CNN International: Difference between revisions
No edit summary Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Use American English|date=February 2017}} |
|||
{{Use mdy dates|date=April 2012}} |
|||
{{Refimprove|date=January 2012}} |
|||
{{Infobox TV channel |
{{Infobox TV channel |
||
| name = CNN International |
| name = CNN International |
||
| logofile = Cnn logo red background.png |
| logofile = Cnn logo red background.png |
||
| logosize |
| logosize = 220px |
||
| branding = CNN |
|||
| logocaption = CNN International logo |
|||
| logoalt = |
| logoalt = |
||
| launch = {{start date and age|1985|9|1}} |
| launch = {{start date and age|1985|9|1}} |
||
Revision as of 12:13, 2 February 2018
| Country | United States |
|---|---|
| Headquarters | CNN Center Atlanta, Georgia, London, Hong Kong, Mumbai and Abu Dhabi |
| Programming | |
| Language(s) | English |
| Ownership | |
| Owner | Turner Broadcasting System (Time Warner) |
CNN International (CNNI), simply referred to on the channel as CNN, is an international 24-hour English language cable, satellite, IPTV and digital terrestrial television channel that is owned by the Turner Broadcasting System division of Time Warner. The channel carries news, current affairs, politics, sports, opinions, features and business programming worldwide; it cooperates with parent network CNN's national and international news bureaus. Unlike its sister channel, CNN, a US-only cable TV service which is mostly broadcast from CNN studios at the Time Warner Center in New York City on weekdays and CNN Center in Atlanta, Georgia at the weekend, CNN International is carried on a variety of TV platforms across the world, and mostly broadcast from studios outside the US, in London, Mumbai, Hong Kong and Abu Dhabi.
CNN International is available in most countries, its international reach includes more than 200 million households, and hotel rooms in over 190 countries. For most viewers it is free-to-air, though some pay television providers include it in their programming packages, or issue a virtual channel to the FTA version on the same satellite. The current managing director of CNN International is Tony Maddox.[2]
History
Early years

CNN International, in large part a result of Ted Turner's globalization ideals, began broadcasting on September 1, 1985, at first primarily broadcasting to American business travelers in hotels. The first studio for CNNI was at CNN's original studio building known as Techwood, home at that time to all of Turner Broadcasting System's channels. Today, it is home to the Turner Studios complex that houses the entertainment channels. Other early studios in Atlanta were tucked away in various corners of the CNN Center, and the newsroom lacked even a digital clock. The vast majority of the network's programming originally consisted of simulcasts of the two domestic CNN channels (CNN/US and Headline News). In 1990, however, the amount of news programming produced by CNNI especially for international viewers increased significantly. A new newsroom and studio complex was built in 1994, as CNN decided to compete against BBC World Service Television's news programming. CNNI emerged as an internationally oriented news channel, with staff members of various national backgrounds, even though some accusations of a pro-U.S. editorial bias persist. CNN International was awarded the Liberty Medal on July 4, 1997. Ted Turner, in accepting the medal on behalf of the network, said: "My idea was, we're just going to give people the facts... We didn't have to show liberty and democracy as good, and show socialism or totalitarianism as bad. If we just showed them both the way they were ... clearly everybody's going to choose liberty and democracy."[3]
New international era (1995–2006)
In 1995, creative director Morgan Almeida defined a progressive rebranding strategy, to target CNNI's diverse global market, making the on-air look less overtly American and with a cleaner, simpler "international" aesthetic going forward. The word "International" in the channel's logo was replaced with a globe, and the new branding featured numerous international locations filmed in time-lapse, channel idents created in CGI with Velvet Design in Munich, and a news brand designed with The Attik in New York.[4]
2006–2009 revamp

The network undertook another major rebranding effort in 2006 overseen by the award-winning creative vision of Mark Wright and London agency Kemistry. The ticker was replaced by a flipper, on-screen graphics were more unified and from October 2007 until August 2008, new studios were progressively rolled out. However, on January 1, 2009, CNN International adopted the "lower-thirds" that CNN/US had introduced a month earlier which were inspired by the clean modern design of the CNNI rebrand efforts.
