User:EEng/sandbox: Difference between revisions
Square 0 for 5.1 (not sure how far I'll be actually get) |
→top: (dummy edit) This is what we're calling V5.2.1 |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
|birth_date = July 9, 1823 (date uncertain)<!--<<see hidden note at beginning of lead re uncertain birthdate--> |
|birth_date = July 9, 1823 (date uncertain)<!--<<see hidden note at beginning of lead re uncertain birthdate--> |
||
|birth_place = [[Grafton County, New Hampshire|Grafton Co., New Hampshire]]{{efn|name=birth_name}}<!--<<cite covers birth date and place, and discusses uncertainty of birthdate--> |
|birth_place = [[Grafton County, New Hampshire|Grafton Co., New Hampshire]]{{efn|name=birth_name}}<!--<<cite covers birth date and place, and discusses uncertainty of birthdate--> |
||
|death_date = {{death date and age|1860|05|21|1823|07|09}}<!--1860 is correct despite Harlow |
|death_date = {{death date and age|1860|05|21|1823|07|09}}<!--1860 is correct despite Harlow 1868 reporting 1861; see Macmillan 2000 p108 --> |
||
|death_place = In or near [[San Francisco]] |
|death_place = In or near [[San Francisco]] |
||
|death_cause = ''[[Status epilepticus]]'' |
|death_cause = ''[[Status epilepticus]]'' |
||
|occupation = {{hlist | Railroad construction foreman | [[Rock blasting|blaster]] | [[stagecoach]]{{nbsp}}driver}} |
|occupation = {{hlist | Railroad construction foreman | [[Rock blasting|blaster]] | [[stagecoach]]{{nbsp}}driver}} |
||
|spouse=None |children=None{{ |
|spouse=None |children=None{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|39,319,327}}<ref name="northstar"/><!--Please don't remove spouse, children even though values are None--> |
||
|residence = {{hlist|[[New England]] | [[Chile]] | [[California]] }} |
|residence = {{hlist|[[New England]] | [[Chile]] | [[California]] }} |
||
|home_town = [[Lebanon, New Hampshire]]{{efn|name=birth_name}}<!--cite covers home_town only--> |
|home_town = [[Lebanon, New Hampshire]]{{efn|name=birth_name}}<!--cite covers home_town only--> |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
|known_for = Personality change after [[Traumatic brain injury|brain{{nbsp}}injury]] |
|known_for = Personality change after [[Traumatic brain injury|brain{{nbsp}}injury]] |
||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Phineas P. Gage''' (1823<!--<<as allowed by MOS, giving only year for birth in lead because exact birthdate is uncertain (full dates and explanation in infobox and its notes)-->{{snd}}May 21, 1860) was an American railroad construction foreman remembered for his improbable{{ |
'''Phineas P. Gage''' (1823<!--<<as allowed by MOS, giving only year for birth in lead because exact birthdate is uncertain (full dates and explanation in infobox and its notes)-->{{snd}}May 21, 1860) was an American railroad construction foreman remembered for his improbable{{sfn|Bigelow 1850}}{{rp|19}} survival of an accident in which a large iron rod was driven completely through his head, destroying much of his brain's left [[frontal lobe]], and for that injury's reported effects on his personality and behavior over the remaining twelve years of his life{{mdashb}}effects so profound (for a time at least) that friends saw him as "no longer Gage". |
||
[[File:Phineas gage - 1868 skull diagram.jpg|thumb|upright=0.48|left|The iron's path, per {{nowrap|Harlow{{ |
[[File:Phineas gage - 1868 skull diagram.jpg|thumb|upright=0.48|left|The iron's path, per {{nowrap|Harlow{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|21}} }} ]] |
||
{{nowrap|Long known as "the}}<!--<<force text below img when window is very narrow--> |
{{nowrap|Long known as "the}}<!--<<force text below img when window is very narrow--> |
||
{{shy|American Crowbar Case"{{mdashb}}once termed "the case which more than all others is calcu|lat|ed to excite our wonder, impair the value of prog|no|sis, and even to subvert our [[physiology|physiolog{{shy}}ical]] doctrines"{{nowrap|{{px1}} |
{{shy|American Crowbar Case"{{mdashb}}once termed "the case which more than all others is calcu|lat|ed to excite our wonder, impair the value of prog|no|sis, and even to subvert our [[physiology|physiolog{{shy}}ical]] doctrines"{{nowrap|{{px1}}<ref name="campbell"/>{{mdash}}}}{{zwsp}}Phineas Gage influenced nineteenth-century discussion about the mind and brain, partic|u|lar|ly debate on [[cerebral localization|cerebral locali{{shy}}za{{shy}}tion]],{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|ch7-9}}{{sfn|Barker 1995}} and was perhaps the first case to suggest that damage to specific parts of the brain might induce specific person|al|i|ty changes. |
||
}}<!--<<end SHY-->{{ |
}}<!--<<end SHY-->{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|1}}{{sfn|Macmillan 2012}}{{rp|C}} |
||
Gage is a fixture in the curricula of [[neurology]], [[psychology]], and related disciplines {{Crossreference|(see [[Neuroscience]])}},{{ |
Gage is a fixture in the curricula of [[neurology]], [[psychology]], and related disciplines {{Crossreference|(see [[Neuroscience]])}},<ref name="larner"/>{{sfn|Macmillan 2001}}{{rp|149}} "a living part of the medical folklore"{{px1}}{{sfn|Ratiu 2004}}{{rp|637}} frequently mentioned in books and scientific papers;{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|ch14}} he even has a minor place in popular culture.{{refn|[[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], ch. 13; [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2008|Macmillan 2008]], p. 830.}} Despite this celebrity, the body of established fact about Gage and what he was like (before or after his injury) is small,{{efn|name=accounts_reliablesources}} which has allowed "the fitting of almost any theory [desired] to the small number of facts we have"{{px1}}{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|290}}{{mdashb}}Gage acting as a "[[Rorschach test|Rorschach inkblot]]"{{px1}}<ref name="mazzoni"/> in which proponents of various conflicting theories of the brain were able to find support for their views. Historically, published accounts (including scientific ones) have almost always severely distorted and exaggerated Gage's behavioral changes, frequently contradicting the known facts. |
||
A report of Gage's physical and mental condition shortly before his death implies that his most serious mental changes were temporary, so that in later life, he was far more functional, and socially far better adapted, than in the years immediately following his accident. A social recovery hypothesis suggests that his employment as a [[stagecoach]] driver in Chile provided daily structure allowing him to regain lost social and personal skills. |
A report of Gage's physical and mental condition shortly before his death implies that his most serious mental changes were temporary, so that in later life, he was far more functional, and socially far better adapted, than in the years immediately following his accident. A social recovery hypothesis suggests that his employment as a [[stagecoach]] driver in Chile provided daily structure allowing him to regain lost social and personal skills. |
||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
Gage was the first of five children born to Jesse Eaton Gage and Hannah Trussell (Swetland) Gage, of [[Grafton County, New Hampshire]].{{efn |
Gage was the first of five children born to Jesse Eaton Gage and Hannah Trussell (Swetland) Gage, of [[Grafton County, New Hampshire]].{{efn |
||
|name=birth_name |
|name=birth_name |
||
|Macmillan{{ |
|Macmillan{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|14-17,31n5,490-1}} discusses Gage's ancestry and early life. The birthdate July 9, 1823 is given by a Gage genealogy<ref name="cv_gage"/><!--need pg#--> without citation,{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|16}} but is consistent with agreement among contemporary sources<ref name="incredible"/> that Gage was 25 years old on the date of his accident, and with his age (36{{nbsp}}years) as given in undertaker's records after his death in May{{nbsp}}1860.{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|108-9}} Possible homes in childhood and youth are [[Lebanon, New Hampshire|Lebanon]] or nearby East Lebanon, [[Enfield, New Hampshire|Enfield]], and/or [[Grafton, New Hampshire|Grafton]] (all in [[Grafton County, New Hampshire]]), though Harlow refers to Lebanon in particular as Gage's "native place"{{px1}}{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|10}} and "his home"{{px1}}{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|12}} (likely that of his parents),{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|30}} to which Gage returned ten weeks{{sfn|Macmillan 2012}}{{rp|C}} after his accident. |
||
{{cite news |date=March 29, 1849 |work=National Eagle |at=p. 2, col. 2 |place=Claremont, New Hampshire |title=Incredible, But True Every Word }} Reprinted: ''True Democrat and Granite State Whig'' (Lebanon, New Hampshire), April 6, 1849, p.{{nbsp}}1, col.{{nbsp}}7. Transcribed in [[#M|Macmillan (2000)]], pp.40{{ndash}}1. |
|||
*[[#H1|Harlow (1848)]], p. 389; [[#B1|Bigelow (1850)]], p. 13; [[#H|Harlow (1868)]], p. 4.}} that Gage was 25 years old on the date of his accident, and with his age (36{{nbsp}}years) as given in undertaker's records after his death in May{{nbsp}}1860.{{ranchor|M|p=108-9}} Possible homes in childhood and youth are [[Lebanon, New Hampshire|Lebanon]] or nearby East Lebanon, [[Enfield, New Hampshire|Enfield]], and/or [[Grafton, New Hampshire|Grafton]] (all in [[Grafton County, New Hampshire]]), though Harlow refers to Lebanon in particular as Gage's "native place"{{px1}}{{ranchor|H|p=10}} and "his home"{{px1}}{{ranchor|H|p=12}} (likely that of his parents),{{ranchor|M|p=30}} to which Gage returned ten weeks{{ranchor|M3|p=C}} after his accident. |
|||
{{paragraph break}} |
{{paragraph break}} |
||
There is nothing to indicate what Gage's middle initial ''P''{{px2}}{{refn|[[#H1|Harlow |
There is nothing to indicate what Gage's middle initial ''P''{{px2}}{{refn|[[#H1|Harlow 1848]], p. 389; [[#Bigelow 1850|Bigelow 1850]], p. 13; [[#H|Harlow 1868]], p. 4; [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], p. 490; [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2008|Macmillan 2008]], p. 839 (fig.).}} stood for. His mother's first, middle, and maiden names are variously given as (respectively) ''Hannah'' or ''Hanna''; ''Trussell'', ''Trusel'', or ''Trussel''; and ''Swetland, Sweatland,'' or ''Sweetland''.{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|490}} |
||
}}<!--<<end efn--> |
}}<!--<<end efn--> |
||
Little is known about his upbringing and education beyond that he was literate.{{ |
Little is known about his upbringing and education beyond that he was literate.{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|17,41,90}}{{sfn|M8}}{{rp|3}} |
||
Town doctor [[John Martyn Harlow]] described Gage as "a perfectly healthy, strong and active young man, twenty-five years of age, nervo-bilious temperament, five feet six inches [{{convert|5|ft|6|in|m|disp=output only}}] in height, average weight one hundred and fifty pounds [{{convert|150|lb|kg|disp=output only }}], possessing an iron will as well as an iron frame; muscular system unusually well developed{{mdashb}}having had scarcely a day's illness from his childhood to the date of [his] injury".{{ |
Town doctor [[John Martyn Harlow]] described Gage as "a perfectly healthy, strong and active young man, twenty-five years of age, nervo-bilious temperament, five feet six inches [{{convert|5|ft|6|in|m|disp=output only}}] in height, average weight one hundred and fifty pounds [{{convert|150|lb|kg|disp=output only }}], possessing an iron will as well as an iron frame; muscular system unusually well developed{{mdashb}}having had scarcely a day's illness from his childhood to the date of [his] injury".{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|4}} (In [[phrenology]]{{mdashb}}then just ending its vogue<ref name="cooter"/>{{mdashb}}''nervo-bilious'' denoted an unusual combination of "excitable and active mental powers" with "energy and strength [of] mind and body [making] possible the endurance of great mental and physical labor".){{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|346-7}}<ref name="fowler"/>{{rp|6}} |
||
Gage may have first worked with explosives during farmwork as a youth, or in nearby mines and quarries.{{ |
Gage may have first worked with explosives during farmwork as a youth, or in nearby mines and quarries.{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|17-18}} He is known to have worked on construction of the [[Hudson River Railroad]] near [[Cortlandt, New York|Cortlandt Town, New York]],<ref name="heart"/>{{sfn|M8}}{{rp|3}} and by the time of his accident he was a [[Rock blasting|blasting]] foreman (possibly an independent contractor) on railway construction projects.{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|18-22,32n9}} His employers' "most efficient and capable foreman{{nbsp}}... a shrewd, smart business man,<!--<<two words, not "businessman"--> very energetic and persistent in executing all his plans of operation",{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|13-14}} he had even commissioned a custom-made [[wikt:tamp#English|tamping iron]]{{mdashb}}a large iron rod{{mdashb}}for use in setting explosive charges.{{sfn|Bigelow 1850}}{{rp|5}}{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|25}} |
||
===Accident=== |
===Accident=== |
||
[[File:RailroadCutCavendishVermontPresumedToBePhineasGageAccidentSite cropped.jpg|thumb|left|upright=1.0|link=File:RailroadCutCavendishVermontPresumedToBePhineasGageAccidentSite.jpg|{{shy|Line of the [[Rutland Railway|Rut{{shy}}land{{nbsp}}& Burling{{shy}}ton Rail{{shy}}road]] passing through "[[cut (earthmoving)|cut]]" in rock south of Caven|dish. Gage met with his accident while setting explo|sives to create either this cut or a similar one nearby.}}{{zwsp}}{{efn|name=steps_setting}} ]] |
[[File:RailroadCutCavendishVermontPresumedToBePhineasGageAccidentSite cropped.jpg|thumb|left|upright=1.0|link=File:RailroadCutCavendishVermontPresumedToBePhineasGageAccidentSite.jpg|{{shy|Line of the [[Rutland Railway|Rut{{shy}}land{{nbsp}}& Burling{{shy}}ton Rail{{shy}}road]] passing through "[[cut (earthmoving)|cut]]" in rock south of Caven|dish. Gage met with his accident while setting explo|sives to create either this cut or a similar one nearby.}}{{zwsp}}{{efn|name=steps_setting}} ]] |
||
{{external media |float=right|width=18em<!--<<expressing width in ems allows controlled linewrap--> |video1= [http://www.nejm.org/action/showMediaPlayer?doi=10.1056%2FNEJMicm031024&aid=NEJMicm031024_attach_1&area= Video reconstruction of tamping iron passing through Gage's skull] (Ratiu et{{nbsp}}al.){{zwsp}}{{ |
{{external media |float=right|width=18em<!--<<expressing width in ems allows controlled linewrap--> |video1= [http://www.nejm.org/action/showMediaPlayer?doi=10.1056%2FNEJMicm031024&aid=NEJMicm031024_attach_1&area= Video reconstruction of tamping iron passing through Gage's skull] (Ratiu et{{nbsp}}al.){{zwsp}}{{sfn|R1}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
| Line 66: | Line 64: | ||
|name=steps_setting |
|name=steps_setting |
||
|Macmillan gives background on Cavendish (at the time called Duttonsville), |
|Macmillan gives background on Cavendish (at the time called Duttonsville), |
||
the location and circumstances of the accident, and the steps in setting a blast.{{ |
the location and circumstances of the accident, and the steps in setting a blast.{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|13,23-9}}{{sfn|Macmillan 2001}}{{rp|151-2}}{{sfn|Macmillan 2012}}{{rp|A}} |
||
The blast hole, about {{frac|1|3|4}} inches (4.5{{nbsp}}cm) in diameter and up to 12 feet (4{{nbsp}}m) deep, might require three men working as much as a day to bore using hand tools. The labor invested in setting each blast, the judgment involved in selecting its location and the quantity of powder to be used, and the often explosive nature of employer-employee relations on this type of job, all underscore the significance of Harlow's statements that Gage has been a "great favorite" with his men, and that his employers had considered him "the most efficient and capable foreman in their employ" prior to the accident.{{ |
The blast hole, about {{frac|1|3|4}} inches (4.5{{nbsp}}cm) in diameter and up to 12 feet (4{{nbsp}}m) deep, might require three men working as much as a day to bore using hand tools. The labor invested in setting each blast, the judgment involved in selecting its location and the quantity of powder to be used, and the often explosive nature of employer-employee relations on this type of job, all underscore the significance of Harlow's statements that Gage has been a "great favorite" with his men, and that his employers had considered him "the most efficient and capable foreman in their employ" prior to the accident.{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|13,22-3,25}} |
||
}}<!--<<end efn--> |
}}<!--<<end efn--> |
||
Gage was doing this around 4:30{{nbsp}}p.m. when (possibly because the sand was omitted){{ |
Gage was doing this around 4:30{{nbsp}}p.m. when (possibly because the sand was omitted){{sfn|Bigelow 1850}}{{rp|13-14}}{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|5}}{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|27}} |
||
the iron sparked against the rock and the powder exploded.<!--Gage had been sitting, head turned etc etc. (/Note/ for even more detail and Macmillan's discussion of conflicting presentations on posture.)--> Rocketing from the hole, the tamping iron{{mdashb}}three feet seven inches (1.1{{nbsp}}m) long and {{fraction|1|1|4}} inches (3.2{{nbsp}}cm) in diameter{{ |
the iron sparked against the rock and the powder exploded.<!--Gage had been sitting, head turned etc etc. (/Note/ for even more detail and Macmillan's discussion of conflicting presentations on posture.)--> Rocketing from the hole, the tamping iron{{mdashb}}three feet seven inches (1.1{{nbsp}}m) long and {{fraction|1|1|4}} inches (3.2{{nbsp}}cm) in diameter{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|5}}{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|25}}{{mdashb}}"entered on the [left] side of [Gage's] face{{nbsp}}... passing back of the left eye, and out at the top of the head".{{efn|name=note_post}} |
||
Despite nineteenth-century references to Gage as "the American Crowbar Case"{{efn |
Despite nineteenth-century references to Gage as "the American Crowbar Case"{{efn |
||
|{{ |
|<ref name="smithW"/>{{rp|54}}{{sfn|T1}} "Harlow always refers to the bar by its proper title, as a tamping iron. Bigelow's reference to a crowbar{{nbsp}}... gave the case its nickname, which is still encountered today."{{px1}}{{sfn|Barker 1995}}{{rp|678}} |
||
}}<!--<<end efn--> |
}}<!--<<end efn--> |
||
his tamping iron did not have the bend or claw sometimes associated with the term ''[[Crowbar (tool)|crowbar]];'' rather, it was a pointed cylinder something like a [[javelin]],{{ |
his tamping iron did not have the bend or claw sometimes associated with the term ''[[Crowbar (tool)|crowbar]];'' rather, it was a pointed cylinder something like a [[javelin]],{{sfn|K}} "round and rendered comparatively smooth by use":{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|5}} |
||
{{imagequote|The end which entered first is pointed; the taper being [eleven inches (27{{nbsp}}cm) long, ending in a {{1/4}}-inch (7{{nbsp}}mm) point]{{px1}}{{ |
{{imagequote|The end which entered first is pointed; the taper being [eleven inches (27{{nbsp}}cm) long, ending in a {{1/4}}-inch (7{{nbsp}}mm) point]{{px1}}{{sfn|V}}{{rp|17}}{{zwj}}... circumstances to which the patient perhaps owes his life. The iron is unlike any other, and was made by a <!--DO NOT AMERICANISE THIS SPELLING>>>>-->{{sic|neighbouring|hide=y}}<!--<<<<DO NOT AMERICANISE THIS SPELLING --> blacksmith to please the fancy of its owner.{{sfn|Bigelow 1850}}{{rp|14}}<!--from Warren catalog, maybe add re "smoothly blunt" point 1/4 inch diam--> |
||
}} |
}} |
||
[[File:PhineasGage IronPaths BigelowVanHornCombined.jpg|thumb|right|upright=1.2|''(l)''{{px2}}Bigelow's estimate of the iron's path.{{ |
[[File:PhineasGage IronPaths BigelowVanHornCombined.jpg|thumb|right|upright=1.2|''(l)''{{px2}}Bigelow's estimate of the iron's path.{{sfn|Bigelow 1850}} {{nowrap|''(r)''{{px2}}Ratiu}} et{{nbsp}}al. and Van Horn et{{nbsp}}al. con{{shy}}cluded Gage's mouth had been open at the crucial moment, and that his skull "hinged" open as the iron passed through.{{refn|[[#R|Ratiu et al.]], p. 639; [[#V|Van Horn et al.]], pp. 4{{ndash}}5, 17}}]] |
||
Weighing {{frac|13|1|4}} pounds (6.0{{nbsp}}kg),{{ |
Weighing {{frac|13|1|4}} pounds (6.0{{nbsp}}kg),{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|5}} the tamping iron was found some 80{{nbsp}}feet (25{{nbsp}}m) away,{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|29}} "smeared with blood and brain".{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|5}} |
||
Gage "was thrown upon his back by the explosion, and gave a few convulsive motions of the extremities, but spoke in a few minutes", walked with little assistance, and sat upright in an oxcart for the {{3/4}}-mile (1.2{{nbsp}}km) ride to his lodgings in town.{{ |
Gage "was thrown upon his back by the explosion, and gave a few convulsive motions of the extremities, but spoke in a few minutes", walked with little assistance, and sat upright in an oxcart for the {{3/4}}-mile (1.2{{nbsp}}km) ride to his lodgings in town.{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|5}} About thirty minutes after the accident Dr. [[Edward H. Williams]], finding Gage sitting in a chair outside the hotel, was greeted with "one of the great understatements of medical history":{{sfn|M5}}{{rp|244}} |
||
{{imagequote|When I drove up he said, "Doctor, here is business enough for you." I first noticed the wound upon the head before I alighted from my carriage, the pulsations of the brain being very distinct. The top of the head appeared somewhat like an inverted funnel, as if some wedge-shaped body had passed from below upward. Mr. Gage, during the time I was examining this wound, was relating the manner in which he was injured to the bystanders. I did not believe Mr. Gage's statement at that time, but thought he was deceived. Mr. Gage persisted in saying that the bar went through his head. Mr.{{nbsp}}G. got up and vomited; the effort of vomiting pressed out about half a teacupful of the brain, which fell upon the floor. |
{{imagequote|When I drove up he said, "Doctor, here is business enough for you." I first noticed the wound upon the head before I alighted from my carriage, the pulsations of the brain being very distinct. The top of the head appeared somewhat like an inverted funnel, as if some wedge-shaped body had passed from below upward. Mr. Gage, during the time I was examining this wound, was relating the manner in which he was injured to the bystanders. I did not believe Mr. Gage's statement at that time, but thought he was deceived. Mr. Gage persisted in saying that the bar went through his head. Mr.{{nbsp}}G. got up and vomited; the effort of vomiting pressed out about half a teacupful of the brain, which fell upon the floor.<ref name="accident_excerpts"/> |
||
}} |
}} |
||
Harlow took charge of the case around 6 p.m.: |
Harlow took charge of the case around 6 p.m.: |
||
{{imagequote|You will excuse me for remarking here, that the picture presented was, to one unaccustomed to [[battlefield medicine|military surgery]], truly terrific; but the patient bore his sufferings with the most heroic firmness. He recognized me at once, and said he hoped he was not much hurt. He seemed to be perfectly conscious, but was getting exhausted from the hemorrhage. His person, and the bed on which he was laid, were literally one [[wikt:gore#English-thickened|gore]] of blood. |
