Sand


glass, dune, quartz,
volcanic, biogenic coral, pink coral,
volcanic, garnet, olivine.
Samples are from the Gobi Desert, Estonia, Hawaii and the mainland United States. (1×1 cm each)[1]
Sand is a granular material composed of finely divided mineral particles. Sand has various compositions but is defined by its grain size. Sand grains are smaller than gravel and coarser than silt. Sand can also refer to a textural class of soil or soil type; i.e., a soil containing more than 85 percent sand-sized particles by mass.[2]
The composition of sand varies, depending on the local rock sources and conditions, but the most common constituent of sand in inland continental settings and non-tropical coastal settings is silica (silicon dioxide, or SiO2), usually in the form of quartz.
Calcium carbonate is the second most common type of sand. One such example of this is aragonite, which has been created over the past 500 million years by various forms of life, such as coral and shellfish. It is the primary form of sand apparent in areas where reefs have dominated the ecosystem for millions of years, as in the Caribbean. Somewhat more rarely, sand may be composed of calcium sulfate, such as gypsum and selenite, as is found in places such as White Sands National Park and Salt Plains National Wildlife Refuge in the U.S.
Sand is a non-renewable resource over human timescales, and sand suitable for making concrete is in high demand.[3] Desert sand, although plentiful, is not suitable for concrete. Fifty billion tons of beach sand and fossil sand are used each year for construction.[4]
Composition



The exact definition of sand varies. The scientific Unified Soil Classification System used in engineering and geology corresponds to US Standard Sieves, and defines sand as particles with a diameter of between 0.074 and 4.75 millimeters.[5] By another definition, in terms of particle size as used by geologists, sand particles range in diameter from 0.0625 mm (or 1⁄16 mm) a volume of approximately 0.00012 cubic millimetres, to 2 mm, a volume of approximately 4.2 cubic millimetres, the difference in volumes being 34,688 measures difference.[6] Any particle falling within this range of sizes is termed a sand grain. Sand grains are between gravel (with particles ranging from 2 mm up to 64 mm by the latter system, and from 4.75 mm up to 75 mm in the former) and silt (particles smaller than 0.0625 mm down to 0.004 mm). The size specification between sand and gravel has remained constant for more than a century, but particle diameters as small as 0.02 mm were considered sand under the Albert Atterberg standard in use during the early 20th century. The grains of sand in Archimedes' The Sand Reckoner written around 240 BCE, were 0.02 mm in diameter. A 1938 specification of the United States Department of Agriculture was 0.05 mm.[7] A 1953 engineering standard published by the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials set the minimum sand size at 0.074 mm. Sand feels gritty when rubbed between the fingers. Silt, by comparison, feels like flour.
ISO 14688 grades sands as fine, medium, and coarse with ranges 0.063 mm to 0.2 mm to 0.63 mm to 2.0 mm. In the United States, sand is commonly divided into five sub-categories based on size: very fine sand (1⁄16 – 1⁄8 mm diameter), fine sand (1⁄8 mm – 1⁄4 mm), medium sand (1⁄4 mm – 1⁄2 mm), coarse sand (1⁄2 mm – 1 mm), and very coarse sand (1 mm – 2 mm). These sizes are based on the Krumbein phi scale, where size is Φ = -log2D; D being the particle size in mm. On this scale, for sand the value of Φ varies from −1 to +4, with the divisions between sub-categories at whole numbers.

The most common constituent of sand, in inland continental settings and non-tropical coastal settings, is silica (silicon dioxide, or SiO2), usually in the form of quartz, which, because of its chemical inertness and considerable hardness, is the most common mineral resistant to weathering.
The composition of mineral sand is highly variable, depending on the local rock sources and conditions. The bright white sands found in tropical and subtropical coastal settings are eroded limestone and may contain coral and shell fragments in addition to other organic or organically derived fragmental material, suggesting that sand formation depends on living organisms, too.[8] The gypsum sand dunes of the White Sands National Park in New Mexico are famous for their bright, white color. Arkose is a sand or sandstone with considerable feldspar content, derived from weathering and erosion of a (usually nearby) granitic rock outcrop. Some sands contain magnetite, chlorite, glauconite, or gypsum. Sands rich in magnetite are dark to black in color, as are sands derived from volcanic basalts and obsidian. Chlorite-glauconite bearing sands are typically green in color, as are sands derived from basaltic lava with a high olivine content. Many sands, especially those found extensively in Southern Europe, have iron impurities within the quartz crystals of the sand, giving a deep yellow color. Sand deposits in some areas contain garnets and other resistant minerals, including some small gemstones.