In the U.S., CNNI North America was distributed overnight and on weekends over the CNNfn financial channel, until that channel's demise in December 2004. It is now available as a standalone, full-time channel, usually as part of digital packages of cable providers including Time Warner Cable, AT&T U-Verse, Verizon FiOS and Cox Communications.
Going beyond borders (2009–2013)
Throughout January until September 2009, CNN International adapted more programs that became geared towards a primetime European audience with a few titled after CNN International personalities, most notably the interview program Amanpour. On September 21, 2009, the channel launched a new tagline "Go Beyond Borders", along with a new logo, and consolidated its general newscasts (World News, CNN Today, World News Asia, World News Europe and Your World Today) into a single newscast entitled World Report.
The slogan "Go Beyond Borders" emphasizes the international perspective that gives the information in this string and the plurality of the audiences. With this tagline, CNN also refers to the various platforms to disseminate their contents. The new image was created by the creativity and marketing department, and agency CNN Tooth & Nail. An important element of the rebrand was a new evening program that adds the broadcast of programs Amanpour and World One. The makeover of CNN International has subject to a lot of criticism on both the new prime time lineup and the redesigned graphics.
On January 11, 2009, in a bid to compete directly with Al Jazeera's then English-language international channel, the network launched a new production center: CNN Abu Dhabi, based in the United Arab Emirates. Then, CNN International adapted half-hour shows in its schedule with a new evening prime program for Middle East viewers, Prism.
In 2010, CNN International launched new programs for its evening lineup in order to improve its schedule. In 2011, programs from CNN U.S. were added to the CNN International schedule, including the talk program Piers Morgan Live which was later cancelled and replaced with CNN Tonight hosted by Don Lemon.

This is CNN (2013–present)
"This is CNN" represents CNN International's rebrand with new sets and output in full 16:9 high definition. The "This is CNN" slogan is also used on its sister network CNN/U.S.
Regional and online versions
There are six variants of CNN International:
- CNN International Asia Pacific, based in Hong Kong SAR,
- CNN International Europe/Middle East/Africa, based in London, United Kingdom
- CNN International Latin America, based in Atlanta, Georgia, U.S.
- CNN International Middle East, based in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
- CNN International North America, based in Atlanta, Georgia, U.S.
- CNN International South Asia, based in New Delhi, India
The schedules of the different regional versions no longer differ significantly from each other, but there are still minor variations such as weather updates and show airtimes - notably Amanpour, which also airs at 22.00 HK time in Asia in lieu of the first half-hour of International Desk, and 23.00 CET in Europe in addition to its original airtime.
CNN has reported that its broadcast agreement in mainland China includes an arrangement that its signal must pass through a Chinese-controlled satellite. With this method of transmission, Chinese authorities have been able to black out CNNI segments at will. CNN has also said that its broadcasts are not widely available in mainland China, but rather only in certain diplomatic compounds, hotels, and apartment blocks.[5]
In June 2015, CNN International was made available online in the United States for CNN/U.S subscribers on participating television providers through the CNNgo service.[6]
Simulcasts between CNNI and CNN/US
Although dramatically scaled down since its early days, CNNI currently (as of mid 2017) draws from the feed of the main CNN channel for all editions of Wolf, Anderson Cooper 360°, the first hour of Monday through Thursday editions of CNN Tonight, the first hour of weekday editions of New Day, Smerconish, the Sunday edition of Inside Politics, State of the Union, Fareed Zakaria GPS, Reliable Sources and some CNN Special Investigations Unit documentaries. The ticker and timepiece of CNN/US are replaced by those of CNNI, although CNN/US's red logo on a white field is retained in the on-screen graphic (rather than replaced by CNNI's white logo on a red field), signifying CNN/US as the originating source.