{{imagequote|You will excuse me for remarking here, that the picture presented was, to one unaccustomed to [[battlefield medicine|military surgery]], truly terrific; but the patient bore his sufferings with the most heroic firmness. He recognized me at once, and said he hoped he was not much hurt. He seemed to be perfectly conscious, but was getting exhausted from the hemorrhage. His person, and the bed on which he was laid, were literally one [[wikt:gore#English-thickened|gore]] of blood.<ref name="accident_excerpts"/> |
||
}} |
}} |
||
| Line 96: | Line 94: | ||
With Williams' assistance{{efn |
With Williams' assistance{{efn |
||
|Williams family lore holds that Harlow did not appear until two days after Gage's accident, but nonetheless "sought eventually to take the whole glory of the successful outcome" of the case, even though Williams "was given full credit by all those who knew of his connection" to it. However, these stories conflict with every other account of Gage, including Williams' own.{{ |
|Williams family lore holds that Harlow did not appear until two days after Gage's accident, but nonetheless "sought eventually to take the whole glory of the successful outcome" of the case, even though Williams "was given full credit by all those who knew of his connection" to it. However, these stories conflict with every other account of Gage, including Williams' own.{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|279-84}} |
||
}}<!--<<end efn--> |
}}<!--<<end efn--> |
||
Harlow shaved the scalp around the region of the tamping iron's exit, then removed coagulated blood, small bone fragments, and an ounce [30{{nbsp}}g] of protruding brain.<!--<< It's unclear whether "1 ounce" means 1 fluid ounce or 1 avoirdupois ounce; luckily, for water (which is what brain essentially is) they're very close to the same thing--> After probing for foreign bodies and replacing two large detached pieces of bone, Harlow closed the wound with adhesive straps, leaving it partially open for drainage;{{ |
Harlow shaved the scalp around the region of the tamping iron's exit, then removed coagulated blood, small bone fragments, and an ounce [30{{nbsp}}g] of protruding brain.<!--<< It's unclear whether "1 ounce" means 1 fluid ounce or 1 avoirdupois ounce; luckily, for water (which is what brain essentially is) they're very close to the same thing--> After probing for foreign bodies and replacing two large detached pieces of bone, Harlow closed the wound with adhesive straps, leaving it partially open for drainage;{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|60-1}}<!--bring in Harlow's comment re hole in roof of mouth--> the entrance wound in the cheek was bandaged only loosely, for the same reason. A wet [[wikt:compress#English-folded cloth|compress]] was applied, then a nightcap, then further bandaging to secure these dressings. Harlow also dressed Gage's hands and forearms (which along with his face had been "deeply burned") and ordered that Gage's head be kept elevated. |
||
Late that evening Harlow noted: "Mind clear. Constant agitation of his legs, being alternately retracted and extended like the shafts of a [[fulling#fulling mill|fulling mill]]. Says he 'does not care to see his friends, as he shall be at work in a few days.{{'"}}{{px1}} |
Late that evening Harlow noted: "Mind clear. Constant agitation of his legs, being alternately retracted and extended like the shafts of a [[fulling#fulling mill|fulling mill]]. Says he 'does not care to see his friends, as he shall be at work in a few days.{{'"}}{{px1}}<ref name="accident_excerpts"/> |
||
====Convalescence==== |
====Convalescence==== |
||
Despite his own optimism, Gage's convalescence was long, difficult, and uneven. Though recognizing his mother and uncle (summoned from [[Lebanon, New Hampshire]], thirty miles away){{ |
Despite his own optimism, Gage's convalescence was long, difficult, and uneven. Though recognizing his mother and uncle (summoned from [[Lebanon, New Hampshire]], thirty miles away){{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|12}}{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|30}} on the morning after the accident, on the second day he "lost control of his mind, and became decidedly delirious". |
||
Two days later he was again "rational{{nbsp}}... knows his friends", and after a week's further progress Harlow entertained, for the first time, the thought "that it was ''possible'' for Gage to recover{{nbsp}}... This improvement, however, was of short duration."{{px1}} |
Two days later he was again "rational{{nbsp}}... knows his friends", and after a week's further progress Harlow entertained, for the first time, the thought "that it was ''possible'' for Gage to recover{{nbsp}}... This improvement, however, was of short duration."{{px1}}<ref name="accident_excerpts"/> |
||
[[File:PhineasGage BostonPostStory.jpg|thumb|left|upright=1.2|{{shy|The ''[[Boston Post]]'' for Sep.{{nbsp}}21, 1848 (under|stating the diame|ter of Gage's tamping iron and over|stating damage to his jaw)}}{{zwsp}}{{efn |
[[File:PhineasGage BostonPostStory.jpg|thumb|left|upright=1.2|{{shy|The ''[[Boston Post]]'' for Sep.{{nbsp}}21, 1848 (under|stating the diame|ter of Gage's tamping iron and over|stating damage to his jaw)}}{{zwsp}}{{efn |
||
|name=note_post |
|name=note_post |
||
| |
|<ref name="anonymous_bostonpost"/> The ''Boston Post'' credits an earlier report (of unknown date) in the ''Ludlow (Vermont) Free Soil Union'', which appears to have been the first report of Gage's accident;{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|11}} although reprinted by several New England papers{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|35-36}} it is itself no longer extant.{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|70n1}} This report confuses the iron's circumference with its diameter,{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|12}} and despite the reference to "shattering the upper jaw", that did not in fact happen.{{refn|[[#H1|Harlow 1848]], p. 389; [[#Bigelow 1850|Bigelow 1850]], p. 21; [[#H|Harlow 1868]], p. 16; [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], pp. 36{{ndash}}7. |
||
}}<!--these may be duplicative, maybe use Bigelow re coronoid process; secondary source in layman's terms desirable, should be something in M2000--> |
}}<!--these may be duplicative, maybe use Bigelow re coronoid process; secondary source in layman's terms desirable, should be something in M2000--> |
||
}} ]] |
}} ]] |
||
Beginning September{{nbsp}}25{{ |
Beginning September{{nbsp}}25{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|53}} Gage was semi-comatose, "seldom speaking unless spoken to, and then answering only in monosyllables", and the next day Harlow noted, "Failing strength{{nbsp}}... coma deepened; the [[Globe (human eye)|globe]] of the left eye became more protuberant, with {{bracket|[[granulation tissue]]}}{{efn |
||
|In keeping with usage of the day{{ |
|In keeping with usage of the day<ref name="hooper"/>{{rp|107}} Harlow used the term ''[[wikt:fungi#English-granulation tissue|fungus]]'' (a word possibly related to the Greek word for "sponge"){{Citation needed|date=September 2014}} in reference to the sponge-like granulation tissue.{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|53}} |
||
}}<!--<<end efn--> |
}}<!--<<end efn--> |
||
pushing out rapidly from the internal [[canthus]] [as well as] from the wounded brain, and coming out at the top of the head." After another day, "The exhalations from the mouth and head [are] horribly fetid. Comatose, but will answer in monosyllables if aroused. Will not take nourishment unless strongly urged. The friends and attendants are in hourly expectancy of his death, and have his coffin and clothes in readiness."{{px1}} |
pushing out rapidly from the internal [[canthus]] [as well as] from the wounded brain, and coming out at the top of the head." After another day, "The exhalations from the mouth and head [are] horribly fetid. Comatose, but will answer in monosyllables if aroused. Will not take nourishment unless strongly urged. The friends and attendants are in hourly expectancy of his death, and have his coffin and clothes in readiness."{{px1}}<ref name="accident_excerpts"/> |
||
Galvanized, Harlow "cut off the [granulation tissue] sprouting out from the top of the brain and filling the opening, and made free application of caustic [i.e. crystalline [[silver nitrate]]]{{ |
Galvanized, Harlow "cut off the [granulation tissue] sprouting out from the top of the brain and filling the opening, and made free application of caustic [i.e. crystalline [[silver nitrate]]]{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|54}} to them. With a scalpel I laid open the {{bracket|[[frontalis muscle]],{{sfn|H1}}{{rp|392}} from the exit wound to the top of the nose}} and immediately there were discharged eight ounces [250{{nbsp}}ml] of [[ill-conditioned pus]], with blood, and excessively fetid."{{px1}}<ref name="accident_excerpts"/> ("Gage was lucky to encounter Dr. Harlow when he did," wrote Barker. "Few doctors in 1848 would have had the experience with cerebral [[abscess]] with which Harlow left {{bracket|[[Jefferson Medical College]]}} and which probably saved Gage's life."{{px1}}{{sfn|Barker 1995}}{{rp|679-80}} ''See [[#Factors favoring|§{{nbsp}}Factors favoring Gage's survival]], below.'') |
||
On October 7, Gage "succeeded in raising himself up, and took one step to his chair". One month later he was walking "up and down stairs, and about the house, into the [[wikt:piazza#English|piazza]]", and while Harlow was absent for a week, Gage was "in the street every day except Sunday", his desire to return to his family in New Hampshire being "uncontrollable by his friends{{nbsp}}... got wet feet and a chill." He soon developed a fever, but by mid-November he was "feeling better in every respect{{nbsp}}... walking about the house again". Harlow's prognosis at this point: Gage "appears to be in a way of recovering, if he can be controlled". |
On October 7, Gage "succeeded in raising himself up, and took one step to his chair". One month later he was walking "up and down stairs, and about the house, into the [[wikt:piazza#English|piazza]]", and while Harlow was absent for a week, Gage was "in the street every day except Sunday", his desire to return to his family in New Hampshire being "uncontrollable by his friends{{nbsp}}... got wet feet and a chill." He soon developed a fever, but by mid-November he was "feeling better in every respect{{nbsp}}... walking about the house again". Harlow's prognosis at this point: Gage "appears to be in a way of recovering, if he can be controlled".<ref name="accident_excerpts"/> |
||
===Subsequent life and travels=== |
===Subsequent life and travels=== |
||
By November 25, Gage was strong enough to return to his parents' home in [[Lebanon, New Hampshire]],<!-- close carriage is at OKF p.29 --> where by late December he was "riding out, improving both mentally and physically"{{px1}}{{ |
By November 25, Gage was strong enough to return to his parents' home in [[Lebanon, New Hampshire]],<!-- close carriage is at OKF p.29 --> where by late December he was "riding out, improving both mentally and physically"{{px1}}{{sfn|H2}} and (as recorded in the notes of a physician who spoke to Gage's mother) "abt. February he was able to do a little work abt.{{nbsp}}ye horses{{nbsp}}& barn, feedg.{{nbsp}}ye cattle{{nbsp}}&c; that as ye time for ploughing came he was able to do half a day's<!--<<silently adding apostrophe--> work after that{{nbsp}}& bore it well."{{px1}}<ref name="jackson1849"/>{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|ix,93-4}} |
||
====Injuries==== |
====Injuries==== |
||
[[File:Phineas Gage Daguerreotype WilgusPhoto2008-12-19 CroppedHeadOnly Unretouched BW ToneCorrected.jpg|right|thumb|upright=0.70|link=File:Phineas_Gage_Cased_Daguerreotype_WilgusPhoto2008-12-19_Unretouched_Color.jpg|{{shy|"Disfigured yet still hand|some".{{ |
[[File:Phineas Gage Daguerreotype WilgusPhoto2008-12-19 CroppedHeadOnly Unretouched BW ToneCorrected.jpg|right|thumb|upright=0.70|link=File:Phineas_Gage_Cased_Daguerreotype_WilgusPhoto2008-12-19_Unretouched_Color.jpg|{{shy|"Disfigured yet still hand|some".{{sfn|T}} Note [[ptosis (eyelid)|ptosis]] of the left eye and ab|scess scar on forehead.}} ]] |
||
In April 1849 Gage returned to Cavendish and paid a visit to Harlow, who noted at that time loss of vision (and [[ptosis (eyelid)|ptosis]]) of the left eye,{{efn |
In April 1849 Gage returned to Cavendish and paid a visit to Harlow, who noted at that time loss of vision (and [[ptosis (eyelid)|ptosis]]) of the left eye,{{efn |
||
|Though "the globe of the left eye was protruded from its orbit by one-half its diameter" by the accident, Gage retained "indistinct" vision in it until the tenth day, when vision was permanently lost.{{ |
|Though "the globe of the left eye was protruded from its orbit by one-half its diameter" by the accident, Gage retained "indistinct" vision in it until the tenth day, when vision was permanently lost.{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|6,8,13}} Ratiu et{{nbsp}}al. conclude that "the optic canal was spared{{nbsp}}... [the vision loss] secondary to acute glaucoma or swelling of the optic nerve and compression against the rigid walls of the optic canal".{{sfn|Ratiu 2004}}{{rp|640}} Harlow added that Gage could "[[wiktionary:adduct#English-move midwise|adduct]] and [[wiktionary:depress#English-move downward|depress]] the globe, but cannot move it in any other direction". |
||
}}<!--<<end efn--> |
}}<!--<<end efn--> |
||
a large scar on the forehead (from Harlow's draining of the abscess){{ |
a large scar on the forehead (from Harlow's draining of the abscess){{sfn|H1}}{{rp|392}} and |
||
{{imagequote|upon the top of the head{{nbsp}}... a deep depression, two inches by one and one-half inches [5{{nbsp}}cm by 4{{nbsp}}cm] wide, beneath which the pulsations of the brain can be perceived. Partial paralysis of the left side of the face. His physical health is good, and I am inclined to say he has recovered. Has no pain in head, but says it has a queer feeling which he is not able to describe.{{ |
{{imagequote|upon the top of the head{{nbsp}}... a deep depression, two inches by one and one-half inches [5{{nbsp}}cm by 4{{nbsp}}cm] wide, beneath which the pulsations of the brain can be perceived. Partial paralysis of the left side of the face. His physical health is good, and I am inclined to say he has recovered. Has no pain in head, but says it has a queer feeling which he is not able to describe.{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|12-13}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
Though a year later some physical weakness remained,{{ |
Though a year later some physical weakness remained,{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|93}}<ref name="ama_standing"/> Harlow later wrote that "physically, the recovery was quite complete during the four years immediately succeeding the injury".{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|19}} |
||
====New England and New York (1849{{ndash}}1852)==== |
====New England and New York (1849{{ndash}}1852)==== |
||
In November 1849 [[Henry Jacob Bigelow]], the Professor of Surgery at [[Harvard Medical School]], brought Gage to Boston "at very considerable expense [and after having] satisfied himself that the bar had actually passed through the man's head",{{ |
In November 1849 [[Henry Jacob Bigelow]], the Professor of Surgery at [[Harvard Medical School]], brought Gage to Boston "at very considerable expense [and after having] satisfied himself that the bar had actually passed through the man's head",<ref name="jackson1870"/>{{rp|149}} presented him to a meeting of the [[Boston Society for Medical Improvement]] and (possibly) to a Medical School class.{{sfn|Bigelow 1850}}{{rp|20}}{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|43,95}}<ref name="bsmi"/> (This may have been one of the earliest cases of a patient entering a hospital primarily to further medical research, rather than for treatment.)<ref name="yakovlev"/> |
||
Unable to return to his railroad work {{see below|mid=y|1=Early observations}} Gage appeared for a time, with his iron, at [[Barnum's American Museum]] in New York City (not the later [[P. T. Barnum#Barnum circus|Barnum's circus]]{{mdashb}}there is no evidence Gage ever exhibited with a troupe or circus, or on a fairground).{{refn| [[#B2|Bigelow |
Unable to return to his railroad work {{see below|mid=y|1=Early observations}} Gage appeared for a time, with his iron, at [[Barnum's American Museum]] in New York City (not the later [[P. T. Barnum#Barnum circus|Barnum's circus]]{{mdashb}}there is no evidence Gage ever exhibited with a troupe or circus, or on a fairground).{{refn| [[#B2|Bigelow 1868]]; [[#H|Harlow 1868]], p. 14; [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], pp. 14,98{{ndash}}9; [[#M8| Macmillan{{nbsp}}& Lena]], pp. 3{{ndash}}4. }} Advertisements have also been found for public appearances by Gage{{mdashb}}which he may have arranged and promoted himself{{mdashb}}in New Hampshire and Vermont,{{sfn|M8}}{{rp|3-4<!--other potential cites are Meet, More About, Unanswered Qs-->}} supporting Harlow's statement that Gage made public appearances in "most of the larger New England towns".{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|14}}{{sfn|Macmillan 2008}}{{rp|829}} (Years later Bigelow wrote that Gage had been "a shrewd and intelligent man and quite disposed to do anything of that sort to turn an honest penny", but had given up such efforts because "[that] sort of thing has not much interest for the general public".){{sfn|B2}}<ref name="bennett"/>{{rp|28}}{{sfn|M8}}{{rp|3-4}} |
||
For about eighteen months he worked for the owner of a livery and coach service in [[Hanover, New Hampshire]].{{ |
For about eighteen months he worked for the owner of a livery and coach service in [[Hanover, New Hampshire]].{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|14}}{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|101}} |
||
====Chile and California (1852{{ndash}}1860)==== |
====Chile and California (1852{{ndash}}1860)==== |
||
In August 1852, Gage was invited to Chile to work as a long-distance [[stagecoach]] driver there, "caring for horses, and often driving a coach heavily laden and drawn by six horses" on the [[Valparaiso]]{{ndash}}[[Santiago, Chile|Santiago]] route.{{ |
In August 1852, Gage was invited to Chile to work as a long-distance [[stagecoach]] driver there, "caring for horses, and often driving a coach heavily laden and drawn by six horses" on the [[Valparaiso]]{{ndash}}[[Santiago, Chile|Santiago]] route.{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|103-4}}{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|14}} After his health began to fail in mid-1859,{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|14-15}}{{efn |
||
|name=death |
|name=death |
||
|Gage's death and original burial are discussed by Mac{{shy}}millan.{{ |
|Gage's death and original burial are discussed by Mac{{shy}}millan.{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|108-9}}{{sfn|Macmillan 2012}}{{rp|D§corrections}} Harlow gives Gage's date of death as May{{nbsp}}21, 1861,{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|15}} but because bound, consecutive interment records<ref name="anonymous_ngray"/> show that Gage was buried May{{nbsp}}23, 1860,{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|122n17}} Mac{{shy}}millan concludes that May{{nbsp}}21, 1860 is the correct death date;{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|122n15}}{{sfn|M8}}{{rp|6}} this is confirmed by a contemporary obituary.<ref name="deaths"/> (Harlow's informant was Gage's mother;{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|15}}{{sfn|M8}}{{rp|6}} Mac{{shy}}millan{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|376}} points out that, when combined with Gage's recorded age at death{{mdashb}}36 years plus an unspecified number of months{{mdashb}}the 1861 date obscures the fact that Gage had been conceived before his parents' April{{nbsp}}27, 1823 marriage.) This implies that certain other dates Harlow gives for events late in Gage's life{{mdashb}}his move from Chile to San Francisco and the onset of his convulsions{{mdashb}}are also mistaken, presumably by the same one year; this article follows Mac{{shy}}millan{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|122n15}} in correcting those dates (each of which carries this annotation). In 1867 Lone Mountain Cemetery was renamed Laurel Hill Cemetery.<ref name="laurel"/> |
||
}}<!--<<end efn--> |
}}<!--<<end efn--> |
||
Gage left Chile for San Francisco, arriving (in his mother's words) "in a feeble condition, having failed very much since he left New Hampshire{{nbsp}}... Had many ill turns while in Valparaiso, especially during the last year, and suffered much from hardship and exposure." In San Francisco he recovered under the care of his mother and sister,{{ |
Gage left Chile for San Francisco, arriving (in his mother's words) "in a feeble condition, having failed very much since he left New Hampshire{{nbsp}}... Had many ill turns while in Valparaiso, especially during the last year, and suffered much from hardship and exposure." In San Francisco he recovered under the care of his mother and sister,{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|15}} who had relocated there from New Hampshire around the time Gage went to Chile.{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|103-4}} Then, "anxious to work", he found employment with a farmer in [[Santa Clara County, California|Santa Clara]].{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|15}} |
||
===Death=== |
===Death=== |
||
[[File:JacksonJBS A descriptive catalogue of the Warren Anatomical Museum 1870 frontispiece 623x1024.jpg|thumb|right|upright=1.2|{{shy|"It is regretted that an autopsy could not have been had, so that the precise condi|tion of the [[wikt:encephalon|{{shy|enceph|a|lon}}]] at the time of his death might have been known. [There|fore] the mother and friends, waiving the claims of personal and private affection, with a magna|nim|ity more than praise|worthy, at my request have cheer|fully placed this skull in my hands, for the benefit of science." Gage's skull (sawn to show interior) and iron, photo|graphed for Harlow in 1868.}}{{refn|[[#H|Harlow |
[[File:JacksonJBS A descriptive catalogue of the Warren Anatomical Museum 1870 frontispiece 623x1024.jpg|thumb|right|upright=1.2|{{shy|"It is regretted that an autopsy could not have been had, so that the precise condi|tion of the [[wikt:encephalon|{{shy|enceph|a|lon}}]] at the time of his death might have been known. [There|fore] the mother and friends, waiving the claims of personal and private affection, with a magna|nim|ity more than praise|worthy, at my request have cheer|fully placed this skull in my hands, for the benefit of science." Gage's skull (sawn to show interior) and iron, photo|graphed for Harlow in 1868.}}{{refn|[[#H|Harlow 1868]], p.21; [[M|Macmillan 2000]], pp.26,115, 479{{ndash}}80}} ]] |
||
In February 1860{{efn|name=death}} Gage had several [[epileptic seizure]]s.{{ |
In February 1860{{efn|name=death}} Gage had several [[epileptic seizure]]s.{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|14}}{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|16}} He lost his job, and (wrote Harlow) as the seizures increased in frequency and severity over the succeeding three months he "continued to work in various places [though he] could not do much". |
||
On May 18 he "left Santa Clara and went home to his mother. At 5{{nbsp}}o'clock, A.M., on the 20th, he had a severe convulsion. The family physician was called in, and [[bloodletting|bled]] him. The convulsions were repeated frequently during the succeeding day and night,"{{px1}}{{ |