Sources
Rocks erode or weather over a long period of time, mainly by water and wind, and their sediments are transported downstream. These sediments continue to break apart into smaller pieces until they become fine grains of sand. The type of rock the sediment originated from and the intensity of the environment give different compositions of sand. The most common rock to form sand is granite, where the feldspar minerals dissolve faster than the quartz, causing the rock to break apart into small pieces. In high energy environments rocks break apart much faster than in more calm settings. In granite rocks this results in more feldspar minerals in the sand because they do not have as much time to dissolve away. The term for sand formed by weathering is "epiclastic."[9]
Sand from rivers are collected either from the river itself or its flood plain and accounts for the majority of the sand used in the construction industry. Because of this, many small rivers have been depleted, causing environmental concern and economic losses to adjacent land. The rate of sand mining in such areas greatly outweighs the rate the sand can replenish, making it a non-renewable resource.[10]
Sand dunes are a consequence of dry conditions or wind deposition. The Sahara Desert is very dry because of its geographic location and proximity to the equator. It is known for its vast sand dunes, which exist mainly due to a lack of vegetation and water. Over time, wind blows away fine particles, such as clay and dead organic matter, leaving only sand and larger rocks. Only 15% of the Sahara is sand dunes, while 70% is bare rock.[11] The wind is responsible for creating these different environments and shaping the sand to be round and smooth. These properties make desert sand unusable for construction.[12]
Beach sand is also formed by erosion. Over thousands of years, rocks are eroded near the shoreline from the constant motion of waves and the sediments build up. Weathering and river deposition also accelerate the process of creating a beach, along with marine animals interacting with rocks, such as eating the algae off of them. Once there is a sufficient amount of sand, the beach acts as a barrier to keep the land from eroding any further. This sand is ideal for construction as it is angular and of various sizes.[13]
Marine sand (or ocean sand) comes from sediments transported into the ocean and the erosion of ocean rocks. The thickness of the sand layer varies, however it is common to have more sand closer to land; this type of sand is ideal for construction and is a very valuable commodity. Europe is the main miners of marine sand, which greatly hurts ecosystems and local fisheries.[10]
Study
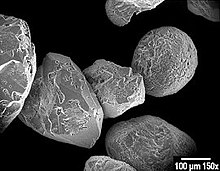

The study of individual grains can reveal much historical information as to the origin and kind of transport of the grain.[14] Quartz sand that is recently weathered from granite or gneiss quartz crystals will be angular. It is called grus in geology or sharp sand in the building trade where it is preferred for concrete, and in gardening where it is used as a soil amendment to loosen clay soils. Sand that is transported long distances by water or wind will be rounded, with characteristic abrasion patterns on the grain surface. Desert sand is typically rounded.
People who collect sand as a hobby are known as arenophiles. Organisms that thrive in sandy environments are psammophiles.[15]
Uses
This section needs additional citations for verification. (January 2018) |

- Abrasion: Before sandpaper, wet sand was used as an abrasive element between rotating devices with elastic surface and hard materials such as very hard stone (making of stone vases), or metal (removal of old stain before re-staining copper cooking pots).
- Agriculture: Sandy soils are ideal for crops such as watermelons, peaches, and peanuts, and their excellent drainage characteristics make them suitable for intensive dairy farming.
- Air filtration: Finer sand particles mixed with cloth was commonly used in certain gas mask filter designs but have largely been replaced by microfibers.
- Aquaria: Sand makes a low-cost aquarium base material which some believe is better than gravel for home use. It is also a necessity for saltwater reef tanks, which emulate environments composed largely of aragonite sand broken down from coral and shellfish.
- Artificial reefs: Geotextile bagged sand can serve as the foundation for new reefs.
- Artificial islands in the Persian Gulf.
- Beach nourishment: Governments move sand to beaches where tides, storms, or deliberate changes to the shoreline erode the original sand.[16]
- Brick: Manufacturing plants add sand to a mixture of clay and other materials for manufacturing bricks.[17]
- Cob: Cob is a building material consisting of water, organic material (like straw), lime, and subsoil, which largely consists of sand. Coarse sand makes up as much as 75% of cob.
- Concrete: Sand is often a principal component of this critical construction material.
- Glass: Sand rich in silica is the principal component in common glasses.