CNNI also simulcasts CNN/U.S. newscasts whenever major events happen in the United States or around the world. Examples include the death and funeral of Ronald Reagan, the crash of Continental Airlines Flight 3407 in the Buffalo suburb of Clarence Center, the Hudson River plane landing, the attempted Christmas Day bombing of flight 253 and the death and memorial service of Michael Jackson as well as scheduled events such as U.S. elections, Presidential inaugurations and the annual New Year's Eve ball drop from Times Square.
Likewise, CNN/U.S. occasionally turns to CNNI newscasts, primarily when major international news breaks during overnight hours in the U.S. A notable case was during the death of Pope John Paul II and the aftermath of the London Underground bombings of July 7, 2005. CNN/U.S. simulcast CNNI coverage of the death of Pakistan's former Prime Minister Benazir Bhutto on the night after her assassination took place. Simulcasts also happened from November 27 to 29, 2008, due to the terror attacks in Mumbai, India, on January 4, 2009, when Israel launched strikes into Gaza, and during the early hours of January 14, 2010, due to the earthquake in Haiti.
From 2005 until early 2008, CNNI's Your World Today aired on CNN/U.S.[7] during the 12–1 p.m. ET timeslot. That program was initially pre-empted by Issue #1, a program dealing in the American economic, financial, and housing sectors as part of the lead-up to the 2008 U.S. presidential election, and permanently replaced by another hour of CNN Newsroom in September 2008.
During the Atlanta tornado outbreak in March 2008, CNN/U.S. and CNNI simulcasted coverage after Anderson Cooper 360° ended. That coverage ended around 12:40 a.m. EDT and the channels resumed their normal programming. Furthermore, the next day, with storms impending, CNN/U.S. had to move onto CNNI's U.S. news set and weather center to avoid water from possible flooding during the storms.
On January 17, 2011, CNN/U.S. dropped its early morning rebroadcasts of ParkerSpitzer and Anderson Cooper 360° during the 4–6 a.m. ET time period, and began to simulcast World Business Today and World One from CNNI in those slots. Both newscasts the only programs broadcast entirely in the 4:3 picture format on CNN/U.S.' standard-definition and high-definition feeds (the SD feed of CNN/US switched to a widescreen letterbox screen format on January 11, 2011). World One was dropped from CNN/U.S. just a few months later to allow the addition of an extra hour of American Morning which has been replaced with Early Start.
As of August 2014, following the unrest in Ferguson, Missouri, a permanent simulcast of CNNI's block of Newsroom with Rosemary Church and Errol Barnett was added to the late-night lineup of CNN/U.S., serving as a lead-in to Early Start. In late 2015, John Vause and anchor Isha Sesay began to anchor a two-hour block of the simulcast from CNN studios in Los Angeles.[8]
Programming
All news programming is replaced by features, except for the following:
- CNN Newsroom
- World Sport
- CNNGo
- iReport for CNN
- Winning Post - Presented by Aly Vance
- On China – Presented by Kristie Lu Stout
- Living Golf – Presented by Shane O'Donoghue
- MainSail – Presented by Shirley Robertson
- CNN Marketplace Africa
- Inside Africa
- Smerconish
- Inside Politics
- State of the Union
- Fareed Zakaria GPS
- Reliable Sources
- Erin Burnett Outfront
- CNN Business Traveller – presented by Richard Quest
- In 24 Hours
- Best Of Quest
- Amanpour Weekend
- African Voices
- Art of Movement
- BackStory
Former programming
- Diplomatic License (1994–2006); debates feature for the United Nations
- NewsNight with Aaron Brown (2001–2005); talk show; produced by CNN/US
- Late Edition (1993–2009); talk show; produced by CNN/US
- Larry King Live (1985–2010); talk show; produced by CNN/US
- Piers Morgan Live (2011–2014); talk show; produced by CNN/US
High definition
CNN International HD is the high definition simulcast feed of the channel broadcasting at 1920x1080i, which was launched in September 2012. Prior to 3 June 2013, only programming from CNN US were available natively in HD, while shows made for CNN International were produced in 4:3 576i. In February 2013, the European SD feed of CNN International began broadcasting in widescreen by downscaling the HD feed, which resulted in all 4:3-native programming being broadcast in pillarbox until the June 3 switchover, finalising on 17 June of the same year, when the switchover was completed.