On May 18 he "left Santa Clara and went home to his mother. At 5{{nbsp}}o'clock, A.M., on the 20th, he had a severe convulsion. The family physician was called in, and [[bloodletting|bled]] him. The convulsions were repeated frequently during the succeeding day and night,"{{px1}}{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|15}} and he died during ''[[status epilepticus]]'',{{sfn|Macmillan 2012}}{{rp|E}} in or near{{sfn|Macmillan 2012}}{{rp|B}} San Francisco, late on May{{nbsp}}21, 1860, just under twelve years after his injury. He was buried in San Francisco's [[Lone Mountain (California)|Lone Mountain Cemetery]].{{efn|name=death}} |
||
==Exhumation== |
==Exhumation== |
||
In 1866, Harlow (who had "lost all trace of [Gage], and had well nigh abandoned all expectation of ever hearing from him again") somehow learned that Gage had died in California, and made contact with his family there. At Harlow's request Gage's grave was opened long enough to remove his skull, which the family then personally delivered to Harlow,{{ |
In 1866, Harlow (who had "lost all trace of [Gage], and had well nigh abandoned all expectation of ever hearing from him again") somehow learned that Gage had died in California, and made contact with his family there. At Harlow's request Gage's grave was opened long enough to remove his skull, which the family then personally delivered to Harlow,{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|108-11}}{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|15-16}}{{sfn|M8}}{{rp|6}} who was by now a prominent physician, business<!--<<two words, not "businessman" -- see Macmillan 2000 Ch. 1>>-->man, and civic leader in [[Woburn, Massachusetts]].{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|351-64}}{{sfn|Macmillan 2001}} |
||
About a year after the accident, Gage had given his tamping iron to Harvard Medical School's [[Warren Anatomical Museum]], but he later reclaimed it{{ |
About a year after the accident, Gage had given his tamping iron to Harvard Medical School's [[Warren Anatomical Museum]], but he later reclaimed it{{sfn|Bigelow 1850}}{{rp|22n}}<ref name="anonymous_bmsj1869_1"/>{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|46-7}} and made what he called "my iron bar"{{px1}}{{sfn|M8}}{{rp|4}}{{sfn|G1}} his "constant companion during the remainder of his life";{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|13}} now it too was delivered by Gage's family to Harlow.{{sfn|M8}}{{rp|6}} (Though some accounts assert that Gage's iron had been buried with him, there is no evidence for this.){{sfn|M8}}{{rp|7}} After studying them for a triumphal{{sfn|Barker 1995}}{{rp|679}} 1868 retrospective paper on Gage{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|3}} Harlow redeposited the iron{{mdashb}}this time with the skull{{mdashb}}in the Warren Museum, where they remain on display today.<ref name="warren_phineas_gage"/> |
||
The iron bears the following inscription, commissioned by Bigelow in conjunction with the iron's first deposit in the Museum |
The iron bears the following inscription, commissioned by Bigelow in conjunction with the iron's first deposit in the Museum<ref name="anonymous_bmsj1869_1"/> (though the date it gives for the accident is one day off, and ''Phinehas'' is not the way Gage spelled his name{{sfn|Macmillan 2008}}{{rp|839fig}}<!--again, check pg #; add cite to N. Gray record; consider Harlow 1868 "Phin."; tie/merge to note re middle initial -->): |
||
{{imagequote|This is the bar that was shot through the head of Mr<!--<<modernizing typography of abbreviation (actual bar has a superscript r)--> Phinehas{{sup|[sic]}} P.{{nbsp}}Gage at Cavendish, Vermont, Sept.{{nbsp}}14,{{sup|[sic]}} 1848. He fully recovered from the injury{{nbsp}}& deposited this bar in the Museum of the Medical College of Harvard University. Phinehas P.{{nbsp}}Gage Lebanon Grafton{{nbsp}}Cy {{nowrap|N{{ndash}}H}} Jan{{nbsp}}6 1850.<!--chk Sept. 14COMMA Jan 6NOCOMMA (as given on Gagepage but chk directly in Warren)-->{{ |
{{imagequote|This is the bar that was shot through the head of Mr<!--<<modernizing typography of abbreviation (actual bar has a superscript r)--> Phinehas{{sup|[sic]}} P.{{nbsp}}Gage at Cavendish, Vermont, Sept.{{nbsp}}14,{{sup|[sic]}} 1848. He fully recovered from the injury{{nbsp}}& deposited this bar in the Museum of the Medical College of Harvard University. Phinehas P.{{nbsp}}Gage Lebanon Grafton{{nbsp}}Cy {{nowrap|N{{ndash}}H}} Jan{{nbsp}}6 1850.<!--chk Sept. 14COMMA Jan 6NOCOMMA (as given on Gagepage but chk directly in Warren)-->{{sfn|Macmillan 2012}}{{rp|D}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
The date ''Jan 6 1850'' falls within the period during which Gage was in Boston under Bigelow's observation.{{ |
The date ''Jan 6 1850'' falls within the period during which Gage was in Boston under Bigelow's observation.{{sfn|Bigelow 1850}}{{rp|20}}{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|4n}}{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|43}} |
||
In 1940 Gage's headless remains were moved to [[Cypress Lawn Memorial Park|Cypress Lawn Cemetery]] as part of a [[Colma, California#cemetery relocations|mandated relocation of San Francisco's dead]] to new resting places outside city limits.{{ |
In 1940 Gage's headless remains were moved to [[Cypress Lawn Memorial Park|Cypress Lawn Cemetery]] as part of a [[Colma, California#cemetery relocations|mandated relocation of San Francisco's dead]] to new resting places outside city limits.{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|119-20}}<ref name="proctor"/> |
||
{{clear}} |
{{clear}} |
||
<imagemap> |
<imagemap> |
||
| Line 189: | Line 187: | ||
==Brain damage and mental changes== |
==Brain damage and mental changes== |
||
[[File:Frontal lobe animation.gif|thumb|left|upright=0.85|{{shy|The left frontal lobe ''(red)'', the for|ward portion of which was damaged by Gage's injury, per Harlow's digi|tal exam|i|na|tion and the dig|i|tal anal|y|ses of Ratiu et{{nbsp}}al. and Van Horn et{{nbsp}}al.}}{{zwsp}}{{ |
[[File:Frontal lobe animation.gif|thumb|left|upright=0.85|{{shy|The left frontal lobe ''(red)'', the for|ward portion of which was damaged by Gage's injury, per Harlow's digi|tal exam|i|na|tion and the dig|i|tal anal|y|ses of Ratiu et{{nbsp}}al. and Van Horn et{{nbsp}}al.}}{{zwsp}}{{sfn|R1}}{{sfn|V}} ]] |
||
===Extent of brain damage=== |
===Extent of brain damage=== |
||
[[File:Simulated Connectivity Damage of Phineas Gage 4 vanHorn PathwaysDamaged left.jpg|thumb|right|upright=0.7|<!--no caption -- let img below act as caption -- there's some way to combine these into one box but for now this will do-->]] |
[[File:Simulated Connectivity Damage of Phineas Gage 4 vanHorn PathwaysDamaged left.jpg|thumb|right|upright=0.7|<!--no caption -- let img below act as caption -- there's some way to combine these into one box but for now this will do-->]] |
||
[[File:Simulated Connectivity Damage of Phineas Gage 4 vanHorn PathwaysDamaged right.jpg|thumb|right|upright=0.7|{{shy|False-color repre|sen|ta|tions of cere|bral fiber path|ways affect|ed, per Van Horn et{{nbsp}}al.}}{{zwsp}}{{ |
[[File:Simulated Connectivity Damage of Phineas Gage 4 vanHorn PathwaysDamaged right.jpg|thumb|right|upright=0.7|{{shy|False-color repre|sen|ta|tions of cere|bral fiber path|ways affect|ed, per Van Horn et{{nbsp}}al.}}{{zwsp}}{{sfn|V}}{{rp|3}} ]] |
||
{{nowrap<!--<<force passage below imgs if window very narrow-->|Debate about whether the}} |
{{nowrap<!--<<force passage below imgs if window very narrow-->|Debate about whether the}} |
||
{{shy| |
{{shy| |
||
trauma and sub|se|quent infection had damaged both of Gage's [[frontal lobes]] (left and right), or only the left, began almost imme|di|ate|ly after his acci|dent.{{efn |
trauma and sub|se|quent infection had damaged both of Gage's [[frontal lobes]] (left and right), or only the left, began almost imme|di|ate|ly after his acci|dent.{{efn |
||
|{{ |
|{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|3,71}} Early attempts to estimate the extent of damage include those by: Harlow;{{sfn|H1}}{{rp|389}} [[Edward Elisha Phelps]]<ref name="jackson1849"/>; Bigelow;{{sfn|Bigelow 1850}}{{rp|21-2}} Harlow;{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|17-19}} Dupuy;<ref name="dupuy"/> Ferrier;<ref name="ferrier1878"/> Bramwell;<ref name="bramwell"/> Cobb;<ref name="cobb"/> Tyler{{nbsp}}& Tyler.{{sfn|T1}}<!--discuss indirect sources of damage -- blood loss, infection, bone fragments, etc. e.g. van horn p.14; merge with "brain moved aside" material from ratiu--> |
||
}}<!--<<end efn--> |
}}<!--<<end efn--> |
||
The 1994 con|clu|sion of [[Hanna Damasio]] et{{nbsp}}al., that both frontal lobes were damaged, was drawn not from Gage's skull but from a "Gage-like" one{{mdashb}}a cadaver skull deformed to match the dimen|sions of Gage's.{{ |
The 1994 con|clu|sion of [[Hanna Damasio]] et{{nbsp}}al., that both frontal lobes were damaged, was drawn not from Gage's skull but from a "Gage-like" one{{mdashb}}a cadaver skull deformed to match the dimen|sions of Gage's.{{sfn|Macmillan 2008}}{{rp|829-30}}<ref name="damasioH_return"/>{{rp|1103-4}} Using [[Computed tomography|CT scans]] of Gage's actual skull, Ratiu et{{nbsp}}al.{{sfn|Ratiu 2004}}{{rp|638}} and Van Horn et{{nbsp}}al.{{sfn|V}}{{rp|4-5}} both rejected that con|clu|sion, agree|ing with Harlow's belief{{mdashb}}based on probing Gage's wounds with his fingers<ref name="fingers"/>{{mdashb}}that only the left frontal lobe had been damaged.{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|19}} |
||
}}<!--end shy--> |
}}<!--end shy--> |
||
In addition, Ratiu et{{nbsp}}al. noted that the opening between the roof of the mouth and the base of the cranium (created as the iron passed through) has a diameter about half that of the iron itself; combining this with the hairline fracture running from behind the exit region down the front of the skull, they concluded that the skull "hinged" open as the iron entered from below, then (once the iron had exited at the top) was pulled closed by the resilience of soft tissues.{{ |
In addition, Ratiu et{{nbsp}}al. noted that the opening between the roof of the mouth and the base of the cranium (created as the iron passed through) has a diameter about half that of the iron itself; combining this with the hairline fracture running from behind the exit region down the front of the skull, they concluded that the skull "hinged" open as the iron entered from below, then (once the iron had exited at the top) was pulled closed by the resilience of soft tissues.{{sfn|Ratiu 2004}}{{rp|640}}{{sfn|Macmillan 2008}}{{rp|830}} |
||
Van Horn et{{nbsp}}al. concluded that damage to Gage's [[white matter]] (of which they made detailed estimates) was as or more significant to Gage's mental changes than [[cerebral cortex]] (gray matter) damage.{{ |
Van Horn et{{nbsp}}al. concluded that damage to Gage's [[white matter]] (of which they made detailed estimates) was as or more significant to Gage's mental changes than [[cerebral cortex]] (gray matter) damage.{{sfn|V}}{{rp|abstr}} |
||
===First-hand reports of mental changes=== |
===First-hand reports of mental changes=== |
||
Gage certainly displayed some kind of change in behavior after his injury,{{ |
Gage certainly displayed some kind of change in behavior after his injury,{{sfn|M8}}{{rp|12-15}}<!--likely other papers + Macmillan 2000 cited too --> but the nature, extent, and duration of this change have been difficult to establish. Only a handful of sources give direct information on what Gage was like (either before or after the accident),{{efn|name=accounts_reliablesources}} the mental changes described after his death were much more dramatic than anything reported while he was alive,{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|375-6}} and few sources are explicit about the period of Gage's life to which their various descriptions of him (which vary widely in their implied level of functional impairment) are meant to apply.{{sfn|M8}}{{rp|6-7}} |
||
====<span id="Early observations"></span>Early observations (1849{{ndash}}1852)==== |
====<span id="Early observations"></span>Early observations (1849{{ndash}}1852)==== |
||
Harlow described the pre-accident Gage as hard-working, responsible, and "a great favorite" with the men in his charge, his employers having regarded him as "the most efficient and capable foreman in their employ". But these same employers, after Gage's accident, "considered the change in his mind so marked that they could not give him his place again": |
Harlow described the pre-accident Gage as hard-working, responsible, and "a great favorite" with the men in his charge, his employers having regarded him as "the most efficient and capable foreman in their employ". But these same employers, after Gage's accident, "considered the change in his mind so marked that they could not give him his place again": |
||
{{imagequote|The equilibrium or balance, so to speak, between his intellectual faculties and animal propensities, seems to have been destroyed. He is fitful, irreverent, indulging at times in the grossest profanity (which was not previously his custom), manifesting but little deference for his fellows, impatient of restraint or advice when it conflicts with his desires, at times pertinaciously obstinate, yet capricious and vacillating, devising many plans of future operations, which are no sooner arranged than they are abandoned in turn for others appearing more feasible. A child in his intellectual capacity and manifestations, he has the animal passions of a strong man. Previous to his injury, although untrained in the schools, he possessed a well-balanced mind, and was looked upon by those who knew him as a shrewd, smart business man<!--<<two words, not "businessman"-->, very energetic and persistent in executing all his plans of operation. In this regard his mind was radically changed, so decidedly that his friends and acquaintances said he was "no longer Gage".{{ |
{{imagequote|The equilibrium or balance, so to speak, between his intellectual faculties and animal propensities, seems to have been destroyed. He is fitful, irreverent, indulging at times in the grossest profanity (which was not previously his custom), manifesting but little deference for his fellows, impatient of restraint or advice when it conflicts with his desires, at times pertinaciously obstinate, yet capricious and vacillating, devising many plans of future operations, which are no sooner arranged than they are abandoned in turn for others appearing more feasible. A child in his intellectual capacity and manifestations, he has the animal passions of a strong man. Previous to his injury, although untrained in the schools, he possessed a well-balanced mind, and was looked upon by those who knew him as a shrewd, smart business man<!--<<two words, not "businessman"-->, very energetic and persistent in executing all his plans of operation. In this regard his mind was radically changed, so decidedly that his friends and acquaintances said he was "no longer Gage".{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|13-14}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
[[File:John-m-harlow cropped.jpg|thumb|right|upright=1.0|link=File:John-m-harlow.jpg|{{shy|"I [[wiktionary:dress#English-treat wound|dressed]] him, God healed him." Dr. [[John Martyn Harlow|J.M. Harlow]], who attended Gage after the "rude missile had been shot through his brain", |
[[File:John-m-harlow cropped.jpg|thumb|right|upright=1.0|link=File:John-m-harlow.jpg|{{shy|"I [[wiktionary:dress#English-treat wound|dressed]] him, God healed him." Dr. [[John Martyn Harlow|J.M. Harlow]], who attended Gage after the "rude missile had been shot through his brain",<ref name="eliot"/> and ob|tained his skull for study after his death, in later life. His inter|est in [[phrenology|phren{{shy}}ology]] pre|pared him to accept that Gage's injury changed his behavior.}}{{refn|[[#H|Harlow 1868]], p. 20; [[#CITEREFBarker 1995|Barker 1995]], p. 672}} ]] |
||
[[File:Henry Jacob Bigelow c1854 cropped.jpg|thumb|right|upright=1.0|link=File:Henry_Jacob_Bigelow_c1854.jpg|{{shy|"The leading feature of this case is its improb|a|bil|ity." Har|vard's [[Henry Jacob Bigelow|H.J. Bige{{shy}}low]] in 1854. His train|ing pre|dis|posed him to mini|mize Gage's behav|ior|al changes.}}{{zwsp}}{{ |
[[File:Henry Jacob Bigelow c1854 cropped.jpg|thumb|right|upright=1.0|link=File:Henry_Jacob_Bigelow_c1854.jpg|{{shy|"The leading feature of this case is its improb|a|bil|ity." Har|vard's [[Henry Jacob Bigelow|H.J. Bige{{shy}}low]] in 1854. His train|ing pre|dis|posed him to mini|mize Gage's behav|ior|al changes.}}{{zwsp}}{{sfn|Barker 1995}}{{rp|672}} ]] |
||
This description ("now routinely quoted", says Kotowicz){{ |
This description ("now routinely quoted", says Kotowicz){{sfn|K2}}{{rp|125}} is from Harlow's observations set down soon after the accident,{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|90,375}}{{sfn|M8}}{{rp|6-9}} but Harlow{{mdashb}}perhaps hesitant to describe his patient negatively while he was still alive{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|375-6}}{{mdashb}}left these observations unpublished until 1868, after Gage had died and his family had supplied "what we so much desired to see" (as Harlow termed Gage's skull).{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|16}} |
||
In the interim, Harlow's 1848 report, published just as Gage was emerging from his convalescence, only hinted at psychological symptoms:{{ |
In the interim, Harlow's 1848 report, published just as Gage was emerging from his convalescence, only hinted at psychological symptoms:{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|169}} |
||
{{imagequote|The mental manifestations of the patient, I leave to a future communication. I think the case{{nbsp}}... is exceedingly interesting to the enlightened physiologist and intellectual philosopher.{{ |
{{imagequote|The mental manifestations of the patient, I leave to a future communication. I think the case{{nbsp}}... is exceedingly interesting to the enlightened physiologist and intellectual philosopher.{{sfn|H1}}{{rp|393}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
But after Bigelow termed Gage "quite recovered in faculties of body and mind", with only "inconsiderable disturbance of function",{{ |
But after Bigelow termed Gage "quite recovered in faculties of body and mind", with only "inconsiderable disturbance of function",{{sfn|Bigelow 1850}}{{rp|13-14}} a rejoinder in the ''American [[Phrenological]] Journal''{{mdashb}} |
||
{{imagequote|That there was no difference in his mental manifestations after the recovery is{{nbsp}}''not'' true{{nbsp}}... The man was gross, profane, coarse, and vulgar, to such a degree that his society was intolerable to decent people. |
{{imagequote|That there was no difference in his mental manifestations after the recovery is{{nbsp}}''not'' true{{nbsp}}... The man was gross, profane, coarse, and vulgar, to such a degree that his society was intolerable to decent people.<ref name="amer_phren"/> |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{mdashb}}was apparently based on information anonymously supplied by Harlow.{{ |
{{mdashb}}was apparently based on information anonymously supplied by Harlow.{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|350-1}} Barker explains these contradictory evaluations (only six months apart) by differences in Bigelow's and Harlow's educational backgrounds: |
||
{{imagequote|Harlow's interest in phrenology prepared him to accept the change in character as a significant clue to cerebral function which merited publication. Bigelow had [been taught] that damage to the cerebral hemispheres had no intellectual effect, and he was unwilling to consider Gage's deficit significant{{nbsp}}... The use of a single case [including Gage's] to prove opposing views on phrenology was not uncommon.{{ |
{{imagequote|Harlow's interest in phrenology prepared him to accept the change in character as a significant clue to cerebral function which merited publication. Bigelow had [been taught] that damage to the cerebral hemispheres had no intellectual effect, and he was unwilling to consider Gage's deficit significant{{nbsp}}... The use of a single case [including Gage's] to prove opposing views on phrenology was not uncommon.{{sfn|Barker 1995}}{{rp|672,678}} |
||
}}<!--other aspects include Harlow knew Gage before accident, and class-based expectations about behavior--> |
}}<!--other aspects include Harlow knew Gage before accident, and class-based expectations about behavior--> |
||
====Later observations (1852{{ndash}}1858)==== |
====Later observations (1852{{ndash}}1858)==== |
||
In 1860, an American physician who had known Gage "well" in Chile reported that Gage remained "engaged in stage driving [and] in the enjoyment of good health, with no impairment whatever of his mental faculties".{{ |
In 1860, an American physician who had known Gage "well" in Chile reported that Gage remained "engaged in stage driving [and] in the enjoyment of good health, with no impairment whatever of his mental faculties".<ref name="hamilton"/>{{sfn|M8}}{{rp|8}} Together with the fact that Gage was hired by his employer in advance, in New England, to be part of the new coaching enterprise in Chile,{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|15}}{{sfn|M8}}{{rp|15}} this implies that Gage's most serious mental changes had been temporary, so that the "fitful, irreverent{{nbsp}}... capricious and vacillating" Gage described by Harlow immediately post-accident became, over time, far more functional and socially far better adapted.{{sfn|Macmillan 2008}}{{rp|831}}{{sfn|M8}}{{rp|2,15}} |
||
This conclusion is reinforced (writes psychologist Malcolm Macmillan) by the responsibilities and challenges associated with stagecoach work such as that done by Gage in Chile, including the requirement that drivers "be reliable, resourceful, and possess great endurance. But above all, they had to have the kind of personality that enabled them to get on well with their passengers."{{px1}} |
This conclusion is reinforced (writes psychologist Malcolm Macmillan) by the responsibilities and challenges associated with stagecoach work such as that done by Gage in Chile, including the requirement that drivers "be reliable, resourceful, and possess great endurance. But above all, they had to have the kind of personality that enabled them to get on well with their passengers."{{px1}}<ref name="austin"/><!--<<get pg#-->{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|104-6}}{{sfn|M8}}{{rp|4-5}} A day's work for Gage meant "a 13-hour journey over 100 miles of poor roads, often in times of political instability or frank revolution. All this{{mdashb}}in a land to whose language and customs Phineas arrived an utter stranger{{mdashb}}militates as much against permanent disinhibition [i.e. an inability to plan and self-regulate] as do the extremely complex sensory-motor and cognitive skills required of a coach driver."{{px1}}{{sfn|M8}}{{rp|5}}{{sfn|Macmillan 2008}}{{rp|831}} (A visitor wrote: "The departure of the coach was always a great event at Valparaiso{{mdashb}}a crowd of ever-astonished Chilenos assembling every day to witness the phenomenon of one man driving six horses.")<ref name="merwin"/>{{rp|73}} |
||
===<span id="Social recovery hypothesis"></span>Social recovery=== |
===<span id="Social recovery hypothesis"></span>Social recovery=== |
||
Macmillan writes that this contrast{{mdashb}}between Gage's early, versus later, post-accident behavior{{mdashb}}reflect Gage's "[gradual change] from the commonly portrayed impulsive and uninhibited person into one who made a reasonable 'social recovery{{'"}}, |