- Hydraulic fracturing: A drilling technique for natural gas, which uses rounded silica sand as a "proppant", a material to hold open cracks that are caused by the hydraulic fracturing process.
- Landscaping: Sand makes small hills and slopes (golf courses would be an example).
- Mortar: Sand is mixed with masonry cement or Portland cement and lime to be used in masonry construction.
- Paint: Mixing sand with paint produces a textured finish for walls and ceilings or non-slip floor surfaces.
- Railroads: Engine drivers and rail transit operators use sand to improve the traction of wheels on the rails.
- Recreation: Playing with sand is a favorite beach activity. One of the most beloved uses of sand is to make sometimes intricate, sometimes simple structures known as sand castles, proverbially impermanent. Special play areas for children, enclosing a significant area of sand and known as sandboxes, are common on many public playgrounds, and even at some single-family homes. Sand dunes are also popular among climbers, motorcyclists and beach buggy drivers.
- Roads: Sand improves traction (and thus traffic safety) in icy or snowy conditions.
- Sand animation: Performance artists draw images in sand. Makers of animated films use the same term to describe their use of sand on frontlit or backlit glass.
- Sand casting: Casters moisten or oil molding sand, also known as foundry sand and then shape it into molds into which they pour molten material. This type of sand must be able to withstand high temperatures and pressure, allow gases to escape, have a uniform, small grain size, and be non-reactive with metals.
- Sandbags: These protect against floods and gunfire. The inexpensive bags are easy to transport when empty, and unskilled volunteers can quickly fill them with local sand in emergencies.
- Sandblasting: Graded sand serves as an abrasive in cleaning, preparing, and polishing.
- Silicon: Quartz sand is a raw material for the production of silicon.
- Thermal weapon: While not in widespread use anymore, sand used to be heated and poured on invading troops in the classical and medieval time periods.
- Water filtration: Media filters use sand for filtering water. It is also commonly used by many water treatment facilities, often in the form of rapid sand filters.
- Tayammum: Tayammum is an Islamic ritual wiping of parts of the body.
- Zoanthid "skeletons": Animals in this order of marine benthic cnidarians related to corals and sea anemones incorporate sand into their mesoglea for structural strength, which they need because they lack a true skeleton.
Resources and environmental concerns
Only some sands are suitable for the construction industry, for example for making concrete. Grains of desert sand are rounded by being blown in the wind, and for this reason do not produce solid concrete, unlike the rough sand from the sea. Because of the growth of population and of cities and the consequent construction activity there is a huge demand for these special kinds of sand, and natural sources are running low. In 2012 French director Denis Delestrac made a documentary called "Sand Wars" about the impact of the lack of construction sand. It shows the ecological and economic effects of both legal and illegal trade in construction sand.[18][19][20]
To retrieve the sand, the method of hydraulic dredging is used. This works by pumping the top few meters of sand out of the water and filling it into a boat, which is then transported back to land for processing. All marine life mixed in with the extracted sand is killed and the ecosystem can continue to suffer for years after the mining is complete. Not only does this affect marine life, but also the local fishing industries because of the loss of life, and communities living close to the water's edge. When sand is taken out of the water it increases the risk of landslides, which can lead to loss of agricultural land and/or damage to dwellings.[21]
Sand's many uses require a significant dredging industry, raising environmental concerns over fish depletion, landslides, and flooding.[22] Countries such as China, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Cambodia ban sand exports, citing these issues as a major factor.[23] It is estimated that the annual consumption of sand and gravel is 40 billion tons and sand is a US$70 billion global industry.[24] With increasing use, more is expected to come from recycling and alternatives to sand.[25]
The global demand for sand in 2017 was 9.55 billion tons as part of a $99.5 billion industry.[26] In April 2022, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) published a report stating that 50 billion tons of sand and gravel were being used every year. The report made 10 recommendations, including a ban on beach extraction, to avert a crisis, and move toward a circular economy for the two resources.[27][28]
Hazards
While sand is generally non-toxic, sand-using activities such as sandblasting require precautions. Bags of silica sand used for sandblasting now carry labels warning the user to wear respiratory protection to avoid breathing the resulting fine silica dust. Safety data sheets for silica sand state that "excessive inhalation of crystalline silica is a serious health concern."[29]
In areas of high pore water pressure, sand and salt water can form quicksand, which is a colloid hydrogel that behaves like a liquid. Quicksand produces a considerable barrier to escape for creatures caught within, who often die from exposure (not from submersion) as a result.