In late 2010, the American CNN channel became available in HD to viewers in Japan under the name CNN HD. The CNN U.S. domestic version (both SD and HD) is also available on Greater China-based satellite service DishHD (subsidiary of Dish Network in U.S.).
On 28 June 2016, CNN International HD was launched for Sky customers in the UK, on channel 506 or 579, making the next news channel launch in the 600's, as it is next to the GOD Channel.
Online
CNN debuted its news website CNN.com (initially an experiment known as CNN Interactive) on August 30, 1995. The site attracted growing interest over its first decade and is now one of the most popular news websites in the world. The widespread growth of blogs, social media and user-generated content have influenced the site, and blogs in particular have focused CNN's previously scattershot online offerings, most noticeably in the development and launch of CNN Pipeline in late 2005. In April 2009, CNN.com ranked third place among online global news sites in unique users in the U.S. according to Nielsen/NetRatings; with an increase of 11% over the previous year.
CNN Pipeline was the name of a paid subscription service, its corresponding website, and a content delivery client that provided streams of live video from up to four sources (or "pipes"), on-demand access to CNN stories and reports, and optional pop-up "news alerts" to computer users. The installable client was available to users of PCs running Microsoft Windows. There was also a browser-based "web client" that did not require installation. In July 2007, the service was discontinued and replaced with a free streaming service.
The now-defunct topical news program Judy Woodruff's Inside Politics was the first CNN program to feature a round-up of blogs in 2005.[9] Blog coverage was expanded when Inside Politics was folded into The Situation Room. In 2006, CNN launched CNN Exchange and CNN iReport, initiatives designed to further introduce and centralize the impact of everything from blogging to citizen journalism within the CNN brand. CNN iReport which features user-submitted photos and video, has achieved considerable traction, with increasingly professional-looking reports filed by amateur journalists, many still in high school or college. The iReport gained more prominence when observers of the Virginia Tech shootings sent-in first hand photos of what was going during the shootings.[10]
In early 2008, CNN began maintaining a live streaming broadcast available to those who receive CNN at home.[11] CNN International is broadcast live, as part of the RealNetworks SuperPass subscription outside the U.S. CNN also offers several RSS feeds and podcasts.
On April 18, 2008, CNN.com was targeted by Chinese hackers in retaliation for the channel's coverage on the 2008 Tibetan unrest. CNN reported that they took preventative measures after news broke of the impending attack.[12][13] The company was honored at the 2008 Technology & Engineering Emmy Awards for development and implementation of an integrated and portable IP-based live, edit and store-and-forward digital newsgathering system.
On October 24, 2009 CNN launched a new version of the CNN.com website, revamping it adding a new "sign up" option where users may create their own user name, a new "CNN Pulse" (beta) feature along with a new red color theme.[14] However, most of the news archived on the website has been deleted. CNN also has a channel in the popular video-sharing site YouTube, but its videos can only be viewed in the United States, a source of criticism among YouTube users worldwide.
In April 2010, CNN announced via Twitter its upcoming food blog called "Eatocracy," in which it will "cover all news related to food – from recalls to health issues to culture."[15] CNN had an internet relay chat (IRC) network at chat.cnn.com. CNN placed a live chat with Benjamin Netanyahu on the network in 1998.[16]
Bureaus
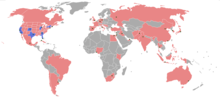


- Note: Boldface indicates that they are CNN's original bureaus, meaning they have been in operation since CNN's founding.
United States
- Atlanta (World Headquarters)
- Boston
- Chicago
- Columbus
- Dallas
- Denver
- Houston
- Las Vegas
- Los Angeles
- Miami
- Minneapolis
- New Orleans
- New York City
- Orlando
- Philadelphia
- Phoenix
- Raleigh-Durham
- San Francisco
- Seattle
- Washington, D.C.