Macmillan writes that this contrast{{mdashb}}between Gage's early, versus later, post-accident behavior{{mdashb}}reflect Gage's "[gradual change] from the commonly portrayed impulsive and uninhibited person into one who made a reasonable 'social recovery{{'"}},<ref name="jarrett"/> citing persons with similar injuries for whom "someone or something gave enough structure to their lives for them to relearn lost social and personal skills":{{sfn|Macmillan 2008}}{{rp|831}} |
||
{{imagequote|Phineas' survival and rehabilitation demonstrated a theory of recovery which has influenced the treatment of frontal lobe damage today. In modern treatment, adding structure to tasks by, for example, mentally visualising a written list, is considered a key method in coping with frontal lobe damage.{{ |
{{imagequote|Phineas' survival and rehabilitation demonstrated a theory of recovery which has influenced the treatment of frontal lobe damage today. In modern treatment, adding structure to tasks by, for example, mentally visualising a written list, is considered a key method in coping with frontal lobe damage.{{sfn|M4}} }} |
||
[[File:Concord_Stagecoach_number_251.JPG|upright=1|thumb|right|A [[Stagecoach#Concord_stagecoaches|Concord coach]], likely the type driven by Gage in Chile{{refn|[[# |
[[File:Concord_Stagecoach_number_251.JPG|upright=1|thumb|right|A [[Stagecoach#Concord_stagecoaches|Concord coach]], likely the type driven by Gage in Chile{{refn|[[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], pp. 104, 121 n13; [[#M8|Macmillan{{nbsp}}& Lena]], p.5}} ]] |
||
According to a contemporary account by visitors to Chile,{{ |
According to a contemporary account by visitors to Chile,{{sfn|Macmillan 2008}}{{rp|831}}<!--<<add ref to full primary text as well--> Gage would have had to |
||
{{imagequote|rise early in the morning, prepare himself, and groom, feed, and harness the horses; he had to be at the departure point at a specified time, load the luggage, charge the fares and get the passengers settled; and then had to care for the passengers on the journey, unload their luggage at the destination, and look after the horses. The tasks formed a structure that required control of any impulsiveness he may have had.{{ |
{{imagequote|rise early in the morning, prepare himself, and groom, feed, and harness the horses; he had to be at the departure point at a specified time, load the luggage, charge the fares and get the passengers settled; and then had to care for the passengers on the journey, unload their luggage at the destination, and look after the horses. The tasks formed a structure that required control of any impulsiveness he may have had.{{sfn|M2}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
| Line 254: | Line 252: | ||
{{imagequote|much foresight was required. Drivers had to plan for turns well in advance, and sometimes react quickly to manoeuvre around other coaches, wagons, and ''[[barouche|birlocho]]s'' travelling at various speeds ... Adaptation had also to be made to the physical condition of the route: although some sections were well-made, others were dangerously steep and very rough. |
{{imagequote|much foresight was required. Drivers had to plan for turns well in advance, and sometimes react quickly to manoeuvre around other coaches, wagons, and ''[[barouche|birlocho]]s'' travelling at various speeds ... Adaptation had also to be made to the physical condition of the route: although some sections were well-made, others were dangerously steep and very rough. |
||
}} |
}} |
||
Thus Gage's stagecoach work{{mdashb}}"a highly structured environment in which clear sequences of tasks were required [but within which] contingencies requiring foresight and planning arose daily"{{mdashb}}resembles rehabilitation regimens first developed by Soviet neuropsychologist [[Alexander Luria]] for the reestablishment of self-regulation in World War{{nbsp}}II soldiers suffering frontal lobe injuries.{{ |
Thus Gage's stagecoach work{{mdashb}}"a highly structured environment in which clear sequences of tasks were required [but within which] contingencies requiring foresight and planning arose daily"{{mdashb}}resembles rehabilitation regimens first developed by Soviet neuropsychologist [[Alexander Luria]] for the reestablishment of self-regulation in World War{{nbsp}}II soldiers suffering frontal lobe injuries.{{sfn|M8}}{{rp|5,11-12,15}} |
||
A neurological basis for such recoveries may be found in emerging evidence "that damaged [[Neural pathway|[neural] tracts]] may re-establish their original connections or build alternative pathways as the brain recovers" from injury. |
A neurological basis for such recoveries may be found in emerging evidence "that damaged [[Neural pathway|[neural] tracts]] may re-establish their original connections or build alternative pathways as the brain recovers" from injury.<ref name="jarrett"/> Macmillan adds that if Gage made such a recovery{{mdashb}}if he eventually "figured out how to live" (as Fleischman put it){{sfn|F}}{{rp|75}} despite his injury{{mdashb}}then it "would add to current evidence that rehabilitation can be effective even in difficult and long-standing cases";{{sfn|Macmillan 2008}}{{rp|831}} and if Gage could achieve such improvement without medical supervision, "what are the limits for those in formal rehabilitation programs?"{{px1}}{{sfn|M2}} As author Sam Kean put it, "If even Phineas Gage bounced back{{mdashb}}that's a powerful message of hope."{{px1}}{{sfn|K}} |
||
===Exaggeration and distortion of mental changes=== |
===Exaggeration and distortion of mental changes=== |
||
| Line 263: | Line 261: | ||
{{Quote box |salign=right|align=left |
{{Quote box |salign=right|align=left |
||
|quote = A moral man, Phineas Gage<br>Tamping powder down holes for his wage<br>Blew his special-made probe<br>Through his left frontal lobe<br>Now he drinks, swears, and flies in a rage. |
|quote = A moral man, Phineas Gage<br>Tamping powder down holes for his wage<br>Blew his special-made probe<br>Through his left frontal lobe<br>Now he drinks, swears, and flies in a rage. |
||
|source = {{mdash}}{{thinsp}}Anonymous{{ |
|source = {{mdash}}{{thinsp}}Anonymous{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|307}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
Macmillan's analysis of scientific and popular accounts of Gage found that they almost always distort and exaggerate his behavioral changes well beyond anything described by anyone who had contact with him.{{efn|name=accounts_reliablesources}} In the words of Barker, "As years passed, the case took on a life of its own, accruing novel additions to Gage's story without any factual basis";{{ |
Macmillan's analysis of scientific and popular accounts of Gage found that they almost always distort and exaggerate his behavioral changes well beyond anything described by anyone who had contact with him.{{efn|name=accounts_reliablesources}} In the words of Barker, "As years passed, the case took on a life of its own, accruing novel additions to Gage's story without any factual basis";{{sfn|Barker 1995}}{{rp|678}} even today (writes historian Zbigniew Kotowicz) "Most commentators still rely on hearsay and accept what others have said about Gage, namely, that after the accident he became a [[psychopath]]."{{px1}}{{sfn|K2}}{{rp|125}} and Grafman has written that "the details of [Gage's] social cognitive impairment have occasionally been inferred or even embellished to suit the enthusiasm of the story teller{{nbsp}}..."{{px1}}{{sfn|G}}{{rp|295}} |
||
{{shy| |
{{shy| |
||
Behaviors ascribed to the post-accident Gage which are either unsupported by, or in contra|dic|tion to, the known facts include mistreat|ment of wife and children (of which Gage had neither); |
Behaviors ascribed to the post-accident Gage which are either unsupported by, or in contra|dic|tion to, the known facts include mistreat|ment of wife and children (of which Gage had neither);<ref name="wife"/> inappro|pri|ate sexual behavior, promiscuity, or impaired sexuality;<ref name="sexuality"/> lack of fore|thought, of concern for the future, or of capacity for embar|rass|ment; parading his self-misery, and vainglory in showing his wounds;<ref name="forethought"/> inability<ref name="inability"/> or refusal<ref name="refusal"/> to hold a job; irrespon|si|bil|ity and untrust|worth|iness;<ref name="irresponsibility"/> aggres|sive|ness and violence;<ref name="aggressiveness"/> vagrancy and begging;<ref name="vagrancy"/> plus drifting,<ref name="drifting"/> drinking,<ref name="drinking"/> bragging,<ref name="bragging"/> lying,<ref name="lying"/> brawling,<ref name="brawling"/> bullying,<ref name="bullying"/> [[psychopathy]],<ref name="psychopathy"/> inability to make ethical decisions, loss of all respect for social conventions, acting "like an idiot",<ref name="idiot"/> and dying "due to a [[wiktionary:debauch#Noun|debauch]]".<ref name="northcarolina"/> None of these behaviors is mentioned by anyone who had met Gage or even his family; |
||
}}<!--<<end shy-->{{efn |
}}<!--<<end shy-->{{efn |
||
|name=accounts_reliablesources |
|name=accounts_reliablesources |
||
|Macmillan{{ |
|Macmillan{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|116-19,ch13-14}}{{sfn|Macmillan 2012}}{{rp|C}}{{sfn|M6}} compares accounts of Gage to one another and against the known facts, as well as contrasting Gage's celebrity{{mdashb}}he is mentioned in 91% of a sample of introductory psychology textbooks published 2012{{ndash}}2014<ref name="griggs"/>{{mdashb}}with what was, until recently, the lack of any major study of him and dearth of papers solely or mainly about him.{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|1-2,11}} |
||
{{paragraph break}} |
{{paragraph break}} |
||
Until 2008{{ |
Until 2008{{sfn|M8}}{{rp|2-3}}{{sfn|Macmillan 2008}}{{rp|830}} the available sources offering significant information on Gage, and for which there is any evidence at all (even merely the source's own claim) of contact with him or with his family, were limited to Harlow (1848, 1849, 1868);{{sfn|H1}}{{sfn|H2}}{{sfn|Harlow 1868}} Bigelow 1850;{{sfn|Bigelow 1850}} and Jackson (1849, 1870).<ref name="jackson1849"/><ref name="jackson1870"/> Macmillan notes that descriptions of Gage's behavior total just 300 words{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|90}} and emphasizes the primacy of Harlow's three publications as sources.{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|94}} (Harlow's original case notes have not been located.{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|90}} A Warren Museum curator referred to the "stately elegance" of Harlow's writings on Gage.)<ref name="yakovlev"/> Mac{{shy}}millan{{nbsp}}& Lena{{sfn|M8}}{{rp|3-6,8}} present previously unknown sources found since 2008. |
||
}} |
}} |
||
as Kotowicz put it, "Harlow does not report a single act that Gage should have been ashamed of."{{px1}}{{ |
as Kotowicz put it, "Harlow does not report a single act that Gage should have been ashamed of."{{px1}}{{sfn|K2}}{{rp|122-3}} Gage is "a great story for illustrating the need to go back to original sources", writes Macmillan.<ref name="benderly"/> |
||
For example, a passage by Harlow{{mdashb}}{{px1}}{{"'}}...{{nbsp}}continued to work in various places;' could not do much, changing often, 'and always finding something that did not suit him in every place he tried{{'"}}{{px1}}{{ |
For example, a passage by Harlow{{mdashb}}{{px1}}{{"'}}...{{nbsp}}continued to work in various places;' could not do much, changing often, 'and always finding something that did not suit him in every place he tried{{'"}}{{px1}}{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|15}}{{mdashb}}has been misinterpreted<ref name="work"/> as meaning Gage could not hold a regular job after his accident,<ref name="hockenbury1997"/><!--get pg#--> "was prone to quit in a capricious fit or be let go because of poor discipline",<ref name="damasioA_descartes"/>{{rp|8-9}} "never returned to a fully independent existence",<ref name="damasioH_return"/>{{rp|1102}} and died "in careless dissipation"<ref name="damasioA_neuropsychology"/> in "the custody of his parents".<ref name="bower"/> In fact, after his initial post-recovery months spent traveling and exhibiting, Gage supported himself{{mdashb}}at a total of two jobs{{mdashb}}from early 1851 until just before his death in 1860.{{sfn|M8}}{{rp|14-15}} (Harlow's "changing often" refers only to Gage's final months, after convulsions had set in, and even then he remained "anxious to work".{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|107}}{{sfn|M8}}{{rp|6}} In Kotowicz's words, "What Harlow is telling us is clear and unambiguous: Gage returns from South America to his mother to recuperate. As soon as he is fit, he goes back to work with horses, which is what he has been doing for years."){{sfn|K2}}{{rp|130n6}} |
||
==<span id="Theoretical use, misuse, and nonuse"></span>Theoretical use and misuse== |
==<span id="Theoretical use, misuse, and nonuse"></span>Theoretical use and misuse== |
||
Though Gage is considered the "[[index case]] for personality change due to frontal lobe damage"{{px1}}{{ |
Though Gage is considered the "[[index case]] for personality change due to frontal lobe damage"{{px1}}{{sfn|Barker 1995}}{{rp|672}}<ref name="stuss_hockenbury2008"/>{{sfn|F1}}{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|1}} his scientific value is undermined by the uncertain extent of his brain damage{{sfn|F1}}<!-- add Macmillan re chain of brain damage uncertainties (path, position of brain, individual locations of regions)--> and the limited understanding of his behavioral changes.{{efn|name=accounts_reliablesources}} Instead, Macmillan writes, "Phineas' story is [primarily] worth remembering because it illustrates how easily a small stock of facts becomes transformed into popular and scientific myth",{{refn| [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2008|Macmillan 2008]], p. 831; [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], chs. 5{{ndash}}6, 9{{ndash}}14; [[#M5|Macmillan 1996]], pp. 251{{ndash}}9. }} the paucity of evidence having allowed "the fitting of almost any theory [desired] to the small number of facts we have".{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|290}} A similar concern was expressed as far back as 1877, when British neurologist [[David Ferrier]] (writing to Harvard's [[Henry Pickering Bowditch]] in an attempt "to have this case definitely settled") complained that |
||
{{imagequote|In investigating reports on diseases and injuries of the brain, I am constantly amazed at the inexactitude and distortion to which they are subject by men who have some pet theory to support. The facts suffer so frightfully{{nbsp}}...{{ |
{{imagequote|In investigating reports on diseases and injuries of the brain, I am constantly amazed at the inexactitude and distortion to which they are subject by men who have some pet theory to support. The facts suffer so frightfully{{nbsp}}...{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|1,75,197-9,464-5}}<ref name="ferrier1877_9"/> |
||
}} |
}} |
||
More recently, neurologist [[Oliver Sacks]] refers to the "interpretations and misinterpretations [of Gage] from 1848 to the present". |
More recently, neurologist [[Oliver Sacks]] refers to the "interpretations and misinterpretations [of Gage] from 1848 to the present".<ref name="sacks"/> |
||
===Cerebral localization===<!-- need expansion --> |
===Cerebral localization===<!-- need expansion --> |
||
In the nineteenth-century controversy over whether the various mental functions are or are not [[cerebral localization|localized in specific regions of the brain]], both sides managed to enlist Gage in support of their theories.{{ |
In the nineteenth-century controversy over whether the various mental functions are or are not [[cerebral localization|localized in specific regions of the brain]], both sides managed to enlist Gage in support of their theories.{{sfn|Barker 1995}}{{rp|678}}{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|ch9}}<!--emph okf p188 material--> For example, after [[Eugene Dupuy|Dupuy]] wrote that Gage proved that the brain is not localized (characterizing him as a "striking case of destruction of the so-called [[Broca's area|speech centre]] without consequent [[aphasia]]")<ref name="dupuy"/> Ferrier made a "devastating reply" in his 1878 [[Goulstonian Lectures]], "On the Localisation of Cerebral Disease", of which Gage (and the woodcuts of his skull and iron from Harlow's 1868 paper) were "an absolutely dominating feature".<ref name="ferrier1878"/>{{sfn|M5}}{{rp|198,253}}<!--<<check page regs exp 198--><!--add frontal function / no function --><!--add re Goulstonian and its effect on opinion--> |
||
===Phrenology=== |
===Phrenology=== |
||
| Line 294: | Line 292: | ||
|{{shy|[[Phrenology|Phrenologists]] contended that destruc|tion of the mental "organs" of Vener|a|tion and Benev|o|lence caused Gage's behav|ior|al changes. Harlow may have believed that the "Organ of Compar|ison" was damaged.}} ]] |
|{{shy|[[Phrenology|Phrenologists]] contended that destruc|tion of the mental "organs" of Vener|a|tion and Benev|o|lence caused Gage's behav|ior|al changes. Harlow may have believed that the "Organ of Compar|ison" was damaged.}} ]] |
||
Throughout the nineteenth century, adherents of [[phrenology]] contended that Gage's mental changes (his profanity, for example){{ |
Throughout the nineteenth century, adherents of [[phrenology]] contended that Gage's mental changes (his profanity, for example)<ref name="amer_phren"/>{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|151}} stemmed from destruction of his mental "organ of [[wikt:benevolence#Noun|Benevolence]]"{{mdashb}}as phrenologists saw it, the part of the brain responsible for "goodness, benevolence, the gentle character{{nbsp}}... [and] to dispose man to conduct himself in a manner conformed to the maintenance of social order"{{mdashb}}and/or the adjacent "organ of [[wikt:veneration#Noun|Veneration]]"{{mdashb}}related to religion and God, and respect for peers and those in authority.{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|150,171n10}}<ref name="gall_sizer"/><ref name="northstar"/> (Phrenology held that the organs of the "grosser and more animal passions are near the base of the brain; literally the lowest and nearest the animal man [while] highest and farthest from the sensual are the moral and religions feelings, as if to be nearest heaven". Thus Veneration and Benevolence are at the apex of the skull{{mdashb}}the region of exit of Gage's tamping iron.)<ref name="apex"/> |
||
Harlow wrote that Gage, during his convalescence, did not "estimate size or money accurately [and] would not take $1000 for a few pebbles";{{ |
Harlow wrote that Gage, during his convalescence, did not "estimate size or money accurately [and] would not take $1000 for a few pebbles";{{sfn|H1}}{{rp|392}} by this he may have been implying damage to phrenology's "Organ of Comparison".{{sfn|Barker 1995}}{{rp|675-6}} |
||
===Psychosurgery and lobotomy=== |
===Psychosurgery and lobotomy=== |
||
It is frequently said that what happened to Gage played a part in the later development of various forms of [[psychosurgery]]{{mdashb}}particularly [[lobotomy]] |
It is frequently said that what happened to Gage played a part in the later development of various forms of [[psychosurgery]]{{mdashb}}particularly [[lobotomy]]<ref name="lobotomy"/><!--extract some additional examples and list here, with some quotes--><!-- add note re Freeman's use of Gage story as delaying tactic-->{{mdashb}}or even that Gage's accident constituted "the first lobotomy".<ref name="vanderkloot"/> Aside from the question of why the unpleasant changes usually (if hyperbolically) attributed to Gage would inspire surgical imitation, there is no such link, according to Macmillan: |
||
{{imagequote|There is simply no evidence that any of these operations were deliberately designed to produce the kinds of changes in Gage that were caused by his accident, nor that knowledge of Gage's fate formed part of the rationale for them{{ |
{{imagequote|There is simply no evidence that any of these operations were deliberately designed to produce the kinds of changes in Gage that were caused by his accident, nor that knowledge of Gage's fate formed part of the rationale for them{{sfn|Macmillan 2012}}{{rp|F}}{{zwj}}... [W]hat his case did show came solely from his surviving his accident: major operations [such as for tumors] could be performed on the brain without the outcome necessarily being fatal.{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|250}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
===Somatic marker hypothesis=== |
===Somatic marker hypothesis=== |
||
A.{{nbsp}}Damasio, in support of his ''[[somatic marker hypothesis]]'' (relating decision-making to emotions and their biological underpinnings), draws parallels between behaviors he attributes to Gage and those of modern patients with damage to the [[orbitofrontal cortex]] and [[amygdala]].{{ |
A.{{nbsp}}Damasio, in support of his ''[[somatic marker hypothesis]]'' (relating decision-making to emotions and their biological underpinnings), draws parallels between behaviors he attributes to Gage and those of modern patients with damage to the [[orbitofrontal cortex]] and [[amygdala]].<ref name="damasioA_descartes"/>{{rp|ch3}}<ref name="damasioA_somatic"/> But A.{{nbsp}}Damasio's depiction of Gage has been criticized by Kotowicz as |
||
{{imagequote|grotesque fabrication{{nbsp}}... ["perpetrating"] the myth of Gage the psychopath{{nbsp}}... Damasio changes [Harlow's] narrative, omits facts, and adds freely{{nbsp}}... It seems that the growing commitment to the frontal lobe doctrine of emotions brought Gage to the limelight and shapes how he is described."{{px1}}{{efn |
{{imagequote|grotesque fabrication{{nbsp}}... ["perpetrating"] the myth of Gage the psychopath{{nbsp}}... Damasio changes [Harlow's] narrative, omits facts, and adds freely{{nbsp}}... It seems that the growing commitment to the frontal lobe doctrine of emotions brought Gage to the limelight and shapes how he is described."{{px1}}{{efn |
||
|{{ |
|{{sfn|K2}}{{rp|125}} Kotowicz continues, "Damasio's account of Gage's last months [is] such a grotesque fabrication that it leaves one baffled",{{sfn|K2}}{{rp|130n6}} then quotes this passage from A.{{nbsp}}Damasio:<ref name="damasioA_descartes"/>{{rp|9-10}} |
||
:In my mind is a picture of 1860s San Francisco as a bustling place, full of adventurous entrepreneurs engaged in mining, farming, and shipping. That is where we can find Gage's mother and sister, the latter married to a prosperous San Francisco merchant {{nowrap|(D.{{thinsp}}D.}} Shattuck, Esquire), and that is where the old Phineas Gage might have belonged. But that is not where we would find him if we could travel back in time. We would probably find him drinking and brawling in a questionable district, not conversing with the captains of commerce, as astonished as anybody when the fault would slip and the earth would shake threateningly. He had joined the tableau of dispirited people who, as [[Nathanael West]] would put it decades later, and a few hundred miles to the south, "had come to California to die." {{cross-reference|(See [[The Day of the Locust]].)}} |
:In my mind is a picture of 1860s San Francisco as a bustling place, full of adventurous entrepreneurs engaged in mining, farming, and shipping. That is where we can find Gage's mother and sister, the latter married to a prosperous San Francisco merchant {{nowrap|(D.{{thinsp}}D.}} Shattuck, Esquire), and that is where the old Phineas Gage might have belonged. But that is not where we would find him if we could travel back in time. We would probably find him drinking and brawling in a questionable district, not conversing with the captains of commerce, as astonished as anybody when the fault would slip and the earth would shake threateningly. He had joined the tableau of dispirited people who, as [[Nathanael West]] would put it decades later, and a few hundred miles to the south, "had come to California to die." {{cross-reference|(See [[The Day of the Locust]].)}} |