People sometimes dig holes in the sand at beaches for recreational purposes, but if too deep they can result in serious injury or death in the event of a collapse.[30]
Manufacture
Manufactured sand (M sand) is sand made from rock by artificial processes, usually for construction purposes in cement or concrete. It differs from river sand by being more angular, and has somewhat different properties.[31]
Case studies
In Dubai, United Arab Emirates, sand needed to construct infrastructure and create the Dubai Islands exceeds local supplies, requiring sand from Australia. The artificial islands required more than 835 million tonnes of sand, at a cost greater than $26 billion USD.[32]
See also
- Aggregate (geology) – Mass of rock, gravel, sand, soil particles, or of minerals in a rock
- Beach – Area of loose particles at the edge of the sea or other body of water
- Construction aggregate – Coarse to fine grain rock materials used in concrete
- Coral Pink Sand Dunes State Park – State park in Utah, US
- Desert sand (color) – Light reddish-yellow color
- Dry quicksand – Conjectural soil type probably not found in nature
- Energetically modified cement – Class of cements, mechanically processed to transform reactivity (EMC)
- Heavy mineral sands ore deposits – Ore deposits of rare earth metals
- Oil sands – Type of unconventional oil deposit
- Papakolea Beach – Green sand beach in Kaʻū district, Hawai'i, US
- Particle size – Notion for comparing dimensions of particles in different states of matter
- Punaluʻu Beach – Black Sand Beach, Big Island, Hawaii, US
- Quicksand – Mixture of sand, silt or clay with water, which creates a liquefied soil when agitated
- Red Sand Beach – Kaihalulu Beach, Maui, Hawaii, US
- Revolving rivers – a surprising, uncommon way of sand pile growth that can be found in a few sands around the world
- Sand art and play – Moulding and sculpting shapes out of moist sand
- Sand Beach (disambiguation)
- Sand equivalent test
- Sand island – Island that is largely made of sand
- Sand mining – Practice used to extract sand
- Sand rat – Genus of rodents
- Sandstone – Type of sedimentary rock
- Sandstorm – Meteorological phenomenon common in arid and semi-arid regions
- Sand theft – Unauthorized or illegal mining of sand
- Singing sand – A phenomenon of sand that produces sound
- White Sands National Park – National park in New Mexico, United States
References
- ^ Siim Sepp. "Sand types". sandatlas.org. Archived from the original on 13 August 2019. Retrieved 17 February 2020.
- ^ Glossary of terms in soil science (PDF). Ottawa: Agriculture Canada. 1976. p. 35. ISBN 978-0662015338. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 February 2019. Retrieved 11 August 2014.
- ^ Constable, Harriet (3 September 2017). "How the demand for sand is killing rivers". BBC News Magazine. Archived from the original on 3 September 2017. Retrieved 9 September 2017.
- ^ Albarazi, Hannah. "The Slippery Slopes of the World Sand Shortage". Archived from the original on 29 March 2019. Retrieved 29 March 2019.
- ^ Unified Soil Classification System[permanent dead link]
- ^ Pettijohn, FJ; Potter, PE; Siever, Raymond (1972). Sand and Sandstone. New York: Springer Verlag. p. 1. ISBN 9780387900711. Archived from the original on 2 July 2021. Retrieved 9 March 2021.
- ^ Urquhart, Leonard Church, "Civil Engineering Handbook" McGraw-Hill Book Company (1959) p. 8-2
- ^ Seaweed also plays a role in the formation of sand Archived 1 July 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Susanscott.net (1 March 2002). Retrieved on 24 November 2011.
- ^ Gilman, Larry (2014). Sand. Vol. 7 (5 ed.). The Gale Encyclopedia of Science. pp. 3823–3824.
- ^ a b Padmalal, Maya (2014). "Sources of Sand and Conservation". Sand Mining. Springer, Dordrecht. pp. 155–160. ISBN 978-94-017-9143-4.
- ^ "Sahara". The Columbia Encyclopedia (6 ed.). Columbia University Press. 2000. ISBN 9780787650155.
- ^ "What is the reason for not using sea and desert sand for construction?". The Hindu. 2 August 2015. ISSN 0971-751X. Archived from the original on 15 December 2019. Retrieved 9 April 2019.
- ^ "How Is A Beach Formed?". WorldAtlas. 19 December 2017. Archived from the original on 13 December 2019. Retrieved 10 April 2019.