Worldwide
- Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
- Amman, Jordan
- Baghdad, Iraq
- Bangkok, Thailand
- Beijing, China
- Beirut, Lebanon
- Berlin, Germany
- British Columbia, Canada
- Buenos Aires, Argentina
- Cairo, Egypt
- Caracas, Venezuela
- Dubai, United Arab Emirates (Middle East regional headquarters)
- Frankfurt, Germany
- Havana, Cuba
- Hong Kong, China (Asia Pacific regional headquarters)
- Islamabad, Pakistan
- Istanbul, Turkey (CNN Türk)
- Jakarta, Indonesia (CNN Indonesia)
- Jerusalem, Israel
- Johannesburg, South Africa (African regional headquarters)
- Kabul, Afghanistan
- Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
- Lagos, Nigeria
- London, United Kingdom (European regional headquarters)
- Ottawa, Ontario, Canada
- Madrid, Spain
- Manila, Philippines (CNN Philippines)
- Mexico City, Mexico (Latin American regional headquarters)
- Moscow, Russia
- Mumbai, India
- Nairobi, Kenya
- New Delhi, India (South Asia, regional headquarters)
- Paris, France
- Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
- Rome, Italy
- Quebec, Canada
- Santiago, Chile (CNN Chile)
- São Paulo, Brazil
- Seoul, South Korea
- Shanghai, China (Asia Pacific regional headquarters)
- Singapore City, Singapore
- Sydney, Australia
- Tokyo, Japan (CNNj)
Present personalities
Anchors and hosts
|
Meteorologists and correspondents
|
Past personalities
- Guillermo Arduino (now with CNN en Español and CNN Latino)
- Terry Baddoo
- Ralph Begleiter
- Satinder Bindra
- Aaron Brown
- Andrew Brown
- Joie Chen (joined Al Jazeera America)
- Patricia Chew
- Jim Clancy
- Stephen Cole (joined Al Jazeera English)
- Jason Dasey
- Eboni Deon (now with WISH-TV)
- Daljit Dhaliwal
- Jill Dougherty
- Anna Edwards
- Adrian Finighan (left CNN in 2009 to set up own company; joined Al Jazeera English)
- Kate Giles (now with Sky Sports News HQ)
- Stan Grant
- Leon Hawthorne
- Jerrold Kessel, Jerusalem correspondent, 1990 to 2003[17]
- Riz Khan (left CNN in 2005 to join Al Jazeera English)[18]
- Larry King
- Jeff Koinange (left CNN in 2007 following personal accusations made against him by an alleged former love interest)[19]
- May Lee (now host of STAR World's The May Lee Show)
- Amber Lyon
- Sheila MacVicar (joined Al Jazeera America)
- Rima Maktabi
- Lola Martinez
- Colleen McEdwards
- Piers Morgan
- Anand Naidoo (now with CCTV America)
- Asieh Namdar (now with CCTV America)
- Robin Oakley
- Femi Oke (joined Al Jazeera English)
- Veronica Pedrosa (joined Al Jazeera English)
- Juanita Phillips
- Pedro Pinto
- Monita Rajpal
- Aneesh Raman
- Mari Ramos
- Anjali Rao
- Afshin Rattansi (now with RT, formerly Russia Today)
- Shihab Rattansi (joined Al Jazeera English)
- Candy Reid
- Maria Ressa (left CNN to become head of ABS-CBN's News and Current Affairs division)
- Hugh Riminton (now with Ten News)
- Dan Rivers (returned to ITV News)
- Sonia Ruseler
- Brent Sadler
- Bill Schneider
- Linden Soles
- Martin Soong (returned to CNBC in 2005)
- Fionnuala Sweeney
- Ralitsa Vassileva
- Ali Velshi
- Zain Verjee
- Alessio Vinci
- Harris Whitbeck
- Eunice Yoon (returned to CNBC Asia)
- John Zarrella
Criticism

Accusations of US-centric viewpoint
Former CNN Beijing and Tokyo bureau chief Rebecca MacKinnon described how the news-gathering priorities of CNN International were skewed to "produce stories and reports that would be of interest to CNN USA." Nevertheless, Jane Arraf, a former correspondent who was with the Council on Foreign Relations and later served as a Middle East-based correspondent for now-defunct Al Jazeera English, noted that when she spoke on international affairs, CNN International would usually give her more airtime than CNN/US. For its own part, former CNN executive Eason Jordan has defended CNN International's "international" perspective, saying "No matter what CNN International does, as long as CNN's headquarters is in the United States people are going to say, well, it's an American service. But the reality is that it's an international service based in the United States, and we don't make any apologies about that."[20]