||
Kotowicz comments: "This little literary flourish is pure invention{{nbsp}}... There is something callous in insinuating that Gage was some riff-raff who in his final days headed for California to drink and brawl himself to death." Mac{{shy}}millan{{ |
Kotowicz comments: "This little literary flourish is pure invention{{nbsp}}... There is something callous in insinuating that Gage was some riff-raff who in his final days headed for California to drink and brawl himself to death." Mac{{shy}}millan{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|116-19,326,331}}<!--notes as well, and other Macmillan papers as well--> gives detailed criticism of A.{{nbsp}}Damasio's various presentations<!--specify which of AD's works--> of Gage (some of them in joint work with H.{{nbsp}}Damasio and others). |
||
}}<!--<<end efn--> |
}}<!--<<end efn--> |
||
}}<!--<<end imagequote--> |
}}<!--<<end imagequote--> |
||
As Kihlstrom put it: |
As Kihlstrom put it: |
||
{{imagequote|[M]any modern commentators exaggerate the extent of Gage's personality change, perhaps engaging in a kind of retrospective reconstruction based on what we now know, or think we do, about the role of the frontal cortex in self-regulation.{{ |
{{imagequote|[M]any modern commentators exaggerate the extent of Gage's personality change, perhaps engaging in a kind of retrospective reconstruction based on what we now know, or think we do, about the role of the frontal cortex in self-regulation.{{sfn|K1}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
| Line 324: | Line 322: | ||
{{nowrap|Two [[daguerreotype]] portraits}} of Gage, identified in 2009 and 2010,{{efn |
{{nowrap|Two [[daguerreotype]] portraits}} of Gage, identified in 2009 and 2010,{{efn |
||
|name=dags |
|name=dags |
||
|The 2009-identified image is from the collection of Jack and Beverly Wilgus.{{ |
|The 2009-identified image is from the collection of Jack and Beverly Wilgus.{{sfn|T}}<!--<<need pg#-->{{sfn|W2}}{{sfn|W}}<!--<<need pg#-->{{sfn|W1}}<!--need page#--> Like almost all daguerreotypes it shows its subject laterally (left-right) reversed, making it appear that Gage's right eye is injured.{{sfn|W}}<!--<<need pg#-->{{sfn|W1}}<!--<<need page#--> However, all Gage's injuries, including to his eye, were on the left; therefore in presenting the image here a second, compensating reversal has been applied so as to show Gage as he appeared in life.{{sfn|L}}{{sfn|W}}<!--<<need pg#--> |
||
{{paragraph break}} |
{{paragraph break}} |
||
The 2010-identified image is in the possession of Tara Gage Miller of Texas; an identical image belongs to Phyllis Gage Hartley of New Jersey.{{ |
The 2010-identified image is in the possession of Tara Gage Miller of Texas; an identical image belongs to Phyllis Gage Hartley of New Jersey.{{sfn|L}} (Both are descended from Gage's brother Roswell Rockwell Gage.){{sfn|M8}}{{rp|4}} Unlike the Wilgus portrait, which is itself a daguerreotype, the Miller and Hartley images are 19th-century photographic reproductions of a common original which remains undiscovered, itself a daguerreotype or other laterally reversing [[History of photography|early-process photograph]];{{sfn|W1}}<!--<<need pg#--> here again a compensating reversal has been applied.{{sfn|L}} |
||
}}<!--end efn--> |
}}<!--end efn--> |
||
are the only like{{shy}}nesses{{ |
are the only like{{shy}}nesses{{sfn|W}}{{rp|343}}{{sfn|T}}{{sfn|W1}}{{rp|8}} of him known other than a [[life mask#lifemask|life mask]] taken for Bigelow in late 1849 (and now in the Warren Museum along with Gage's skull and iron).<!--img of lifemask would be good-->{{sfn|Bigelow 1850}}{{rp|22n}}<ref name="jackson1870"/>{{rp|149}}{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|ii,42}} The first shows "a disfigured yet still-handsome" Gage{{sfn|T}} with one eye closed and scars clearly visible, "well dressed and confident, even proud"{{px1}}{{sfn|W}}{{rp|343}} and holding his iron, on which portions of its inscription can be made out.{{sfn|W2}} (For decades the portrait's owners had imagined the subject was an injured whaler with his [[harpoon]].){{sfn|W2}} |
||
The second portrait, copies of which are in the possession of two different branches of the Gage family, shows Gage in a somewhat different pose, wearing a different shirt and different tie, but the same [[waistcoat]] and possibly the same jacket.{{ |
The second portrait, copies of which are in the possession of two different branches of the Gage family, shows Gage in a somewhat different pose, wearing a different shirt and different tie, but the same [[waistcoat]] and possibly the same jacket.{{sfn|W3}} |
||
Authenticity was confirmed in several ways (including photo-overlaying the inscription, as seen in the portraits, against that on the actual tamping iron, and matching the subject's injuries to those preserved in the life mask){{ |
Authenticity was confirmed in several ways (including photo-overlaying the inscription, as seen in the portraits, against that on the actual tamping iron, and matching the subject's injuries to those preserved in the life mask){{sfn|W}}{{rp|342-3}} but about when, where, and by whom they were taken nothing is known, except that they were created no earlier than January 1850 (when the inscription was added to the tamping iron),{{sfn|M8}}{{rp|4}} on different occasions, and are likely by different photographers.{{sfn|W1}}{{rp|8}} |
||
The portraits add to the evidence that Gage's most serious mental changes were temporary {{see above|mid=yes|Social recovery}}.{{ |
The portraits add to the evidence that Gage's most serious mental changes were temporary {{see above|mid=yes|Social recovery}}.{{sfn|M2}}<ref name="smithS_carey"/> "That [Gage] was any form of vagrant following his injury is belied by these remarkable images", wrote Van Horn et{{nbsp}}al.{{sfn|V}}{{rp|13}} "Although just one picture," Kean commented in reference to the first image discovered, "it exploded the common image of Gage as a dirty, disheveled misfit. This Phineas was proud, well-dressed, and disarmingly handsome."{{px1}}{{sfn|K}} |
||
==Early medical attitudes== |
==Early medical attitudes== |
||
A tone of amused wonderment was common in nineteenth-century medical writing about Gage (as well as about victims of other unlikely-sounding brain-injury accidents, including encounters with axes, bolts, low bridges, exploding firearms, a revolver shot to the nose, more tamping irons, and "even [[Eucalyptus#Unexpected branch drops|falling gum tree branches]]").{{ |
A tone of amused wonderment was common in nineteenth-century medical writing about Gage (as well as about victims of other unlikely-sounding brain-injury accidents, including encounters with axes, bolts, low bridges, exploding firearms, a revolver shot to the nose, more tamping irons, and "even [[Eucalyptus#Unexpected branch drops|falling gum tree branches]]").{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|62-7}} The ''Boston Medical{{nbsp}}& Surgical Journal'', for example, termed Gage "the patient whose cerebral organism had been comparatively so little disturbed by its abrupt and intrusive visitor".<ref name="anonymous_bmsj1869_1"/> |
||
===Skepticism=== |
===Skepticism=== |
||
Barker notes that Harlow's original 1848 report of Gage's recovery "was widely disbelieved, for obvious reasons"{{px1}}{{ |
Barker notes that Harlow's original 1848 report of Gage's recovery "was widely disbelieved, for obvious reasons"{{px1}}{{sfn|Barker 1995}}{{rp|676}} |
||
and Harlow himself, in his 1868 retrospective, recalled this early skepticism: |
and Harlow himself, in his 1868 retrospective, recalled this early skepticism: |
||
{{imagequote|The case occurred nearly twenty years ago, in an obscure country town{{nbsp}}..., was attended and reported by an obscure country physician, and was received by the Metropolitan doctors with several grains of caution, insomuch that many utterly refused to believe that the man had risen, until they had thrust their fingers into the hole [in] his head, ''{{bracket|see [[Doubting Thomas]]}}'' and even then they required of the Country Doctor attested statements, from clergymen and lawyers, before they could or would believe{{mdashb}}many eminent surgeons regarding such an occurrence as a physiological impossibility, the appearances presented by the subject being variously explained away. |
{{imagequote|The case occurred nearly twenty years ago, in an obscure country town{{nbsp}}..., was attended and reported by an obscure country physician, and was received by the Metropolitan doctors with several grains of caution, insomuch that many utterly refused to believe that the man had risen, until they had thrust their fingers into the hole [in] his head, ''{{bracket|see [[Doubting Thomas]]}}'' and even then they required of the Country Doctor attested statements, from clergymen and lawyers, before they could or would believe{{mdashb}}many eminent surgeons regarding such an occurrence as a physiological impossibility, the appearances presented by the subject being variously explained away. |
||
}} |
}} |
||
"A distinguished Professor of Surgery in a distant city", Harlow said, had even dismissed Gage as a "Yankee invention".{{ |
"A distinguished Professor of Surgery in a distant city", Harlow said, had even dismissed Gage as a "Yankee invention".{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|3,18}} |
||
According to the ''Boston Medical and Surgical Journal'', it was the 1850 report on Gage by Bigelow{{mdashb}}Harvard's Professor of Surgery and "a majestic and authoritative figure on the medical scene of those times"{{px1}} |
According to the ''Boston Medical and Surgical Journal'', it was the 1850 report on Gage by Bigelow{{mdashb}}Harvard's Professor of Surgery and "a majestic and authoritative figure on the medical scene of those times"{{px1}}<ref name="yakovlev"/>{{mdashb}}that "finally succeeded in forcing [the case's] authenticity upon the credence of the profession{{nbsp}}... as could hardly have been done by any one in whose sagacity and surgical knowledge his ''confrères'' had any less confidence".<ref name="anonymous_bmsj1869_1"/>{{Citation needed|date=March 2015}}<!--get further background on this from Macmillan 2000--> Noting that, "The leading feature of this case is its improbability{{nbsp}}... This is the sort of accident that happens in the pantomime at the theater, not elsewhere", and calling the case "perhaps unparalleled in the annals of surgery", Bigelow emphasized that though "at first wholly skeptical, I have been personally convinced".{{efn |
||
|In addition to the "attested statements" mentioned by Harlow (which Harlow had gathered at Bigelow's request) and his own examination of Gage, Bigelow pointed out that the accident had occurred "in open day" with many witnesses, and that "in a thickly populated country neighbourhood, to which all the facts were matter of daily disucssion at the time of their occurrence, there is no difference of belief, nor has there been at any time doubt that the iron was actually driven through the brain. A considerable number of medical gentlemen also visited the case at various times to satisfy their incredulity."{{px1}}{{ |
|In addition to the "attested statements" mentioned by Harlow (which Harlow had gathered at Bigelow's request) and his own examination of Gage, Bigelow pointed out that the accident had occurred "in open day" with many witnesses, and that "in a thickly populated country neighbourhood, to which all the facts were matter of daily disucssion at the time of their occurrence, there is no difference of belief, nor has there been at any time doubt that the iron was actually driven through the brain. A considerable number of medical gentlemen also visited the case at various times to satisfy their incredulity."{{px1}}{{sfn|Bigelow 1850}}{{rp|13,19-20}}{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|42}}<!--<<OKF page range might need expanding--> |
||
}}<!--<<end efn--> |
}}<!--<<end efn--> |
||
Nonetheless (Bigelow wrote just before Harlow's 1868 presentation of Gage's skull) though "the nature of [Gage's] injury and its ''reality'' are now ''beyond doubt''{{nbsp}}... I have recd a letter within a month [purporting] to prove that{{nbsp}}... the accident ''could not have happened''{{px1}}",{{ |
Nonetheless (Bigelow wrote just before Harlow's 1868 presentation of Gage's skull) though "the nature of [Gage's] injury and its ''reality'' are now ''beyond doubt''{{nbsp}}... I have recd a letter within a month [purporting] to prove that{{nbsp}}... the accident ''could not have happened''{{px1}}",{{sfn|B2}} and two years later Jackson was still able to write that |
||
{{imagequote|The very small amount of attention that has been given to [the Gage case] can only be explained by the fact that it far transcends any case of recovery from injury of the head that can be found in the records of surgery. It was too monstrous for belief{{nbsp}}...{{px1}}{{ |
{{imagequote|The very small amount of attention that has been given to [the Gage case] can only be explained by the fact that it far transcends any case of recovery from injury of the head that can be found in the records of surgery. It was too monstrous for belief{{nbsp}}...{{px1}}<ref name="jackson1870"/>{{rp|149}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
| Line 359: | Line 357: | ||
[[File:Simulated Connectivity Damage of Phineas Gage SkullDisplayWarren.jpg|thumb|left|upright=0.70| |
[[File:Simulated Connectivity Damage of Phineas Gage SkullDisplayWarren.jpg|thumb|left|upright=0.70| |
||
{{shy|"[Few objects] have attract|ed more vis|i|tors and spread farther the fame of the [[Warren Anatomical Museum|Muse{{shy}}um]]"{{px1}} |
{{shy|"[Few objects] have attract|ed more vis|i|tors and spread farther the fame of the [[Warren Anatomical Museum|Muse{{shy}}um]]"{{px1}}<ref name="yakovlev"/> |
||
than its "most valu|able spec|i|men".}}{{zwsp}}{{ |
than its "most valu|able spec|i|men".}}{{zwsp}}<ref name="jackson1870"/>{{rp|v}} ]] |
||
As the reality of Gage's accident and survival gained credence, it became "the standard against which other injuries to the brain were judged". After a miner survived traversal of his skull by a gas pipe (extracted "not without considerable difficulty and force, owing to a bend in the portion of the rod in his skull") his physician invoked Gage as the "only case comparable with this, in the amount of brain injury, that I have seen reported".{{efn| |
As the reality of Gage's accident and survival gained credence, it became "the standard against which other injuries to the brain were judged". After a miner survived traversal of his skull by a gas pipe (extracted "not without considerable difficulty and force, owing to a bend in the portion of the rod in his skull") his physician invoked Gage as the "only case comparable with this, in the amount of brain injury, that I have seen reported".{{efn| |
||
{{ |
{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|66}} At the very meeting at which Harlow unveiled Gage's skull and iron, Bigelow ("in one of those ''coup dramatiques'' which were now and then incidents of his surgical communications [and] without giving notice that he intended to do so")<ref name="memoir_hjb"/>{{rp|123}} actually produced this patient, Joel Lenn, together with "the gas pipe which had pierced his head from the right forehead to left occiput, and the hat he had been wearing (with entrance and exit holes){{nbsp}}... This ''coup de théâtre'' must have been a painful coda for Harlow, eclipsing the pinnacle of his medical career."{{px1}}{{sfn|Barker 1995}}{{rp|679}} |
||
{{paragraph break}} |
{{paragraph break}} |
||
A side effect of Lenn's post-accident medical treatment was to rid him of a 17-foot [[tapeworm]]. Months after the accident, his surgeon reported, "He seems to be perfectly rational, and will reply correctly in ''monosyllables'' to questions, but is entirely unable to ''connect words''. He succeeds best, when excited, in swearing in French."{{px1}} |
A side effect of Lenn's post-accident medical treatment was to rid him of a 17-foot [[tapeworm]]. Months after the accident, his surgeon reported, "He seems to be perfectly rational, and will reply correctly in ''monosyllables'' to questions, but is entirely unable to ''connect words''. He succeeds best, when excited, in swearing in French."{{px1}}<ref name="jewett"/> |
||
}}<!--<<end enf--> |
}}<!--<<end enf--> |
||
Often these comparisons carried hints of competitiveness, humor, or both,{{ |
Often these comparisons carried hints of competitiveness, humor, or both,{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|66}} as when a Kentucky doctor, reporting a patient's survival of a gunshot to the nose, bragged: |
||
{{imagequote|If you [[Yankee]]s can send a tamping bar through a fellow's brain and not kill him, I guess there are not many can shoot a bullet between a man's mouth and his brains, stopping just short of the medulla oblongata, and not touch either. |
{{imagequote|If you [[Yankee]]s can send a tamping bar through a fellow's brain and not kill him, I guess there are not many can shoot a bullet between a man's mouth and his brains, stopping just short of the medulla oblongata, and not touch either.<ref name="sutton"/> |
||
}} |
}} |
||
Similarly, when a lumbermill foreman returned to work soon after a saw cut three inches (8{{nbsp}}cm) into his skull from just between the eyes to behind the top of his head, his surgeon (who had removed from this wound "thirty-two pieces of bone, together with considerable sawdust") termed the case "second to none reported, save the famous tamping-iron case of Dr. Harlow", though apologizing that "I cannot well gratify the desire of my professional brethren to possess [the patient's] skull, until he has no further use for it himself."{{px1}} |
Similarly, when a lumbermill foreman returned to work soon after a saw cut three inches (8{{nbsp}}cm) into his skull from just between the eyes to behind the top of his head, his surgeon (who had removed from this wound "thirty-two pieces of bone, together with considerable sawdust") termed the case "second to none reported, save the famous tamping-iron case of Dr. Harlow", though apologizing that "I cannot well gratify the desire of my professional brethren to possess [the patient's] skull, until he has no further use for it himself."{{px1}}<ref name="folsom"/> |
||
As these and other remarkable brain-injury survivals accumulated, the ''Boston Medical{{nbsp}}& Surgical Journal'' (1869) pretended to wonder whether the brain has any function at all: "Since the antics of iron bars, gas pipes, and the like skepticism is discomfitted, and dares not utter itself. Brains do not seem to be of much account now-a-days."{{px1}} |
As these and other remarkable brain-injury survivals accumulated, the ''Boston Medical{{nbsp}}& Surgical Journal'' (1869) pretended to wonder whether the brain has any function at all: "Since the antics of iron bars, gas pipes, and the like skepticism is discomfitted, and dares not utter itself. Brains do not seem to be of much account now-a-days."{{px1}}<ref name="anonymous_bmsj1869_2"/> The ''Transactions of the Vermont Medical Society'' was similarly facetious: {{"'}}The times have been,'<!-- /The times have been/ is given in the source, though line actually reads, /The time has been/--> says Macbeth {{bracket|[[s:The Tragedy of Macbeth/Act III#Blood hath been shed ere now|Act{{nbsp}}III]]}}, 'that when the brains were out the man would die. But now they rise again.' Quite possibly we shall soon hear that some German professor is [[wikt:exsect|exsecting]] it."{{px1}}<ref name="smithW"/>{{rp|53-4}} |
||
{{clear}} |
{{clear}} |
||
==<span id="Factors favoring"></span>Factors favoring Gage's survival== |
==<span id="Factors favoring"></span>Factors favoring Gage's survival== |
||
[[File:Recovery from the passage of an iron bar through the head p2 rotateRt0pt47 crop.jpg|thumb|right|upright=1.0 |link=https://www.countway.harvard.edu/menuNavigation/chom/warren/exhibits/HarlowBMSJ1860.pdf|{{shy|"I have the pleas|ure of being able to pres|ent to you [a case] without paral|lel in the annals of surgery."{{px1}}{{ |
[[File:Recovery from the passage of an iron bar through the head p2 rotateRt0pt47 crop.jpg|thumb|right|upright=1.0 |link=https://www.countway.harvard.edu/menuNavigation/chom/warren/exhibits/HarlowBMSJ1860.pdf|{{shy|"I have the pleas|ure of being able to pres|ent to you [a case] without paral|lel in the annals of surgery."{{px1}}{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|3}} Har|low's 1868 pres|en|ta|tion to the [[Massachusetts Medical Society|{{shy|Massa|chu|setts Medi|cal Soci|e|ty}}]]{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|tp}} of Gage's skull, iron, and post-accident history.}} ]] |
||
Harlow saw Gage's survival as demonstrating "the wonderful resources of the system in enduring the shock and in overcoming the effects of so frightful a lesion, and as a beautiful display of the recuperative powers of nature", and listed what he saw as the circumstances favoring it: |
Harlow saw Gage's survival as demonstrating "the wonderful resources of the system in enduring the shock and in overcoming the effects of so frightful a lesion, and as a beautiful display of the recuperative powers of nature", and listed what he saw as the circumstances favoring it: |
||
{{imagequote| |
{{imagequote| |
||
1st. The subject was the man for the case. His physique, will, and capacity of endurance, could scarcely be excelled.{{ |
1st. The subject was the man for the case. His physique, will, and capacity of endurance, could scarcely be excelled.{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|18}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{See above|pre=For Harlow's description of the pre-accident Gage|Background}} |
{{See above|pre=For Harlow's description of the pre-accident Gage|Background}} |
||
{{imagequote| |
{{imagequote| |
||
2d. The shape of the missile{{mdashb}}being pointed, round and comparatively smooth, not leaving behind it prolonged concussion or compression.{{ |
2d. The shape of the missile{{mdashb}}being pointed, round and comparatively smooth, not leaving behind it prolonged concussion or compression.{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|18}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
Despite its very large diameter and mass (compared to a weapon-fired projectile) the tamping iron's relatively low velocity drastically reduced the energy available to compressive and concussive "shock waves".{{ |
Despite its very large diameter and mass (compared to a weapon-fired projectile) the tamping iron's relatively low velocity drastically reduced the energy available to compressive and concussive "shock waves".{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|56,68n3}}<ref name="ordia"/><ref name="mitchell"/><!--<<get page#--> Ratiu et{{nbsp}}al.'s conclusion, that Gage's skull "hinged open" as the iron passed through,{{sfn|Ratiu 2004}}{{rp|639}} implies a further reduction in such effects because of the increased volume available into which the brain could shift temporarily.{{Citation needed|date=September 2014}}<!-- "This hypothesis has the further advantage that it helps explain Gage's very survival: the cranium's temporarily increased volume allowed the brain to move aside as the iron passed through, limiting the concussive effect to surrounding tissues." -- check exact wording here; need cite on brain moved aside; integrate with Harlow quote elsewhere on shape of iron; integrate with ratiu and other comments on infection etc. --> |
||
Harlow continued: |
Harlow continued: |
||
{{imagequote| |
{{imagequote| |
||
3d. The point of entrance outside of the [[superior maxillary]] bone{{mdashb}}[the tamping iron] did little injury until it reached the floor of the cranium, when, at the same time that it did irreparable damage, it [created the] opening in the base of the skull, for drainage, [without which] recovery would have been impossible.{{ |
