Buenos Aires Province, reaching cities such as General Villegas and Victorino de la Plaza. Other lines connected Buenos Aires with the port of La Plata and Rosario.
The other two branches were originally part of British-owned Buenos Aires Midland Railway that began its operations in 1906, extending its network to the city of Carhué in the south-west of the Province. From Puente Alsina station (Midland terminus) it runs to Aldo Bonzi. The other branch (15-km length) departs from Tapiales station, extending to Marinos del Crucero Gral. Belgrano in Merlo Partido.
See also
[edit]Bibliography
[edit]- British Railways in Argentina 1860–1948, H. R. Stones, edited by P. E. Waters & Associates, Bromley, Kent, England, 1993.
References
[edit]- ^ "Carta del Belgrano Cargas". Archived from the original on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2015-01-26.
- ^ Puerto Vilelas - Servicio local: Resistencia - Puerto Tirol - Satélite Ferroviario
- ^ Trenes Argentinos - Informe de Gestión - Primer Trimestre (pag 21-25)
- ^ Roque Sáenz Peña - Chorotis - Satélite Ferroviario
- ^ Resistencia - Cacuí - Los Amores - Satélite Ferroviario
- ^ Patric, Anthony (January 19, 1947). "Railway Across South America Nears Reality". Chicato Tribune. p. 22. Retrieved 2 May 2016.
The strategical railroad linking the Brazilian Atlantic port of Santos to the Chilean Pacific port of Arica is nearing reality. Despite wartime shortages of material and equipment, the Bolivian Brazilian Commission in charge of the construction of the line has performed a near miracle...
- ^ Riester, Jürgen (1975). Indians of Eastern Bolivia: Aspects of their present situation. IWGIA document. Copenhagen: IWGIA. p. 20.
- ^ "La primera estación", La Gaceta, 18 May 2012
- ^ "La popular línea y estación del "Provincial" by Alberto Elsinger, La Gaceta, 8 Jun 2012
- ^ "Patrio de la Madera" on Municipality of Rosario website
- ^ "SEFECHA pasó a la Nación", Diaro Norte, 5 May 2010
- ^ "Sefecha pasó a la Nación", Diario Norte, 5 May 2010
- ^ "Estadísticas del total de pasajeros"[permanent dead link], CNRT
- Railway companies of Argentina
- Metre gauge railways in Argentina
- Rail transport in Buenos Aires Province
- Rail transport in Santa Fe Province
- Rail transport in Rosario, Santa Fe
- Rail transport in Córdoba Province, Argentina
- Transport in Tucumán Province
- Transport in Santiago del Estero Province
- Transport in La Rioja Province, Argentina
- Transport in Catamarca Province
- Transport in Chaco Province
- Transport in Formosa Province
- Transport in Mendoza Province