Accusations of anti-Israel bias
In 2002, Honest Reporting spearheaded a campaign to expose CNN for pro-Palestinian bias, citing public remarks in which Ted Turner equated Palestinian suicide bombing with Israeli military strikes.[21] On November 18, 2014, a misleading headline was posted by CNN. Two Palestinian terrorists had entered a synagogue with knives and a gun, killing four Jewish worshippers and wounding seven. The headline stated instead that two Palestinian were killed by Israeli police, thus equating the perpetrators of the massacre of Jews with the killing of the armed terrorists. The headline failed to mention the four Jews who were murdered in this 2014 Jerusalem synagogue attack. CNN stated that the attack occurred at a mosque, when in fact the synagogue was attacked, compounding the bias.[22][23][24]
Accusations of pro-American bias
CNN is one of the world's largest news organizations, and its international channel, CNN International is the leading international news channel in terms of viewer reach.[25][26] Unlike the BBC and its network of reporters and bureaus, CNN International makes extensive use of affiliated reporters that are local to, and often directly affected by, the events they are reporting. The effect is a more immediate, less detached style of on-the-ground coverage. This has done little to stem criticism, largely from Middle Eastern nations, that CNN International reports news from a pro-American perspective. This is a marked contrast to domestic criticisms that often portray CNN as having a "liberal" or "anti-American" bias.
Accusations of anti-China bias
A Chinese website, anti-cnn.com,[27] has accused CNN and western media in general of biased reporting against China, with the catchphrase "Don't be so CNN" catching on in the Chinese mainstream as jokingly meaning "Don't be so biased". Pictures used by CNN are allegedly edited to have completely different meanings from the original ones. In addition, the channel was accused of largely ignoring pro-China voices during the Olympic Torch Relay debacle in San Francisco.
On July 7, 2010, Octavia Nasr, senior Middle East editor and a CNN journalist for 20 years, was fired after she expressed admiration on her Twitter account for a militant Muslim cleric and former Hezbollah leader who had recently died.[28]
Accusations of propaganda and censorship
In October 2011, Amber Lyon claimed to the Syrian government news agency SANA that she had been directed by CNN to report selectively, repetitively, and falsely in order to sway public opinion in favor of direct American aggression against Iran and Syria,[29] and that this was common practice under CNN. She subsequently repeated this claim, addressing the degraded state of journalistic ethics in an interview[30][citation needed] during which she also discussed the Bahraini episode, suggesting paid-for content was also taken from Georgia, Kazakhstan, and other states, that the War on Terrorism had also been employed as a pretext to pre-empt substantive investigative journalism within the U.S., and that following the Bahrain reporting, her investigative department had been terminated and "reorganized", and her severance and employee benefits used as a threat to intimidate and attempt to purchase her subsequent silence.
Lyon claimed to have met with Tony Maddox, president of CNN International, twice about this issue in 2011 and had claimed that during the second meeting she was threatened and intimated to stop speaking on the matter.[31] CNN issued a detailed response to Lyon's claims about its coverage of Bahrain.[32]
Lyon also claimed on the Russian news channel RT that CNN reporters, headed by Maddox, have been instructed to over-cover Iran as a form of propaganda, and that CNN International has been paid by the Bahraini government to produce and air news segments intentionally painting them in a positive light.[citation needed]
See also
References
- ^ "NSS 7 (20.0°W) Transponder 24 – KingOfSat". kingodsat.net. Retrieved 3 June 2013.