- ^ Krinsley, D.H., Smalley, I.J. 1972. Sand. American Scientist 60, 286–291
- ^ "Psammophile". Merriam-Webster.com. Archived from the original on 9 July 2017. Retrieved 27 January 2016.
- ^ "Importing Sand, Glass May Help Restore Beaches". NPR.org. 17 July 2007. Archived from the original on 2 July 2021. Retrieved 4 April 2018.
- ^ Yong, Syed E. Hasan, Benedetto De Vivo, Bernhard Grasemann, Kurt Stüwe, Jan Lastovicka, Syed M. Hasan, Chen (5 December 2011). Environmental and Engineering Geology -Volume III. EOLSS Publications. p. 80. ISBN 978-1-84826-357-4. Archived from the original on 2 July 2021. Retrieved 19 October 2019.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "SAND WARS". www.sand-wars.com. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- ^ Simon Ings (26 April 2014). "The story of climate change gets star treatment". New Scientist: 28–9. Archived from the original on 4 November 2014. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ^ Strände in Gefahr? Archived 24 September 2015 at the Wayback Machine Arte Future, last updated 23 April 2014
- ^ Kim, Tae Goun (14 September 2007). "The economic costs to fisheries because of marine sand mining in Ongjin Korea: Concepts, methods, and illustrative results". Ecological Economics. 65 (3): 498–507. doi:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2007.07.016.
- ^ Torres, Aurora; et al. (8 September 2017). "The world is facing a global sand crisis". The Conversation. Archived from the original on 9 July 2018. Retrieved 9 September 2017.
- ^ "The hourglass effect". The Economist. 8 October 2009. Archived from the original on 16 December 2018. Retrieved 14 October 2009.
- ^ Beiser, Vince (26 March 2015). "The Deadly Global War for Sand". Wired. Archived from the original on 16 April 2018. Retrieved 26 March 2015.
- ^ Torres, Aurora; Simoni, Mark U.; Keiding, Jakob K.; Müller, Daniel B.; zu Ermgassen, Sophus O.S.E.; Liu, Jianguo; Jaeger, Jochen A.G.; Winter, Marten; Lambin, Eric F. (May 2021). "Sustainability of the global sand system in the Anthropocene". One Earth. 4 (5): 639–650. Bibcode:2021OEart...4..639T. doi:10.1016/j.oneear.2021.04.011.
- ^ Doyle, Alister (11 February 2019). "As ice melts, Greenland could become big sand exporter: study". reuters.com. Archived from the original on 7 August 2020. Retrieved 12 February 2019.
- ^ "Our use of sand brings us "up against the wall", says UNEP report" (Press release). Geneva: United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). 26 April 2022. Retrieved 28 April 2022.
- ^ "The world is using sand faster than it can be replaced". ABC News. Reuters. 28 April 2022. Retrieved 28 April 2022.
- ^ Silica sand MSDS Archived 11 March 2006 at the Wayback Machine. Simplot (13 March 2011). Retrieved on 24 November 2011.
- ^ Ellement, John R.; Yan, Matt; Annear, Steve (18 May 2022). "Maine man, 18, killed in sand collapse on New Jersey beach; dad recalls his 'quirky' personality". BostonGlobe.com. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- ^ Pilegis, M.; Gardner, D.; Lark, R. (2016). "An Investigation into the Use of Manufactured Sand as a 100% Replacement for Fine Aggregate in Concrete". Materials. 9 (6): 440. Bibcode:2016Mate....9..440P. doi:10.3390/ma9060440. PMC 5456819. PMID 28773560.
- ^ Peduzzi, Pascal (April 2014). "Sand, rarer than one thinks". Environmental Development. 11: 208–218. doi:10.1016/j.envdev.2014.04.001. Archived from the original on 29 May 2019. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
Further reading
- Vince Beiser (2018). The World in a Grain: The Story of Sand and How It Transformed Civilization. Riverhead Books. ISBN 978-0399576423.
External links
- Beach Sand: What It Is, Where It Comes From and How It Gets Here - Beaufort County Library
- Beach, Chandler B., ed. (1914). . . Chicago: F. E. Compton and Co.
- Sand mining side-effects
- The World Is Running Out Of Sand - New York Times
- Sand Mining In India Rivers Causing Problems - New York Times
- How Demand For Sand Is Killing Rivers In Africa - BBC
- Dubai Imports Sand - BBC
- Sand crisis looms as world population surges, U.N. warns - Reuters