3d. The point of entrance outside of the [[superior maxillary]] bone{{mdashb}}[the tamping iron] did little injury until it reached the floor of the cranium, when, at the same time that it did irreparable damage, it [created the] opening in the base of the skull, for drainage, [without which] recovery would have been impossible.{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|18}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
Barker writes that "[Head injuries] from falls, horse kicks, and gunfire, were well known in {{nowrap|pre{{ndash}}Civil}} War America [and] every contemporary course of lectures on surgery described the diagnosis and treatment" of such injuries. But to Gage's benefit, surgeon [[Joseph Pancoast]] had performed "his most celebrated operation for head injury before Harlow's medical school class, {{bracket|[[trephining]]}} to drain the pus, resulting in temporary recovery. Unfortunately, symptoms recurred and the patient died. At autopsy, reaccumulated pus was found: [[granulation tissue]] had blocked the opening in the [[Dura mater|dura]]." By keeping the exit wound open and elevating Gage's head to encourage drainage from the cranium through the hole in the roof of the mouth, Harlow "had not repeated Professor Pancoast's mistake".{{ |
Barker writes that "[Head injuries] from falls, horse kicks, and gunfire, were well known in {{nowrap|pre{{ndash}}Civil}} War America [and] every contemporary course of lectures on surgery described the diagnosis and treatment" of such injuries. But to Gage's benefit, surgeon [[Joseph Pancoast]] had performed "his most celebrated operation for head injury before Harlow's medical school class, {{bracket|[[trephining]]}} to drain the pus, resulting in temporary recovery. Unfortunately, symptoms recurred and the patient died. At autopsy, reaccumulated pus was found: [[granulation tissue]] had blocked the opening in the [[Dura mater|dura]]." By keeping the exit wound open and elevating Gage's head to encourage drainage from the cranium through the hole in the roof of the mouth, Harlow "had not repeated Professor Pancoast's mistake".{{sfn|Barker 1995}}{{rp|675}}{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|58}}<ref name="pancoast"/> |
||
Finally, |
Finally, |
||
{{imagequote| |
{{imagequote| |
||
4th. The portion of the brain traversed was, for several reasons, the best fitted of any part of the cerebral substance to sustain the injury.{{ |
4th. The portion of the brain traversed was, for several reasons, the best fitted of any part of the cerebral substance to sustain the injury.{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|18}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
Precisely what Harlow's "several reasons" were is unclear, but he was likely referring, at least in part, to the understanding (slowly developing since ancient times) that injuries to the ''rear'' of the brain are especially dangerous, because they frequently interrupt vital functions such as breathing and circulation {{ |
Precisely what Harlow's "several reasons" were is unclear, but he was likely referring, at least in part, to the understanding (slowly developing since ancient times) that injuries to the ''rear'' of the brain are especially dangerous, because they frequently interrupt vital functions such as breathing and circulation {{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|126,142}} As British surgeon [[James Earle]] wrote in 1790, "[A] great part of the [[cerebrum]] may be taken away without destroying the animal, or even depriving it of its faculties, whereas the [[cerebellum]] will scarcely admit the smallest injury, without being followed by mortal symptoms."{{px1}}{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|128}}<ref name="pott"/> |
||
Ratiu et{{nbsp}}al. and Van Horn et{{nbsp}}al. both concluded that the [[superior sagittal sinus]] must have remained intact, for otherwise Gage would almost certainly have suffered fatal blood loss or [[air embolism]].{{ |
Ratiu et{{nbsp}}al. and Van Horn et{{nbsp}}al. both concluded that the [[superior sagittal sinus]] must have remained intact, for otherwise Gage would almost certainly have suffered fatal blood loss or [[air embolism]].{{sfn|Ratiu 2004}}{{rp|642}}{{sfn|V}}{{rp|17}} |
||
As to his own role in Gage's survival, Harlow merely averred, "I can only say{{nbsp}}... with good old [[Ambroise Paré]], I [[wiktionary:dress#English-treat wound|dressed]] him, God healed him",{{ |
As to his own role in Gage's survival, Harlow merely averred, "I can only say{{nbsp}}... with good old [[Ambroise Paré]], I [[wiktionary:dress#English-treat wound|dressed]] him, God healed him",{{sfn|Harlow 1868}}{{rp|20}} but Macmillan calls this self-assessment far too modest.{{refn| [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], p. 12, ch. 4, pp. 355{{ndash}}9; [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2008|Macmillan 2008]], pp. 28{{ndash}}9; [[#Macmillan 2001|Macmillan 2001]], pp. 151{{ndash}}3. }} Noting that Harlow had been a "relatively inexperienced local physician{{nbsp}}... graduated four and a half years earlier",{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|12}} Macmillan's discussion of Harlow's "skillful and imaginative adaptation" of "conservative and progressive elements from the available therapies to the particular needs posed by Gage's injuries" emphasizes that he "did not apply rigidly what he had learned", for example foregoing an exhaustive search for bone fragments (which risked hemorrhage and further brain injury) and applying caustic silver nitrate to the granulation tissue instead of excising it (which risked hemorrhage) or forcing it into the wound (which risked compressing the brain).{{sfn|Macmillan 2000}}{{rp|58-62}} |
||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
| Line 415: | Line 413: | ||
==References== |
==References== |
||
;For general readers |
|||
{{refbegin|30em}} |
|||
{{rma| {{nbsp}}H. |{{cite journal |ref=H |
|||
|last=Harlow |first=John Martyn |year=1868 |
|||
|title=Recovery from the Passage of an Iron Bar through the Head |
|||
|work=Publications of the Massachusetts Medical Society |volume=2 |
|||
|pages=327{{ndash}}47<!--something somewhere says n3 of v2--> |
|||
|url=https://www.countway.harvard.edu/menuNavigation/chom/warren/exhibits/HarlowBMSJ1860.pdf |
|||
}} Reprinted as ''Recovery from the Passage of an Iron Bar through the Head'' (David Clapp{{nbsp}}& Son, 1869). 22 pages. {{open access}} }} |
|||
{{rma| {{nbsp}}K. |{{cite news |ref=K |
|||
|title=Phineas Gage, Neuroscience's Most Famous Patient |work=Slate |date=May 6, 2014 |last=Kean |first=Sam |
|||
|url=http://www.slate.com/articles/health_and_science/science/2014/05/phineas_gage_neuroscience_case_true_story_of_famous_frontal_lobe_patient.html |
|||
}} {{open access}} }} |
|||
{{rma| {{nbsp}}M. |{{cite book |ref=M |
|||
|last=Macmillan |first=Malcolm B. |year=2000 |
|||
|title=An Odd Kind of Fame: Stories of Phineas Gage |publisher=[[MIT Press]] |
|||
|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=Qx4fMsTqGFYC |
|||
|id=ISBN 0-262-13363-6 (hbk, 2000) ISBN 0-262-63259-4 (pbk, 2002) |
|||
}} {{open access}} {{bullet}}''See also'' [http://www.uakron.edu/gage/book.dot "''An Odd Kind of Fame'' §Corrections"]. {{open access}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{rma| M1. |{{cite journal |author-mask=2 |ref=M1 |
|||
|last=Macmillan |first=Malcolm B. |date=September 2008 |publisher=[[British Psychological Society]] |
|||
|url=http://thepsychologist.bps.org.uk/volume-21/edition-9/phineas-gage-unravelling-myth |
|||
|title=Phineas Gage{{mdashb}}Unravelling the myth |work=The Psychologist |volume=21 |number=9 |
|||
|pages=828{{ndash}}31.<!--Possible problem re pg#s, online vs paper?--check all cites to this--> |
|||
}} {{open access}} }} |
|||
{{rma| M2. |{{cite web |author-mask=2 |ref=M2 |
|||
|url=http://brightbytes.com/phineasgage/more.html |last=Macmillan |first=Malcolm B. |date=July 2009 |
|||
|title=More About Phineas Gage, Especially After the Accident |accessdate=July 27, 2013 |
|||
}} {{open access}} }} |
|||
{{rma| M3. |{{cite web |author-mask=2 |ref=M3 |
|||
|last=Macmillan |first=Malcolm B. |year=2012<!--latest changes--> |url=http://www.uakron.edu/gage/index.dot |
|||
|title=The Phineas Gage Information Page |publisher=The University of Akron |accessdate=July 22, 2013 }} Includes: |
|||
A. {{cite web |url=http://www.uakron.edu/gage/sites-and-plaque.dot |title=Phineas Gage Sites in Cavendish}} {{open access}} |
|||
<br/>B. {{cite web |url=http://www.uakron.edu/gage/questions.dot |title=Phineas Gage: Unanswered questions}} {{open access}} |
|||
<br/>C. {{cite web |url=http://www.uakron.edu/gage/story.dot |title=Phineas Gage's Story}} {{open access}} |
|||
<br/>D. {{cite web |url=http://www.uakron.edu/gage/book.dot |title=Corrections to ''An Odd Kind of Fame''}} {{open access}} |
|||
<br/>E. {{cite web |url=http://www.uakron.edu/gage/adaptation.dot |title=Phineas Gage: Psychosocial Adaptation}} {{open access}} |
|||
<br/>F. {{cite web |url=http://www.uakron.edu/gage/lobotomy.dot |title=Phineas Gage and Frontal Lobotomies}} {{open access}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{rma| M4. |{{cite interview |ref=M4 |
|||
|last1=Macmillan |first1=Malcolm B. |date=March 6, 2011 |last2=Aggleton |first2=John |
|||
|interviewer=Claudia Hammond; Dave Lee |type=Audio interview |program=Health Check |callsign=BBC World Service |
|||
|title=Phineas Gage: The man with a hole in his head |url=http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/health-12649555 |
|||
}} {{open access}} }} |
|||
{{rma| {{nbsp}}{{nbsp}}T. |{{cite journal |ref=T |
|||
|last=Twomey |first=S. |date=January 2010 |volume=40 |issue=10 |journal=[[Smithsonian Magazine|Smithsonian]] |
|||
|url=http://www.smithsonianmag.com/history-archaeology/78437017.html |title=Finding Phineas |pages=8{{ndash}}10 |
|||
}} {{open access}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{refend}} |
|||
;For young readers |
|||
{{refbegin}} |
|||
{{rma| {{nbsp}}F. |{{cite book |ref=F |
|||
|title=Phineas Gage: A Gruesome but True Story About Brain Science |year=2002 |isbn=0-618-05252-6 |
|||
|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=XXxtmdcj_04C |last=Fleischman |first=J. |
|||
}} {{open access}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{refend}} |
|||
;For researchers and specialists |
|||
{{refbegin|30em}} |
|||
{{rma| {{nbsp}}{{nbsp}}B. |{{cite journal |ref=B |
|||
|last=Barker |first=F. G. II |year=1995 |
|||
|pmid=7897537 |url=http://mysois.uwm.edu/omeka/archive/files/b7cf786e3d97d4cf63ac3b7d14e1f88e.pdf |
|||
|title=Phineas among the phrenologists: the American crowbar case and nineteenth-century theories of cerebral localization |
|||
|work=Journal of Neurosurgery |volume=82 |pages=672{{ndash}}82 |doi=10.3171/jns.1995.82.4.0672 |issue=4 |
|||
}} {{open access}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{rma| B1. |{{cite journal |ref=B1 |
|||
|last=Bigelow |first=Henry Jacob |work=[[American Journal of the Medical Sciences]] |
|||
|title=Dr. Harlow's Case of Recovery from the Passage of an Iron Bar through the Head |
|||
|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=pgMHAAAAcAAJ&pg=PA12-IA2 <!--https://archive.org/stream/orthopedicsurge00bige#page/172/mode/2up may have(?) ocr usable at Wikisource--> |
|||
|date=July 1850<!--<<July is per Harlow (1868)--> |volume=20 |pages=13{{ndash}}22 |
|||
}} {{open access}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{rma| B2. |{{cite letter |author-mask=2 |ref=B2 |
|||
|first=Henry Jacob |last=Bigelow |recipient=M. Jewett |type=manuscript |
|||
|subject=Your favor of April 29th is before me |date=May 12, 1868 |
|||
}} Records of the Warren Anatomical Museum, 1828{{ndash}}1892 (inclusive) (AA 192.5), Harvard Medical Library in the Francis A. Countway Library of Medicine. |
|||
}} |
|||
{{rma| F1. |{{cite book |ref=F1 |
|||
|last=Fuster |first=Joaquin M. |title=The prefrontal cortex |
|||
|publisher=Elsevier/Academic Press |year=2008 |page=172 |isbn=0-12-373644-7 |
|||
|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=zuZlvNICdhUC&pg=PA172 |
|||
}} {{closed access}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{rma| {{nbsp}}{{nbsp}}G. |{{cite book |ref=G |
|||
|chapter=The Structured Event Complex and the Human Prefrontal Cortex |doi=10.1093/acprof:oso/9780195134971.003.0019 |
|||
|title=Principles of Frontal Lobe Function |editors=Stuss, D. T.; Knight, R. T. |
|||
|pages=292{{ndash}}310 |year=2002 |isbn=978-0-195-13497-1 |last1=Grafman |first1=J. |
|||
}} {{closed access}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{anchor|G1}}{{rma| G1. |
|||
|Gage, P.P. (185[4?]). "Please give my iron bar to the bearer" (Note to unknown recipient). Records of the Warren Anatomical Museum, 1828{{ndash}}1892 (inclusive) (AA 192.5), Harvard Medical Library in the Francis A. Countway Library of Medicine, Box 1. |
|||
}} |
|||
{{rma| H1. |{{cite journal |ref=H1 |
|||
|last=Harlow |first=John Martyn |date=December 13, 1848 |volume=39 |title=Passage of an Iron Rod Through the Head |url=https://www.countway.harvard.edu/menuNavigation/chom/warren/exhibits/HarlowBMSJ1848.pdf |
|||
|work=[[Boston Medical and Surgical Journal|Boston Medical & Surgical Journal]] |number=20 |pages=389{{ndash}}93 |doi=10.1056/nejm184812130392001 |
|||
}} {{open access}} ([[s:Passage of an Iron Rod Through the Head|Transcription]].) |
|||
}} |
|||
{{rma| H2. |{{cite journal |author-mask=2 |ref=H2 |
|||
|last=Harlow |first=John Martyn |date=January 3, 1849 |title=Medical Miscellany (letter) |
|||
|work=[[Boston Medical and Surgical Journal|Boston Medical & Surgical Journal]] |volume=39 |page=507 |
|||
}} Reproduced in [[#M|Macmillan (2000)]], p. 389. |
|||
}} |
|||
{{rma| K1. |{{cite journal |ref=K1 |
|||
|url=http://ist-socrates.berkeley.edu/~kihlstrm/SocialNeuroscience07.htm |last=Kihlstrom |
|||
|first=J. F. |year=2010 |title=Social neuroscience: The footprints of Phineas Gage |
|||
|journal=Social Cognition |volume=28 |pages=757{{ndash}}82 |doi=10.1521/soco.2010.28.6.757 |issue=6 |
|||
}} {{open access}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{rma| {{nbsp}}{{nbsp}}L. |{{cite news |ref=L |
|||
|last1=Lena |first1=M. L. |last2=Macmillan |first2=Malcolm B. |
|||
|date=March 2010 |url=http://www.smithsonianmag.com/arts-culture/Letters-201003.html#article-text |
|||
|title=Picturing Phineas Gage (Invited comment) |page=4<!-- is it volume=10 |issue=4? --> |
|||
|work=[[Smithsonian Magazine|Smithsonian]] |
|||
}} {{open access}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{rma| K2. |{{cite journal |ref=K2 |
|||
|last1=Kotowicz |first1=Z. |doi=10.1177/0952695106075178 |pages=115{{ndash}}31 |year=2007 |
|||
|title=The strange case of Phineas Gage |journal=History of the Human Sciences |volume=20 |issue=1 |
|||
}} {{closed access}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{rma| M5. |{{cite news |ref=M5 |
|||
|last=Macmillan |first=Malcolm B. |year=1996 |pages=243{{ndash}}62 |title=Phineas Gage: A Case for All Reasons |
|||
|location=London |publisher=Erlbaum |work=Classic Cases in Neuropsychology |
|||
|editor1-last=Code |editor1-first=C. |editor2-last=Wallesch |editor2-first=C. W. |
|||
|editor3-last=Lecours |editor3-first=A. R. |editor4-last=Joanette |editor4-first=U. |displayeditors=4 |
|||
}} }} |
|||
{{rma| M6. |{{cite journal |author-mask=2 |ref=M6 |
|||
|last1=Macmillan |first1=Malcolm B. |
|||
|title=Restoring Phineas Gage: A 150th Retrospective |doi=10.1076/0964-704X(200004)9:1;1-2;FT046 |
|||
|journal=Journal of the History of the Neurosciences |volume=9 |issue=1 |
|||
|pages=46{{ndash}}66 |year=2000 |pmid=11232349 }} {{closed access}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{rma| M7. |{{cite journal |author-mask=2 |ref=M7 |
|||
|last1=Macmillan |first1=Malcolm B. |
|||
|title=John Martyn Harlow: Obscure Country Physician? |doi=10.1076/jhin.10.2.149.7254 |year=2001 |
|||
|journal=Journal of the History of the Neurosciences |volume=10 |issue=2 |pages=149{{ndash}}162 |pmid=11512426 |
|||
}} {{closed access}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{rma| M8. |{{cite journal |author-mask=2 |ref=M8 |
|||
|url=https://elearning.unipd.it/scuolapsicologia/pluginfile.php/13618/mod_folder/content/0/Rehabilitating%20Phineas%20Gage.pdf |
|||
|last1=Macmillan |first1=Malcolm B. |last2=Lena |first2=M. L. |doi=10.1080/09602011003760527 |
|||
|title=Rehabilitating Phineas Gage |journal=Neuropsychological Rehabilitation |volume=20 |issue=5 |
|||
|pages=641{{ndash}}658 |year=2010 |pmid=20480430 |
|||
}} {{open access}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{rma| {{nbsp}}{{nbsp}}R. |{{cite journal |ref=R |
|||
|last1=Ratiu |first1=P. |last2=Talos |first2=I. F. |last3=Haker |first3=S. |last4=Lieberman |pages=637{{ndash}}643 |
|||
|first4=D. |last5=Everett |first5=P. |title=The Tale of Phineas Gage, Digitally Remastered |pmid=15165371 |
|||
|doi=10.1089/089771504774129964 |journal=Journal of Neurotrauma |volume=21 |issue=5 |year=2004 |
|||
}} {{closed access}}<!--confusing ratiu cites and page #s need checking--> |
|||
}} |
|||
{{rma| R1. |{{cite journal |ref=R1 |
|||
|last1=Ratiu |first1=P. |last2=Talos |first2=I. F. |doi=10.1056/NEJMicm031024 |pmid=15575047 |
|||
|title=The Tale of Phineas Gage, Digitally Remastered |journal=New England Journal of Medicine |
|||
|volume=351 |issue=23 |pages=e21 |url=http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMicm031024 |year=2004 |
|||
}} {{open access}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{rma| T1. |{{cite journal |ref=T1 |
|||
|last1=Tyler |first1=K.L. |last2=Tyler |first2=H.R. |year=1982 |volume=32 |page=A191 |
|||
|title=A 'Yankee Invention': the celebrated American crowbar case |work=Neurology |
|||
}} {{closed access}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{rma| {{nbsp}}{{nbsp}}V. |{{cite journal |ref=V |
|||
|last1=Van Horn |first1=J. D. |last2=Irimia |first2=A. |last3=Torgerson |first3=C. M. |
|||
|last4=Chambers |first4=M. C. |last5=Kikinis |first5=R. |last6=Toga |first6=A. W. |
|||
|title=Mapping Connectivity Damage in the Case of Phineas Gage |doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0037454 |
|||
|journal=PLoS ONE |volume=7 |issue=5 |pages=e37454 |year=2012 |pmid=22616011 |pmc=3353935 |
|||
}} {{open access}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{rma| {{nbsp}}W. |{{cite journal |ref=W |
|||
|last=Wilgus |first=B. & J. |year=2009 |title=Face to Face with Phineas Gage |
|||
|url=http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/09647040903018402#preview |pmid=20183215 |
|||
|journal=Journal of the History of the Neurosciences |volume=18 |issue=3 |pages=340{{ndash}}5 |doi=10.1080/09647040903018402 |
|||
}} {{closed access}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{rma| W1. |{{cite journal |author-mask=2 |ref=W1 |
|||
|last=Wilgus |first=B. & J. |date=July{{ndash}}September 2009 |title=Phineas Gage{{snd}}Hiding in Plain Sight <!--derre.o/soc'y--> |
|||
|journal=The Daguerreian Society Newsletter |volume=21 |issue=3 |pages=6{{ndash}}9 |
|||
}} }} |
|||
{{rma| W2. |{{cite web |author-mask=2 |ref=W2 |
|||
|last=Wilgus |first=B. & J. |year=2009 |title=Meet Phineas Gage |
|||
|url=http://www.brightbytes.com/phineasgage/index.html |accessdate=October 18, 2014 |
|||
}} {{open access}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{rma| W3. |{{cite web |author-mask=2 |ref=W3 |
|||
|last=Wilgus |first=B. & J. |year=2010 |title=A New Image of Phineas Gage |
|||
|url=http://www.brightbytes.com/phineasgage/new_image.html |accessdate=March 10, 2010 |
|||
}} {{open access}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{refend}} |
|||
;Other sources cited |
|||
{{Reflist |30em |refs= |
{{Reflist |30em |refs= |
||
{{refn |name=accident_excerpts |
{{refn | name=accident_excerpts |
||
|Excerpted from Williams' and Harlow's statements in: [[#H1|Harlow |
|Excerpted from Williams' and Harlow's statements in: [[#H1|Harlow 1848]], pp. 390{{ndash}}3; [[#Bigelow 1850|Bigelow 1850]], p. 16; [[#H|Harlow 1868]], pp. 7{{ndash}}10. |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{refn |name=ama_standing|{{cite book |
{{refn | name=ama_standing|{{cite book |
||
|author=American Medical Association |year=1850 |pages=345 |work=The Transactions of the American Medical Association |
|author=American Medical Association |year=1850 |pages=345 |work=The Transactions of the American Medical Association |
||
|title=Report of the Standing Committee on Surgery |url=http://books.google.com/books?id=C8QCAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA345 |
|title=Report of the Standing Committee on Surgery |url=http://books.google.com/books?id=C8QCAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA345 |
||
}} {{open access}} }} |
}} {{open access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=amer_phren |{{cite journal |
{{refn | name=amer_phren |{{cite journal |
||
|author=<!--anon--> |work=American Phrenological Journal and Repository of Science, Literature, and General Intelligence |
|author=<!--anon--> |work=American Phrenological Journal and Repository of Science, Literature, and General Intelligence |
||
|title=A most remarkable case |publisher=Fowler & Wells |volume=13 |number=4 |
|title=A most remarkable case |publisher=Fowler & Wells |volume=13 |number=4 |
||
| Line 661: | Line 430: | ||
}} {{open access}} }} |
}} {{open access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=anonymous_ngray |
{{refn | name=anonymous_ngray |
||
|author=<!--anon--> |''Volume 3: Lone Mountain register, 1850{{ndash}}1862'', Halsted N. Gray{{snd}}Carew & English Funeral Home Records (SFH 38), San Francisco History Center, San Francisco Public Library. p. 285. |
|author=<!--anon--> |''Volume 3: Lone Mountain register, 1850{{ndash}}1862'', Halsted N. Gray{{snd}}Carew & English Funeral Home Records (SFH 38), San Francisco History Center, San Francisco Public Library. p. 285. |
||
}}<!--chk exact cite/name of merged firm--><!--formalize cite--> |
}}<!--chk exact cite/name of merged firm--><!--formalize cite--> |
||
{{refn |name=anonymous_bmsj1869_1 |{{cite journal |
{{refn | name=anonymous_bmsj1869_1 |{{cite journal |
||
|author=<!--anon--> |title=Bibliographical Notice |work=Boston Medical & Surgical Journal |date=March 18, 1869 |
|author=<!--anon--> |title=Bibliographical Notice |work=Boston Medical & Surgical Journal |date=March 18, 1869 |
||
|volume=3 n.s. |pages=116{{ndash}}7 |issue=7 |
|volume=3 n.s. |pages=116{{ndash}}7 |issue=7 |
||
}} }} |
}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=anonymous_bmsj1869_2 |{{cite journal |
{{refn | name=anonymous_bmsj1869_2 |{{cite journal |
||
|author=<!--anon--> |title=Medical Intelligence. Extraordinary Recovery |work=Boston Medical & Surgical Journal |date=April 29, 1869 |volume=3 n.s. |pages=230{{ndash}}1 |issue=13 |
|author=<!--anon--> |title=Medical Intelligence. Extraordinary Recovery |work=Boston Medical & Surgical Journal |date=April 29, 1869 |volume=3 n.s. |pages=230{{ndash}}1 |issue=13 |
||
}} }} |
}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=anonymous_bostonpost |{{cite news |
{{refn | name=anonymous_bostonpost |{{cite news |
||
|author=<!--anon--> |date=September 21, 1848 |work=Boston Post |title=Horrible Accident |
|author=<!--anon--> |date=September 21, 1848 |work=Boston Post |title=Horrible Accident |
||
}} }} |
}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=austin |{{cite book |
{{refn | name=austin |{{cite book |
||
|last=Austin |first=K. A. |year=1977 |
|last=Austin |first=K. A. |year=1977 |
||
|title=A Pictorial History of Cobb and Co.: The Coaching Age in Australia, 1854{{ndash}}1924 |
|title=A Pictorial History of Cobb and Co.: The Coaching Age in Australia, 1854{{ndash}}1924 |
||
| Line 684: | Line 453: | ||
}} }} |
