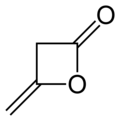
Diketene
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-Methylideneoxetan-2-one | |||
| Other names
γ-Methylenepropiolactone
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.562 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2521 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H4O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 84.074 g·mol−1 | ||
| Density | 1.09 g cm−3 | ||
| Melting point | −7 °C (19 °F; 266 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 127 °C (261 °F; 400 K) | ||
| Viscosity | 0.88 mPa.s | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
   
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H226, H301, H302, H315, H318, H330, H331, H332, H335 | |||
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P284, P301+P310, P301+P312, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P311, P312, P320, P321, P330, P332+P313, P362, P370+P378, P403+P233, P403+P235, P405, P501 | |||
| Flash point | 33 °C (91 °F; 306 K) | ||
| 275 | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Diketene is an organic compound with the molecular formula C4H4O2, and which is sometimes written as (CH2CO)2. It is formed by dimerization of ketene, H2C=C=O. Diketene is a member of the oxetane family. It is used as a reagent in organic chemistry.[1] It is a colorless liquid.
Production
[edit]Diketene is produced on commercial scale by dimerization of ketene.[2]
Reactions
[edit]Heating or irradiation with UV light[3] regenerates the ketene monomer:
Alkylated ketenes also dimerize with ease and form substituted diketenes.
Diketene readily hydrolyzes in water forming acetoacetic acid. Its half-life in water is approximately 45 min. a 25 °C at 2 < pH < 7.[4]
Certain diketenes with two aliphatic chains, such as alkyl ketene dimers (AKDs), are used industrially to improve hydrophobicity in paper.
At one time acetic anhydride was prepared by the reaction of ketene with acetic acid:[5]
Acetoacetylation
[edit]Diketene also reacts with alcohols and amines to the corresponding acetoacetic acid derivatives. The process is sometimes called acetoacetylation. An example is the reaction with 2-aminoindane:[6]
Diketene is an important industrial intermediate used for the production of acetoacetate esters and amides as well as substituted 1-phenyl-3-methylpyrazolones. The latter are used in the manufacture of dyestuffs and pigments.[7] A typical reaction is:
These acetoacetamides are precursors to arylide yellow and diarylide pigments.[8]
Use
[edit]Diketenes with two alkyl chains are used in the manufacture of paper for sizing of paper in order to improve their printability (by hydrophobization). Besides the rosin resins with about 60% share of world consumption, long chain diketenes called alkylketene dimers (AKD) are with 16% share the most important synthetic paper sizes, they are usually used in concentrations of 0.15%, meaning 1.5 kg solid AKD/t paper.
The preparation of AKD is carried out by chlorination of long chain fatty acids (such as stearic acid, using chlorinating agents such as thionyl chloride) to give the corresponding acid chlorides and subsequent elimination of HCl by amines (for example triethylamine) in toluene or other solvents:[9]
Furthermore, diketenes are used as intermediates in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals, insecticides and dyes. For example pyrazolones are formed from substituted phenylhydrazines, they were used as analgetics but are now largely obsolete. With methylamine diketenes reacts to N,N'-dimethylacetoacetamide which is chlorinated with sulfuryl chloride and reacted with trimethyl phosphite to the highly toxic insecticide monocrotophos (especially toxic to bees). Diketenes react with substituted aromatic amines to acetoacetanilides, which are important precursors for mostly yellow, orange or red azo dyes and azo pigments.
Exemplary for the synthesis of arylides by the reaction of diketenes with aromatic amines is:
Aromatic diazonium coupling with arylides to form azo dyes, such as Pigment Yellow 74:
The industrial synthesis of the sweetener acesulfam-K is based on the reaction of diketene with sulfamic acid and cyclization by sulfur trioxide (SO3).[10]
Drugs made from Diketene include:
Safety
[edit]Despite its high reactivity as an alkylating agent, and unlike analogue β-lactones propiolactone and β-butyrolactone, diketene is inactive as a carcinogen, possibly due to the instability of its DNA adducts.[11]
References
[edit]- ^ Beilstein E III/IV 17: 4297.
- ^ Miller, Raimund; Abaecherli, Claudio; Said, Adel; Jackson, Barry (2001). "Ketenes". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. doi:10.1002/14356007.a15_063. ISBN 978-3-527-30385-4.
- ^ Susana Breda; Igor Reva; Rui Fausto (2012). "UV Induced Unimolecular Photochemistry of Diketene Isolated in Cryogenic Inert Matrices". J. Phys. Chem. A. 116 (9): 2131–2140. Bibcode:2012JPCA..116.2131B. doi:10.1021/jp211249k. PMID 22273010.
- ^ Rafael Gómez-Bombarelli; Marina González-Pérez; María Teresa Pérez-Prior; José A. Manso; Emilio Calle; Julio Casado (2008). "Kinetic Study of the Neutral and Base Hydrolysis of Diketene". J. Phys. Org. Chem. 22 (5): 438–442. doi:10.1002/poc.1483.
- ^ Arpe, Hans-Jürgen (2007), Industrielle organische Chemie: Bedeutende vor- und Zwischenprodukte (in German) (6th ed.), Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, pp. 200–1, ISBN 978-3-527-31540-6[permanent dead link]
- ^ Kiran Kumar Solingapuram Sai; Thomas M. Gilbert; Douglas A. Klumpp (2007). "Knorr Cyclizations and Distonic Superelectrophiles". J. Org. Chem. 72 (25): 9761–9764. doi:10.1021/jo7013092. PMID 17999519.
- ^ Ashford's Dictionary of Industrial Chemicals, Third Edition, 2011, pages 3241-2.
- ^ Hunger, K.; Herbst, W. (2012). "Pigments, Organic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a20_371. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ Wolf S. Schultz: Sizing Agents in Fine Paper[permanent dead link] Retrieved 1 March 2012.
- ^ EP 0218076 Process for the preparation of the non-toxic salts of 6-methyl-3,4-dihydro-1,2,3-oxathiazin-4-on-2,2-dioxide.
- ^ Rafael Gómez-Bombarelli; Marina González-Pérez; María Teresa Pérez-Prior; José A. Manso; Emilio Calle; Julio Casado (2008). "Chemical Reactivity and Biological Activity of Diketene". Chem. Res. Toxicol. 21 (10): 1964–1969. doi:10.1021/tx800153j. PMID 18759502.