- ^ Why didn't CNN's international arm air its own documentary on Bahrain's Arab Spring repression? CNNi's president, Tony Maddox
- ^ "CNN International - National Constitution Center". National Constitution Center – constitutioncenter.org.
- ^ "CNN International | Idents". TVARK. Retrieved 2016-08-07.
- ^ Vause, John (2008-04-09). "San Francisco Torch Relay Broadcast". CNN.
- ^ "CNN International Now Available on CNNgo". TVNewser. Retrieved 2 July 2015.
- ^ Home+ (2015-09-01). "Breaking News, Latest News and Videos - CNN.com". Edition.cnn.com. Retrieved 2016-08-07.
- ^ "John Vause, Isha Sesay To Anchor CNN International Show From Los Angeles". TVNewser. Retrieved 9 December 2015.
- ^ Johnson, Peter (2005-03-20). "It's prime time for blogs on CNN's 'Inside Politics'". USA Today. Retrieved 2009-01-24.
- ^ Cobb, Chris (2008-04-12). "'Citizen journalist' often there first to snap photos". Regina Leader-Post. Retrieved 2009-01-24.
- ^ "CNN.com Live". Edition.cnn.com. Retrieved 2016-08-07.
- ^ "CNN Web site targeted - CNN.com". Edition.cnn.com. 2008-04-18. Retrieved 2016-08-07.
- ^ Claburn, Thomas: "CNN Faces Cyberattack Over Tibet Coverage" InformationWeek, 2008
- ^ "Welcome to the New CNN.com – Interactive tour". CNN. Retrieved 2010-02-20.
- ^ Brion, Raphael (2010-04-13). "Eatocracy: CNN Gets in the Food Blog Business". Eater.com.
- ^ "CNN Community". Edition.cnn.com. Retrieved 2016-08-07.
- ^ "Jerrold Kessel, former CNN correspondent, dies at 66". Variety. 2011-02-24. Retrieved 2011-02-26.
- ^ Wall Street Journal, requires subscription
- ^ Brian (2007-05-29). "Jeff Koinange No Longer Employed By CNN | TVNewser". Mediabistro.com. Retrieved 2016-08-07.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on December 30, 2006. Retrieved 2007-01-28.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Oliver Burkeman; Peter Beaumont. "CNN chief accuses Israel of terror | Media". The Guardian. Retrieved 2016-08-07.
- ^ Johnson, Alan (November 20, 2014). "Blaming Israel for Palestinian violence is racist: it denies that Arabs are moral agents". The Telegraph. Retrieved November 21, 2014.
- ^ CNN apologizes for bias, Hollywoodreporter.com; accessed November 21, 2014.
- ^ "CNN Describes Muslim Terror Attack on Synagogue as Israel Killing Palestinians". Frontpage Mag. 2014-11-18. Retrieved 2016-08-07.
- ^ "About Us". CNN. Retrieved 2010-02-20.
- ^ "CNN tops European news channels according to EMS – Brand Republic News". Brand Republic. Retrieved 2010-02-20.
- ^ "四月网_M4.CN_全球视野,中国情怀". M4.cn. 2015-06-01. Retrieved 2016-08-07.
- ^ Gold, Matea (2010-07-07). "CNN Mideast Affairs editor loses post after tweeting her respect for militant cleric". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ "Ex-CNN Reporter: I Received Orders to Manipulate News to Demonize Syria and Iran". Archived from the original on April 2, 2013. Retrieved March 4, 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "An Interview With Alex Jones, America's Leading (and Proudest) Conspiracy Theorist". Nymag.com. 2013-11-17. Retrieved 2016-08-07.
- ^ Glenn Greenwald. "Why didn't CNN's international arm air its own documentary on Bahrain's Arab Spring repression? | Glenn Greenwald | US news". The Guardian. Retrieved 2016-08-07.
- ^ "CNN International's Response to the Guardian – Update". CNN. September 5, 2012.