}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=benderly |{{cite journal |
{{refn | name=benderly |{{cite journal |
||
|last=Benderly |first=Beryl Lieff | date=September 2012 |title=Psychology’s tall tales |
|last=Benderly |first=Beryl Lieff | date=September 2012 |title=Psychology’s tall tales |
||
|url=http://www.apa.org/gradpsych/2012/09/tall-tales.aspx|page=20 |
|url=http://www.apa.org/gradpsych/2012/09/tall-tales.aspx|page=20 |
||
| Line 690: | Line 459: | ||
}} {{open access}} }} |
}} {{open access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=bower |{{cite journal |
{{refn | name=bower |{{cite journal |
||
|title=The Social Brain: New Clues from Old Skull |first= B. |last= Bower |jstor=3978044 |
|title=The Social Brain: New Clues from Old Skull |first= B. |last= Bower |jstor=3978044 |
||
}} {{closed access}} }} |
}} {{closed access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=wife | |
{{refn | name=wife | |
||
{{cite encyclopedia |
{{cite encyclopedia |
||
|last=Moffat |first=Gregory K. |year=2012 |page=44 |title=Fundamentals of Aggression |
|last=Moffat |first=Gregory K. |year=2012 |page=44 |title=Fundamentals of Aggression |
||
| Line 706: | Line 475: | ||
|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=sRmgAAAAMAAJ |pages=366{{ndash}}7 |
|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=sRmgAAAAMAAJ |pages=366{{ndash}}7 |
||
}} {{closed access}} |
}} {{closed access}} |
||
* [[#anonymous_northstar|Anonymous (1848)]]; [[# |
* [[#anonymous_northstar|Anonymous (1848)]]; [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], p. 39. |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{refn |name=sexuality| |
{{refn | name=sexuality| |
||
{{cite book |
{{cite book |
||
|last1=Beaumont |first1=Graham |last2=Kenealy |first2=Pamela |last3=Rogers |first3=Marcus |date=1991 |publisher=Wiley |
|last1=Beaumont |first1=Graham |last2=Kenealy |first2=Pamela |last3=Rogers |first3=Marcus |date=1991 |publisher=Wiley |
||
| Line 722: | Line 491: | ||
|year=1995 |publisher=Worth Publishers |isbn=978-0-87901-644-9 |title=Psychology |
|year=1995 |publisher=Worth Publishers |isbn=978-0-87901-644-9 |title=Psychology |
||
}} {{closed access}} |
}} {{closed access}} |
||
* [[# |
* [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], pp. 319, 327{{ndash}}8 |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{refn |name= |
{{refn | name=inability| |
||
[[#damasio1994|Damasio (1994)]], pp. 11, 51; [[#M|Macmillan (2000)]], pp. 119, 331. |
|||
}} |
|||
{{refn |name=inability| |
|||
{{cite book |
{{cite book |
||
|last1=Groves |first1=Philip M. |last2=Schlesinger |first2=K. |year=1982 |location=Dubuque, Iowa |
|last1=Groves |first1=Philip M. |last2=Schlesinger |first2=K. |year=1982 |location=Dubuque, Iowa |
||
| Line 743: | Line 508: | ||
|last=Smith |first=A. |year=1985 |title=The Body |location=Harmondsworth, England |publisher=Penguin |
|last=Smith |first=A. |year=1985 |title=The Body |location=Harmondsworth, England |publisher=Penguin |
||
}} |
}} |
||
* [[# |
* [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], p. 323. |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{refn |name=refusal| |
{{refn | name=refusal| |
||
{{cite book |
{{cite book |
||
|last=Altrocchi |first=John |year=1980 |title=Abnormal Behavior |publisher=Harcourt, Brace, Jovanovich |isbn=978-0-15-500370-5 |
|last=Altrocchi |first=John |year=1980 |title=Abnormal Behavior |publisher=Harcourt, Brace, Jovanovich |isbn=978-0-15-500370-5 |
||
| Line 753: | Line 518: | ||
|last=Morris |first=C. G. |year=1996 |title=Psychology: An Introduction |edition=9th |publisher=Prentice-Hall |
|last=Morris |first=C. G. |year=1996 |title=Psychology: An Introduction |edition=9th |publisher=Prentice-Hall |
||
}} |
}} |
||
* [[# |
* [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], pp. 107, 323. |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{refn |name=irresponsibility| |
{{refn | name=irresponsibility| |
||
{{cite news |ref=blakeslee |
{{cite news |ref=blakeslee |
||
|last=Blakeslee |first=Sandra |date=May 24, 1994 |page=C1 |
|last=Blakeslee |first=Sandra |date=May 24, 1994 |page=C1 |
||
|title=Old Accident Points to Brain's Moral Center |work=New York times |
|title=Old Accident Points to Brain's Moral Center |work=New York times |
||
}} |
}} |
||
* [[#damasio_etal1994|Damasio et al. |
* [[#damasio_etal1994|Damasio et al. 1994]], p. 1102; [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], p. 116. |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{refn |name=aggressiveness| |
{{refn | name=aggressiveness| |
||
{{cite book |
{{cite book |
||
|last=Dimond |first=Stuart J. |year=1980 |location=London |publisher=Butterworths |
|last=Dimond |first=Stuart J. |year=1980 |location=London |publisher=Butterworths |
||
|title=Neuropsychology: A Textbook of Systems and Psychological Functions of the Human Brain |
|title=Neuropsychology: A Textbook of Systems and Psychological Functions of the Human Brain |
||
}} |
}} |
||
* [[# |
* [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], pp. 321, 331. |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{refn |name=vagrancy| |
{{refn | name=vagrancy| |
||
{{cite book |
{{cite book |
||
|last=Restak |first=Richard M. |title=The Brain |publisher=Bantam Books |year=1984 |
|last=Restak |first=Richard M. |title=The Brain |publisher=Bantam Books |year=1984 |
||
| Line 780: | Line 545: | ||
|title=Personality changes following frontal leucotomy: a clinical and experimental study of the functions of the frontal lobes in man. With a foreword by Sir Russell Brain |
|title=Personality changes following frontal leucotomy: a clinical and experimental study of the functions of the frontal lobes in man. With a foreword by Sir Russell Brain |
||
}} |
}} |
||
* [[# |
* [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], p. 323. |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{refn |name=drifting| |
{{refn | name=drifting| |
||
{{cite book |
{{cite book |
||
|last=Blakemore |first=Colin |title=Mechanics of the mind |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=1977 |
|last=Blakemore |first=Colin |title=Mechanics of the mind |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=1977 |
||
| Line 795: | Line 560: | ||
|title=How the Brain Works: A New Understanding of Human Learning, Emotion, and Thinking |
|title=How the Brain Works: A New Understanding of Human Learning, Emotion, and Thinking |
||
}} |
}} |
||
* [[# |
* [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], pp. 316, 323. |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{refn |name=drinking| |
{{refn | name=drinking| |
||
{{cite journal |
{{cite journal |
||
|last=Hughes |first=C. D. |year=1897 |pages=315{{ndash}}23 |title=Neurological progress in America |
|last=Hughes |first=C. D. |year=1897 |pages=315{{ndash}}23 |title=Neurological progress in America |
||
| Line 809: | Line 574: | ||
|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=MRQJAAAAIAAJ&pg=PA68 |volume=CCXLIV |work=Gentleman's Magazine |
|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=MRQJAAAAIAAJ&pg=PA68 |volume=CCXLIV |work=Gentleman's Magazine |
||
}} {{open access}} |
}} {{open access}} |
||
* [[# |
* [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], pp. 118, 316, 321. |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{refn |name= |
{{refn | name=bullying| |
||
{{cite book |
|||
[[#nye|Nye (1942)]], pp. 366{{ndash}}7 |
|||
|last=Sdorow |first=Lester |year=1990 |title=Psychology |location=Dubuque, Iowa |publisher=Brown |
|||
}} |
|||
* [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2008|Macmillan 2008]], p. 830; [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], p. 321. |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
{{refn |name= |
{{refn | name=bragging| |
||
[[#nye|Nye 1942]], pp. 366{{ndash}}7 |
|||
[[#blakeslee|Blakeslee (1994)]]; [[#M|Macmillan (2000)]], pp. 119, 321. |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
{{refn |name= |
{{refn | name=lying| |
||
[[# |
[[#blakeslee|Blakeslee 1994]]; [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], pp. 119, 321. |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{refn |name= |
{{refn | name=brawling| |
||
[[#damasio1994|Damasio 1994]], p. 9; [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], p. 119. |
|||
{{cite book |
|||
|last=Sdorow |first=Lester |year=1990 |title=Psychology |location=Dubuque, Iowa |publisher=Brown |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
* [[#M1|Macmillan (2008)]], p. 830; [[#M|Macmillan (2000)]], p. 321. |
|||
{{refn |name=forethought| |
|||
[[#damasio1994|Damasio 1994]], pp. 11, 51; [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], pp. 119, 331. |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
{{refn |name= |
{{refn |name=idiot| |
||
[[#blakeslee|Blakeslee 1994]]; [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], p. 39. |
|||
}} |
|||
{{refn |name=work |
|||
| [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], pp. 119,316,323; [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2008|Macmillan 2008]], p. 830; [[#K2|Kotowicz]], p. 130 n6. |
|||
}} |
|||
{{refn | name=psychopathy| |
|||
{{cite book |
{{cite book |
||
|last=Changeux |first=Jean-Pierre |year=1985 |pages=158{{ndash}}9 |title=Neuronal Man: The Biology of the Mind |
|last=Changeux |first=Jean-Pierre |year=1985 |pages=158{{ndash}}9 |title=Neuronal Man: The Biology of the Mind |
||
|others=Tr. by Laurence Garey |publisher=Pantheon Books |edition=1st American ed. |
|others=Tr. by Laurence Garey |publisher=Pantheon Books |edition=1st American ed. |
||
}} |
}} |
||
* [[# |
* [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], 321. |
||
}} |
|||
{{refn |name=idiot| |
|||
[[#blakeslee|Blakeslee (1994)]]; [[#M|Macmillan (2000)]], p. 39. |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
{{refn|name=lobotomy| |
{{refn | name=lobotomy| |
||
{{cite book |
{{cite book |
||
|last=Carlson |first=N. R. |title=Physiology of Behavior |year=1994 |page=341 |isbn=0-205-07264-X |
|last=Carlson |first=N. R. |title=Physiology of Behavior |year=1994 |page=341 |isbn=0-205-07264-X |
||
}} |
}} |
||
* [[# |
* [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], pp. 246; 252{{ndash}}3 n9,10. |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{refn |name=bennett |{{cite journal |
{{refn | name=bennett |{{cite journal |
||
|last=Bennett |first=W. |date=July{{ndash}}August 1987 |page=24{{ndash}}31 |
|last=Bennett |first=W. |date=July{{ndash}}August 1987 |page=24{{ndash}}31 |
||
|title=Dr. Warren's Possessions |work=Harvard Magazine |volume=89 |number=6 |
|title=Dr. Warren's Possessions |work=Harvard Magazine |volume=89 |number=6 |
||
| Line 856: | Line 629: | ||
}} }} |
}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=bsmi | |
{{refn | name=bsmi | |
||
[[Boston Society for Medical Improvement]] (1849). ''Records'' '''6'''. pp. 103–4. |
[[Boston Society for Medical Improvement]] (1849). ''Records'' '''6'''. pp. 103–4. |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{refn |name=bramwell |{{cite journal |
{{refn | name=bramwell |{{cite journal |
||
|last1=Bramwell |first1=B. |doi=10.1136/bmj.1.1425.835 |
|last1=Bramwell |first1=B. |doi=10.1136/bmj.1.1425.835 |
||
|title=The Process of Compensation and some of its Bearings on Prognosis and Treatment |
|title=The Process of Compensation and some of its Bearings on Prognosis and Treatment |
||
| Line 866: | Line 639: | ||
}} {{open access}} }} |
}} {{open access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=campbell |{{cite journal |last=Campbell |first=H. F. |year=1851 |title=Injuries of the Cranium{{mdashb}}[[Trepanning]] |work=Ohio Medical & Surgical Journal |volume=4 |number=1 |pages=20{{ndash}}24 |postscript= |
{{refn | name=campbell |{{cite journal |last=Campbell |first=H. F. |year=1851 |title=Injuries of the Cranium{{mdashb}}[[Trepanning]] |work=Ohio Medical & Surgical Journal |volume=4 |number=1 |pages=20{{ndash}}24 |postscript= |
||
}} (crediting the ''Southern Medical & Surgical Journal'', unknown date). }} |
}} (crediting the ''Southern Medical & Surgical Journal'', unknown date). }} |
||
{{refn |name=cobb |{{cite journal |
{{refn | name=cobb |{{cite journal |
||
|last=Cobb |first=S. |year=1940 |title=Review of neuropsychiatry for 1940 |
|last=Cobb |first=S. |year=1940 |title=Review of neuropsychiatry for 1940 |
||
|work=Archives of Internal Medicine |volume=66 |pages=1341{{ndash}}54 |
|work=Archives of Internal Medicine |volume=66 |pages=1341{{ndash}}54 |
||
| Line 879: | Line 652: | ||
}} }} |
}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=cooter|{{cite book |
{{refn | name=cooter|{{cite book |
||
|author=Roger Cooter|isbn=978-0-521-22743-8|page=20 |
|author=Roger Cooter|isbn=978-0-521-22743-8|page=20 |
||
|title=The Cultural Meaning of Popular Science: Phrenology and the Organization of Consent in Nineteenth-century Britain |
|title=The Cultural Meaning of Popular Science: Phrenology and the Organization of Consent in Nineteenth-century Britain |
||
| Line 885: | Line 658: | ||
}} }} |
}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=damasioA_somatic|{{cite journal |
{{refn | name=damasioA_somatic|{{cite journal |
||
|title=The Somatic Marker Hypothesis and the Possible Functions of the Prefrontal Cortex [and Discussion] |
|title=The Somatic Marker Hypothesis and the Possible Functions of the Prefrontal Cortex [and Discussion] |
||
|first1=Antonio R. |last1=Damasio |first2=B. J. |last2=Everitt |first3=D. |last3=Bishop |
|first1=Antonio R. |last1=Damasio |first2=B. J. |last2=Everitt |first3=D. |last3=Bishop |
||
| Line 893: | Line 666: | ||
}} {{closed access}} }} |
}} {{closed access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=damasioA_neuropsychology |{{cite book |
{{refn | name=damasioA_neuropsychology |{{cite book |
||
|last1=Damasio |first1=A. R.|authorlink1=Antonio Damasio |last2=Van Hoesen |first2=G. W. |
|last1=Damasio |first1=A. R.|authorlink1=Antonio Damasio |last2=Van Hoesen |first2=G. W. |
||
|title=Emotional disturbances associated with focal lesions of the limbic frontal lobe |
|title=Emotional disturbances associated with focal lesions of the limbic frontal lobe |
||
| Line 901: | Line 674: | ||
}} {{closed access}} }} |
}} {{closed access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=damasioA_descartes |{{cite book |ref=damasio1994 |
{{refn | name=damasioA_descartes |{{cite book |ref=damasio1994 |
||
|last=Damasio |first=Antonio R. |authorlink=Antonio Damasio |publisher=Quill |
|last=Damasio |first=Antonio R. |authorlink=Antonio Damasio |publisher=Quill |
||
|title=Descartes' error: emotion, reason, and the human brain |year=1994 |
|title=Descartes' error: emotion, reason, and the human brain |year=1994 |
||
| Line 907: | Line 680: | ||
}} {{closed access}} }} |
}} {{closed access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=damasioH_return |{{cite journal |ref=damasio_etal1994 |
{{refn | name=damasioH_return |{{cite journal |ref=damasio_etal1994 |
||
|last1=Damasio |first1=H. |last2=Grabowski |first2=T. |last3=Frank |first3=R. |last4=Galaburda |first4=A. M. |last5=Damasio |
|last1=Damasio |first1=H. |last2=Grabowski |first2=T. |last3=Frank |first3=R. |last4=Galaburda |first4=A. M. |last5=Damasio |
||
|first5=A. R. |title=The return of Phineas Gage: Clues about the brain from the skull of a famous patient |
|first5=A. R. |title=The return of Phineas Gage: Clues about the brain from the skull of a famous patient |
||
| Line 913: | Line 686: | ||
}} {{closed access}} }} |
}} {{closed access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=apex| |
{{refn | name=apex| |
||
{{cite book |
{{cite book |
||
|last=Burton |first=Warren |authorlink=Warren Burton (1800{{ndash}}1866) |location=New York |page=217 |
|last=Burton |first=Warren |authorlink=Warren Burton (1800{{ndash}}1866) |location=New York |page=217 |
||
| Line 932: | Line 705: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
{{refn |name=deaths|{{cite newspaper |
{{refn | name=deaths|{{cite newspaper |
||
|work=New Hampshire Statesman|date= July 21, 1860| number=2042 |at=col. D|title=Deaths |
|work=New Hampshire Statesman|date= July 21, 1860| number=2042 |at=col. D|title=Deaths |
||
}} }} |
}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=dupuy |{{cite journal |
{{refn | name=dupuy |{{cite journal |
||
|last=Dupuy |first=Eugene |year=1877 |volume=II |pages=356{{ndash}}8 |
|last=Dupuy |first=Eugene |year=1877 |volume=II |pages=356{{ndash}}8 |
||
|title=A critical review of the prevailing theories concerning the physiology and the pathology of the brain: localisation of functions, and mode of production of symptoms. Part II. |
|title=A critical review of the prevailing theories concerning the physiology and the pathology of the brain: localisation of functions, and mode of production of symptoms. Part II. |
||
| Line 942: | Line 715: | ||
}} {{open access}} }} |
}} {{open access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=eliot |{{cite book |
{{refn | name=eliot |{{cite book |
||
|editor-last=Eliot |editor-first=Samuel Atkins |
|editor-last=Eliot |editor-first=Samuel Atkins |
||
|year=1911 |publisher=Massachusetts Biographical Society <!--book is unpaginated--> |
|year=1911 |publisher=Massachusetts Biographical Society <!--book is unpaginated--> |
||
| Line 949: | Line 722: | ||
}} {{open access}} }} |
}} {{open access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=ferrier1877_9 |{{cite journal |last=Ferrier |first=David |year=1877{{ndash}}79 |
{{refn | name=ferrier1877_9 |{{cite journal |last=Ferrier |first=David |year=1877{{ndash}}79 |
||
|title=Correspondence with Henry Pickering Bowditch |
|title=Correspondence with Henry Pickering Bowditch |
||
|work=Countway Library (Harvard Univ.) Mss.|at=HMS c5.2.}} |
|work=Countway Library (Harvard Univ.) Mss.|at=HMS c5.2.}} |
||
Transcribed in [[# |
Transcribed in [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], pp. 464{{ndash}}5. |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{refn |name=ferrier1878 |{{cite journal |last=Ferrier |first=David |year=1878 |
{{refn | name=ferrier1878 |{{cite journal |last=Ferrier |first=David |year=1878 |
||
|title=The Goulstonian lectures on the Localisation of Cerebral Disease. Lecture I (concluded) |
|title=The Goulstonian lectures on the Localisation of Cerebral Disease. Lecture I (concluded) |
||
|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2220379/?page=3 |
|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2220379/?page=3 |
||
| Line 961: | Line 734: | ||
}} {{open access}} }} |
}} {{open access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=fingers |
{{refn | name=fingers |
||
|[[#L|Lena{{nbsp}}& Macmillan]], p. 9; [[#H|Harlow |
|[[#L|Lena{{nbsp}}& Macmillan]], p. 9; [[#H|Harlow 1868]], pp. 6,19; [[#Bigelow 1850|Bigelow 1850]], p. 16{{ndash}}17; [[#H1|Harlow 1848]], p. 390; [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], p. 86. |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{refn |name=folsom |{{cite news |last=Folsom |first=A. C. |work=Pacific Medical and Surgical Journal |title=Extraordinary Recovery from Extensive Saw-Wound of the Skull |date=May 1869 |pages=550{{ndash}}555 |
{{refn | name=folsom |{{cite news |last=Folsom |first=A. C. |work=Pacific Medical and Surgical Journal |title=Extraordinary Recovery from Extensive Saw-Wound of the Skull |date=May 1869 |pages=550{{ndash}}555 |
||
}} }} |
}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=fowler |{{cite book |
{{refn | name=fowler |{{cite book |
||
|last=Fowler |first=O. S. |year=1838 |page=6 |
|last=Fowler |first=O. S. |year=1838 |page=6 |
||
|title=Synopsis of phrenology: and the phrenological developments: together with the character and talents of ________ as given by ________: with references to those pages of "Phrenology proved, illustrated and applied," in which will be found a full and correct delineation of the intellectual and moral character and manifestations of the above-named individual |
|title=Synopsis of phrenology: and the phrenological developments: together with the character and talents of ________ as given by ________: with references to those pages of "Phrenology proved, illustrated and applied," in which will be found a full and correct delineation of the intellectual and moral character and manifestations of the above-named individual |
||
| Line 974: | Line 747: | ||
}} {{open access}} }} |
}} {{open access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=cv_gage |{{cite book |
{{refn | name=cv_gage |{{cite book |
||
|title=John Gage of Ipswich, Mass. and his descendants: an historical, genealogical and biographical record, as developed from sources explained herein |
|title=John Gage of Ipswich, Mass. and his descendants: an historical, genealogical and biographical record, as developed from sources explained herein |
||
|first=Clyde Van Tassel |last=Gage |location=Worcester, N.Y. |publisher=C.V. Gage |year=1964 |
|first=Clyde Van Tassel |last=Gage |location=Worcester, N.Y. |publisher=C.V. Gage |year=1964 |
||
}} }} |
}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=gall_sizer |{{cite book |
{{refn | name=gall_sizer |{{cite book |
||
|last=Gall |first=Franz Joseph |series=The phrenological library. |editor-first=Nahum |editor-last=Capen |
|last=Gall |first=Franz Joseph |series=The phrenological library. |editor-first=Nahum |editor-last=Capen |
||
|title=On the functions of the brain and of each of its parts: with observations on the possibility of determining the instincts, propensities, and talents, or the moral and intellectual dispositions of men and animals, by the configuration of the brain and head<!--need pg#s--> |
|title=On the functions of the brain and of each of its parts: with observations on the possibility of determining the instincts, propensities, and talents, or the moral and intellectual dispositions of men and animals, by the configuration of the brain and head<!--need pg#s--> |
||
| Line 992: | Line 765: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
{{refn |name=griggs |{{cite journal<!--<<get full cite, pg#s--> |
{{refn | name=griggs |{{cite journal<!--<<get full cite, pg#s--> |
||
|title=Coverage of the Phineas Gage Story in Introductory Psychology Textbooks: Was Gage No Longer Gage? |
|title=Coverage of the Phineas Gage Story in Introductory Psychology Textbooks: Was Gage No Longer Gage? |
||
|first=Richard A. |last=Griggs |work=Teaching of Psychology|year=2015|doi=10.1177/0098628315587614|volume=42|pages=195–202 |
|first=Richard A. |last=Griggs |work=Teaching of Psychology|year=2015|doi=10.1177/0098628315587614|volume=42|pages=195–202 |
||
}} }} |
}} }} |
||
{{refn|name=hamilton |{{cite journal |
{{refn<font color="#777777"> </font> |name=hamilton |{{cite journal |
||
|last=Hamilton |first=J. W. |year=1860 |volume=13 |page=174 |work=Ohio Medical and Surgical Journal |
|last=Hamilton |first=J. W. |year=1860 |volume=13 |page=174 |work=Ohio Medical and Surgical Journal |
||
|title=Editorial and Miscellaneous. The Man Through Whose Head an Iron Rod Passed Is Still Living |
|title=Editorial and Miscellaneous. The Man Through Whose Head an Iron Rod Passed Is Still Living |
||
}} Reprinted: {{cite book|editor=Samuel Worcester Butler|title=Medical and Surgical Reporter|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=lkWgAAAAMAAJ&pg=PA183|volume=5|date=November 17, 1860|publisher=Crissly & Markley|location=Philadelphia|page=183|number=7|editor2=D G. Brinton}} {{open access}} }} |
}} Reprinted: {{cite book|editor=Samuel Worcester Butler|title=Medical and Surgical Reporter|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=lkWgAAAAMAAJ&pg=PA183|volume=5|date=November 17, 1860|publisher=Crissly & Markley|location=Philadelphia|page=183|number=7|editor2=D G. Brinton}} {{open access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=heart |{{cite book |
{{refn | name=heart |{{cite book |
||
|author=Rutland Railroad Company |title=Heart of the Green mountains. Souvenir edition. Season of 1897 |
|author=Rutland Railroad Company |title=Heart of the Green mountains. Souvenir edition. Season of 1897 |
||
|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=ZC0TAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA41 |
|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=ZC0TAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA41 |
||
| Line 1,008: | Line 781: | ||
}} {{open access}} }} |
}} {{open access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=hooper |{{cite book |
{{refn | name=hooper |{{cite book |
||
|last=Hooper |first=Robert |authorlink=Robert Hooper (physician)|location=London |year=1809 |page=107 |
|last=Hooper |first=Robert |authorlink=Robert Hooper (physician)|location=London |year=1809 |page=107 |
||
|title=The surgeon's vade-mecum: containing the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of surgical diseases{{nbsp}}... |
|title=The surgeon's vade-mecum: containing the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of surgical diseases{{nbsp}}... |
||
| Line 1,016: | Line 789: | ||
}} {{open access}} }} |
}} {{open access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=hockenbury1997 |{{cite book |
{{refn | name=hockenbury1997 |{{cite book |
||
|last1=Hockenbury |first1=Don H. |last2=Hockenbury |first2=Sandra |title=Psychology|isbn=978-1-57259-396-1 |
|last1=Hockenbury |first1=Don H. |last2=Hockenbury |first2=Sandra |title=Psychology|isbn=978-1-57259-396-1 |
||
|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=I15rPQAACAAJ |date=1997 |publisher=Worth Publishers |
|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=I15rPQAACAAJ |date=1997 |publisher=Worth Publishers |
||
}} {{closed access}} }} |
}} {{closed access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name= |
{{refn | name=incredible |{{cite news |
||
|date=March 29, 1849 |work=National Eagle |at=p. 2, col. 2 |place=Claremont, New Hampshire |title=Incredible, But True Every Word }} Reprinted: ''True Democrat and Granite State Whig'' (Lebanon, New Hampshire), April 6, 1849, p.{{nbsp}}1, col.{{nbsp}}7. Transcribed in [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], pp.40{{ndash}}1. |
|||
*[[#H1|Harlow 1848]], p. 389; [[#Bigelow 1850|Bigelow 1850]], p. 13; [[#H|Harlow 1868]], p. 4. |
|||
}} |
|||
{{refn | name=jackson1849 | |
|||
Jackson, J.B.S. (1849). ''Medical Cases'' '''4''''. Case 1777. Countway Library (Harvard Univ.) Mss., HMSb72.4.<!--Get pg no & check case no--><!--chk final fmt incl detailed punct against Countway catalog cite--> |
Jackson, J.B.S. (1849). ''Medical Cases'' '''4''''. Case 1777. Countway Library (Harvard Univ.) Mss., HMSb72.4.<!--Get pg no & check case no--><!--chk final fmt incl detailed punct against Countway catalog cite--> |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{refn |name=jackson1870 |{{cite journal |
{{refn | name=jackson1870 |{{cite journal |
||
|last=Jackson |first=J. B. S. |year=1870 |at=Frontis. and Nos. 949{{ndash}}51, 3106 |
|last=Jackson |first=J. B. S. |year=1870 |at=Frontis. and Nos. 949{{ndash}}51, 3106 |
||
|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=F8UZAAAAIAAJ&pg=PA145 |title=A Descriptive Catalog of the Warren Anatomical Museum |
|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=F8UZAAAAIAAJ&pg=PA145 |title=A Descriptive Catalog of the Warren Anatomical Museum |
||
}} {{open access}} }} |
}} {{open access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=jarrett |{{cite web |
{{refn | name=jarrett |{{cite web |
||
|url=http://digest.bps.org.uk/2012/05/neuroscience-still-haunted-by-phineas.html |
|url=http://digest.bps.org.uk/2012/05/neuroscience-still-haunted-by-phineas.html |
||
|first=Christian |last= Jarrett |title=Neuroscience still haunted by Phineas Gage |
|first=Christian |last= Jarrett |title=Neuroscience still haunted by Phineas Gage |
||
| Line 1,036: | Line 814: | ||
}} {{open access}} }} |
}} {{open access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=jewett |{{cite journal |
{{refn | name=jewett |{{cite journal |
||
|last=Jewett |first=M. |title=Extraordinary Recovery after Severe Injury to the Head |
|last=Jewett |first=M. |title=Extraordinary Recovery after Severe Injury to the Head |
||
|work=Western Journal of Medicine |volume=43 |pages=241 |year=1868 |
|work=Western Journal of Medicine |volume=43 |pages=241 |year=1868 |
||
| Line 1,042: | Line 820: | ||
}} {{open access}} }} |
}} {{open access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name= larner |{{cite journal |
{{refn | name= larner |{{cite journal |
||
|url=http://www.acnr.co.uk/pdfs/volume2issue3/v2i3history.pdf |volume=2 |number=3 |
|url=http://www.acnr.co.uk/pdfs/volume2issue3/v2i3history.pdf |volume=2 |number=3 |
||
|date=July{{ndash}}August 2002 |page=26 |title=Phineas Gage and the beginnings of neuropsychology |
|date=July{{ndash}}August 2002 |page=26 |title=Phineas Gage and the beginnings of neuropsychology |
||
| Line 1,049: | Line 827: | ||
}} {{open access}} }} |
}} {{open access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=laurel|{{cite news |
{{refn | name=laurel|{{cite news |
||
|work=Daily Alta California|date=April 12, 1867|title=Laurel Hill Cemetery |
|work=Daily Alta California|date=April 12, 1867|title=Laurel Hill Cemetery |
||
}} }} |
}} }} |
||
{{refn|name=mazzoni |{{cite book |
{{refn | name=mazzoni |{{cite book |
||
|last1=Mazzoni|first1=Giuliana|last2=Nelson|first2=Thomas O. |
|last1=Mazzoni|first1=Giuliana|last2=Nelson|first2=Thomas O. |
||
|title=Metacognition and Cognitive Neuropsychology: Monitoring and Control Processes |
|title=Metacognition and Cognitive Neuropsychology: Monitoring and Control Processes |
||
| Line 1,060: | Line 838: | ||
}} {{open access}} }} |
}} {{open access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=merwin |{{cite book |
{{refn | name=merwin |{{cite book |
||
|title=Three Years in {{sic|Chili|hide=y}} |last=Merwin |first=Mrs. George B. |
|title=Three Years in {{sic|Chili|hide=y}} |last=Merwin |first=Mrs. George B. |
||
|year=1863<!--check earlier ed-->|location=New York |publisher=Follett, Foster and Company |
|year=1863<!--check earlier ed-->|location=New York |publisher=Follett, Foster and Company |
||
| Line 1,066: | Line 844: | ||
}} {{open access}} }} |
}} {{open access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=memoir_hjb |{{cite book |
{{refn | name=memoir_hjb |{{cite book |
||
|title=A Memoir of Henry Jacob Bigelow|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=hmISAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA119|year=1894|publisher=Little, Brown|location=Boston |
|title=A Memoir of Henry Jacob Bigelow|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=hmISAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA119|year=1894|publisher=Little, Brown|location=Boston |
||
}} {{open access}} }} |
}} {{open access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=mitchell |{{cite journal |
{{refn | name=mitchell |{{cite journal |
||
|last1=Mitchell|first1= B.D.|first2=B.D. |last2=Fox|first3= W.E.|last3= Humphries|first4= A. |last4=Jalali|first5=S. |last5=Gopinath |
|last1=Mitchell|first1= B.D.|first2=B.D. |last2=Fox|first3= W.E.|last3= Humphries|first4= A. |last4=Jalali|first5=S. |last5=Gopinath |
||
|title=Phineas Gage revisited: Modern management of large-calibre penetrating brain injury |
|title=Phineas Gage revisited: Modern management of large-calibre penetrating brain injury |
||
| Line 1,076: | Line 854: | ||
}} {{closed access}} }} |
}} {{closed access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=northcarolina |{{cite journal |
{{refn | name=northcarolina |{{cite journal |
||
|editor-last=Wood |editor-first=Thomas F. |volume=1|number=1 |location=Wilmington |
|editor-last=Wood |editor-first=Thomas F. |volume=1|number=1 |location=Wilmington |
||
|work=North Carolina Medical Journal| date=July 1882 |page=60{{ndash}}2 |
|work=North Carolina Medical Journal| date=July 1882 |page=60{{ndash}}2 |
||
| Line 1,083: | Line 861: | ||
}} }} |
}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=northstar |{{cite news |ref=anonymous_northstar |
{{refn | name=northstar |{{cite news |ref=anonymous_northstar |
||
|author=Anonymous |work=North Star |location=[[Danville, Vermont]] |date=November 6, 1848 |
|author=Anonymous |work=North Star |location=[[Danville, Vermont]] |date=November 6, 1848 |
||
|title=Alive from the Dead, Almost |at=p. 1, col. 2 |
|title=Alive from the Dead, Almost |at=p. 1, col. 2 |
||
}} Transcribed in [[# |
}} Transcribed in [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], pp. 39{{ndash}}40}} |
||
{{refn |name=ordia|{{cite journal |
{{refn | name=ordia|{{cite journal |
||
|last=Ordia |first=J. I. |year=1989 |
|last=Ordia |first=J. I. |year=1989 |
||
|title=Neurologic function seven years after crowbar impalement of the brain |
|title=Neurologic function seven years after crowbar impalement of the brain |
||
| Line 1,094: | Line 872: | ||
}} }} |
}} }} |
||
{{refn|name=pancoast|{{cite book |
{{refn| name=pancoast|{{cite book |
||
|last=Pancoast|first=Joseph|edition=3rd|year=1852|publisher=A. Hart|location=Philadelphia|page=106 |
|last=Pancoast|first=Joseph|edition=3rd|year=1852|publisher=A. Hart|location=Philadelphia|page=106 |
||
|title=A Treatise on Operative Surgery: Comprising a Description of the Various Processes of the Art, Including All the New Operations; Exhibiting the State of Surgical Science in Its Present Advanced Condition |
|title=A Treatise on Operative Surgery: Comprising a Description of the Various Processes of the Art, Including All the New Operations; Exhibiting the State of Surgical Science in Its Present Advanced Condition |
||
| Line 1,100: | Line 878: | ||
}} {{open access}} }} |
}} {{open access}} }} |
||
{{refn|name=pott|{{cite book |
{{refn | name=pott|{{cite book |
||
|author=[[Percivall Pott|Pott, Percivall]] |
|author=[[Percivall Pott|Pott, Percivall]] |
||
|title=The chirurgical works : of Percivall Pott, F.R.S. Surgeon to St. Bartholomew’s Hospital. A new edition, with his last corrections. To which are added a short account of the life of the author{{nbsp}}... |
|title=The chirurgical works : of Percivall Pott, F.R.S. Surgeon to St. Bartholomew’s Hospital. A new edition, with his last corrections. To which are added a short account of the life of the author{{nbsp}}... |
||
| Line 1,107: | Line 885: | ||
}} {{open access}} }} |
}} {{open access}} }} |
||
{{refn|name=proctor|{{cite |
{{refn | name=proctor|{{cite |
||
|url=http://www.sfgenealogy.com/sf/history/hcmcpr.htm|year=1950 |
|url=http://www.sfgenealogy.com/sf/history/hcmcpr.htm|year=1950 |
||
|title=Location, regulation, and removal of cemeteries in the City and County of San Francisco |
|title=Location, regulation, and removal of cemeteries in the City and County of San Francisco |
||
| Line 1,123: | Line 901: | ||
}} {{closed access}} }} |
}} {{closed access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=smithS_carey |{{cite news |
{{refn | name=smithS_carey |{{cite news |
||
|url=http://www.boston.com/news/local/massachusetts/articles/2009/07/22/newly_discovered_image_offers_fresh_insights_about_1848_medical_miracle/ |
|url=http://www.boston.com/news/local/massachusetts/articles/2009/07/22/newly_discovered_image_offers_fresh_insights_about_1848_medical_miracle/ |
||
|last=Smith |first=Stephen |work=Boston Globe |date=July 22, 2009 <!--get pg#--> |
|last=Smith |first=Stephen |work=Boston Globe |date=July 22, 2009 <!--get pg#--> |
||
| Line 1,134: | Line 912: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
{{refn |name=smithW |{{cite news |
{{refn | name=smithW |{{cite news |
||
|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=jcwDAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA54 |title=Lesions of the Cerebral Hemispheres |year=1886 |
|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=jcwDAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA54 |title=Lesions of the Cerebral Hemispheres |year=1886 |
||
|work=Transactions of the Vermont Medical Society for the Year 1885 |pages=46{{ndash}}58 |last=Smith |first=William T. |
|work=Transactions of the Vermont Medical Society for the Year 1885 |pages=46{{ndash}}58 |last=Smith |first=William T. |
||
}} {{open access}} }} |
}} {{open access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=stuss_hockenbury2008 |{{cite journal |
{{refn | name=stuss_hockenbury2008 |{{cite journal |
||
|last1=Stuss |first1=D. T. |last2=Gow |first2=C. A. |last3=Hetherington |first3=C. R. |doi=10.1037/0022-006X.60.3.349 |
|last1=Stuss |first1=D. T. |last2=Gow |first2=C. A. |last3=Hetherington |first3=C. R. |doi=10.1037/0022-006X.60.3.349 |
||
|title=<!--<<thinsp should be used to separate ' at start of title from " automatically added by template--> |
|title=<!--<<thinsp should be used to separate ' at start of title from " automatically added by template--> |
||
| Line 1,151: | Line 929: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
{{refn |name=sutton |{{cite journal |
{{refn | name=sutton |{{cite journal |
||
|last=Sutton |first=W. L. |title=A Centre<!--<<do not Americanise!--> Shot |
|last=Sutton |first=W. L. |title=A Centre<!--<<do not Americanise!--> Shot |
||
|work=Boston Medical & Surgical Journal |volume=3 |pages=151{{ndash}}2 |year=1850 |
|work=Boston Medical & Surgical Journal |volume=3 |pages=151{{ndash}}2 |year=1850 |
||
| Line 1,157: | Line 935: | ||
}} {{open access}} }} |
}} {{open access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name=vanderkloot|{{cite book |
{{refn | name=vanderkloot|{{cite book |
||
|author=William G. Van der Kloot|title=Readings in Behavior|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=Bsw12aCjmhYC&pg=PA289|year=1974|publisher=Ardent Media|isbn=978-0-03-084077-7|page=289 |
|author=William G. Van der Kloot|title=Readings in Behavior|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=Bsw12aCjmhYC&pg=PA289|year=1974|publisher=Ardent Media|isbn=978-0-03-084077-7|page=289 |
||
}} {{open access}} }} |
}} {{open access}} }} |
||
{{refn |name= |
{{refn | name=yakovlev |{{cite journal |
||
| [[#M|Macmillan (2000)]], pp. 119,316,323; [[#M1|Macmillan (2008)]], p. 830; [[#K2|Kotowicz]], p. 130 n6. |
|||
}} |
|||
{{refn |name=yakovlev |{{cite journal |
|||
|title=The "Crowbar Skull" and Mementoes of "Phrenological Hours" |
|title=The "Crowbar Skull" and Mementoes of "Phrenological Hours" |
||
|pages=19{{ndash}}24 |work=Harvard Medical Alumni Bulletin |
|pages=19{{ndash}}24 |work=Harvard Medical Alumni Bulletin |
||
| Line 1,173: | Line 947: | ||
}}<!--<<end reflist--> |
}}<!--<<end reflist--> |
||
==Sources== |
|||
;For general readers |
|||
{{refbegin|30em}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |ref=CITEREFHarlow 1868 |
|||
|last=Harlow |first=John Martyn |year=1868 |
|||
|title=Recovery from the Passage of an Iron Bar through the Head |
|||
|work=Publications of the Massachusetts Medical Society |volume=2 |
|||
|pages=327{{ndash}}47<!--something somewhere says n3 of v2--> |
|||
|url=https://www.countway.harvard.edu/menuNavigation/chom/warren/exhibits/HarlowBMSJ1860.pdf |
|||
}} Reprinted as ''Recovery from the Passage of an Iron Bar through the Head'' (David Clapp{{nbsp}}& Son, 1869). 22 pages. {{open access}} |
|||
*{{cite news |ref=CITEREFK |
|||
|title=Phineas Gage, Neuroscience's Most Famous Patient |work=Slate |date=May 6, 2014 |last=Kean |first=Sam |
|||
|url=http://www.slate.com/articles/health_and_science/science/2014/05/phineas_gage_neuroscience_case_true_story_of_famous_frontal_lobe_patient.html |
|||
}} {{open access}} |
|||
*{{cite book |ref=CITEREFMacmillan 2000 |
|||
|last=Macmillan |first=Malcolm B. |year=2000 |
|||
|title=An Odd Kind of Fame: Stories of Phineas Gage |publisher=[[MIT Press]] |
|||
|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=Qx4fMsTqGFYC |
|||
|id=ISBN 0-262-13363-6 (hbk, 2000) ISBN 0-262-63259-4 (pbk, 2002) |
|||
}} {{open access}} {{bullet}}''See also'' [http://www.uakron.edu/gage/book.dot "''An Odd Kind of Fame'' §Corrections"]. {{open access}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |author-mask=2 |ref=CITEREFMacmillan 2008 |
|||
|last=Macmillan |first=Malcolm B. |date=September 2008 |publisher=[[British Psychological Society]] |
|||
|url=http://thepsychologist.bps.org.uk/volume-21/edition-9/phineas-gage-unravelling-myth |
|||
|title=Phineas Gage{{mdashb}}Unravelling the myth |work=The Psychologist |volume=21 |number=9 |
|||
|pages=828{{ndash}}31.<!--Possible problem re pg#s, online vs paper?--check all cites to this--> |
|||
}} {{open access}} |
|||
*{{cite web |author-mask=2 |ref=CITEREFM2 |
|||
|url=http://brightbytes.com/phineasgage/more.html |last=Macmillan |first=Malcolm B. |date=July 2009 |
|||
|title=More About Phineas Gage, Especially After the Accident |accessdate=July 27, 2013 |
|||
}} {{open access}} |
|||
*{{cite web |author-mask=2 |ref=CITEREFMacmillan 2012 |
|||
|last=Macmillan |first=Malcolm B. |year=2012<!--latest changes--> |url=http://www.uakron.edu/gage/index.dot |
|||
|title=The Phineas Gage Information Page |publisher=The University of Akron |accessdate=July 22, 2013 }} Includes: |
|||
::A. {{cite web |url=http://www.uakron.edu/gage/sites-and-plaque.dot |title=Phineas Gage Sites in Cavendish}} {{open access}} |
|||
::B. {{cite web |url=http://www.uakron.edu/gage/questions.dot |title=Phineas Gage: Unanswered questions}} {{open access}} |
|||
::C. {{cite web |url=http://www.uakron.edu/gage/story.dot |title=Phineas Gage's Story}} {{open access}} |
|||
::D. {{cite web |url=http://www.uakron.edu/gage/book.dot |title=Corrections to ''An Odd Kind of Fame''}} {{open access}} |
|||
::E. {{cite web |url=http://www.uakron.edu/gage/adaptation.dot |title=Phineas Gage: Psychosocial Adaptation}} {{open access}} |
|||
::F. {{cite web |url=http://www.uakron.edu/gage/lobotomy.dot |title=Phineas Gage and Frontal Lobotomies}} {{open access}} |
|||
*{{cite interview |ref=CITEREFM4 |
|||
|last1=Macmillan |first1=Malcolm B. |date=March 6, 2011 |last2=Aggleton |first2=John |
|||
|interviewer=Claudia Hammond; Dave Lee |type=Audio interview |program=Health Check |callsign=BBC World Service |
|||
|title=Phineas Gage: The man with a hole in his head |url=http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/health-12649555 |
|||
}} {{open access}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |ref=CITEREFT |
|||
|last=Twomey |first=S. |date=January 2010 |volume=40 |issue=10 |journal=[[Smithsonian Magazine|Smithsonian]] |
|||
|url=http://www.smithsonianmag.com/history-archaeology/78437017.html |title=Finding Phineas |pages=8{{ndash}}10 |
|||
}} {{open access}} |
|||
{{refend}} |
|||
;For young readers |
|||
{{refbegin}} |
|||
*{{cite book |ref=CITEREFF |
|||
|title=Phineas Gage: A Gruesome but True Story About Brain Science |year=2002 |isbn=0-618-05252-6 |
|||
|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=XXxtmdcj_04C |last=Fleischman |first=J. |
|||
}} {{open access}} |
|||
*{{refend}} |
|||
;For researchers and specialists |
|||
{{refbegin|30em}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |ref=CITEREFBarker 1995 |
|||
|last=Barker |first=F. G. II |year=1995 |
|||
|pmid=7897537 |url=http://mysois.uwm.edu/omeka/archive/files/b7cf786e3d97d4cf63ac3b7d14e1f88e.pdf |
|||
|title=Phineas among the phrenologists: the American crowbar case and nineteenth-century theories of cerebral localization |
|||
|work=Journal of Neurosurgery |volume=82 |pages=672{{ndash}}82 |doi=10.3171/jns.1995.82.4.0672 |issue=4 |
|||
}} {{open access}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |ref=CITEREFBigelow 1850 |
|||
|last=Bigelow |first=Henry Jacob |work=[[American Journal of the Medical Sciences]] |
|||
|title=Dr. Harlow's Case of Recovery from the Passage of an Iron Bar through the Head |
|||
|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=pgMHAAAAcAAJ&pg=PA12-IA2 <!--https://archive.org/stream/orthopedicsurge00bige#page/172/mode/2up may have(?) ocr usable at Wikisource--> |
|||
|date=July 1850<!--<<July is per Harlow 1868--> |volume=20 |pages=13{{ndash}}22 |
|||
}} {{open access}} |
|||
*{{cite letter |author-mask=2 |ref=CITEREFB2 |
|||
|first=Henry Jacob |last=Bigelow |recipient=M. Jewett |type=manuscript |
|||
|subject=Your favor of April 29th is before me |date=May 12, 1868 |
|||
}} Records of the Warren Anatomical Museum, 1828{{ndash}}1892 (inclusive) (AA 192.5), Harvard Medical Library in the Francis A. Countway Library of Medicine. |
|||
*{{cite book |ref=CITEREFF1 |
|||
|last=Fuster |first=Joaquin M. |title=The prefrontal cortex |
|||
|publisher=Elsevier/Academic Press |year=2008 |page=172 |isbn=0-12-373644-7 |
|||
|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=zuZlvNICdhUC&pg=PA172 |
|||
}} {{closed access}} |
|||
*{{cite book |ref=CITEREFG |
|||
|chapter=The Structured Event Complex and the Human Prefrontal Cortex |doi=10.1093/acprof:oso/9780195134971.003.0019 |
|||
|title=Principles of Frontal Lobe Function |editors=Stuss, D. T.; Knight, R. T. |
|||
|pages=292{{ndash}}310 |year=2002 |isbn=978-0-195-13497-1 |last1=Grafman |first1=J. |
|||
}} {{closed access}} |
|||
{{anchor|CITEREFG1}} |
|||
*Gage, P.P. (185[4?]). "Please give my iron bar to the bearer" (Note to unknown recipient). Records of the Warren Anatomical Museum, 1828{{ndash}}1892 (inclusive) (AA 192.5), Harvard Medical Library in the Francis A. Countway Library of Medicine, Box 1. |
|||
*{{cite journal |ref=CITEREFH1 |
|||
|last=Harlow |first=John Martyn |date=December 13, 1848 |volume=39 |title=Passage of an Iron Rod Through the Head |url=https://www.countway.harvard.edu/menuNavigation/chom/warren/exhibits/HarlowBMSJ1848.pdf |
|||
|work=[[Boston Medical and Surgical Journal|Boston Medical & Surgical Journal]] |number=20 |pages=389{{ndash}}93 |doi=10.1056/nejm184812130392001 |
|||
}} {{open access}} ([[s:Passage of an Iron Rod Through the Head|Transcription]].) |
|||
*{{cite journal |author-mask=2 |ref=CITEREFH2 |
|||
|last=Harlow |first=John Martyn |date=January 3, 1849 |title=Medical Miscellany (letter) |
|||
|work=[[Boston Medical and Surgical Journal|Boston Medical & Surgical Journal]] |volume=39 |page=507 |
|||
}} Reproduced in [[#CITEREFMacmillan 2000|Macmillan 2000]], p. 389. |
|||
*{{cite journal |ref=CITEREFK1 |
|||
|url=http://ist-socrates.berkeley.edu/~kihlstrm/SocialNeuroscience07.htm |last=Kihlstrom |
|||
|first=J. F. |year=2010 |title=Social neuroscience: The footprints of Phineas Gage |
|||
|journal=Social Cognition |volume=28 |pages=757{{ndash}}82 |doi=10.1521/soco.2010.28.6.757 |issue=6 |
|||
}} {{open access}} |
|||
*{{cite news |ref=CITEREFL |
|||
|last1=Lena |first1=M. L. |last2=Macmillan |first2=Malcolm B. |
|||
|date=March 2010 |url=http://www.smithsonianmag.com/arts-culture/Letters-201003.html#article-text |
|||
|title=Picturing Phineas Gage (Invited comment) |page=4<!-- is it volume=10 |issue=4? --> |
|||
|work=[[Smithsonian Magazine|Smithsonian]] |
|||
}} {{open access}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |ref=CITEREFK2 |
|||
|last1=Kotowicz |first1=Z. |doi=10.1177/0952695106075178 |pages=115{{ndash}}31 |year=2007 |
|||
|title=The strange case of Phineas Gage |journal=History of the Human Sciences |volume=20 |issue=1 |
|||
}} {{closed access}} |
|||
*{{cite news |ref=CITEREFM5 |
|||
|last=Macmillan |first=Malcolm B. |year=1996 |pages=243{{ndash}}62 |title=Phineas Gage: A Case for All Reasons |
|||
|location=London |publisher=Erlbaum |work=Classic Cases in Neuropsychology |
|||
|editor1-last=Code |editor1-first=C. |editor2-last=Wallesch |editor2-first=C. W. |
|||
|editor3-last=Lecours |editor3-first=A. R. |editor4-last=Joanette |editor4-first=U. |displayeditors=4 |
|||
}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |author-mask=2 |ref=CITEREFM6 |
|||
|last1=Macmillan |first1=Malcolm B. |
|||
|title=Restoring Phineas Gage: A 150th Retrospective |doi=10.1076/0964-704X(200004)9:1;1-2;FT046 |
|||
|journal=Journal of the History of the Neurosciences |volume=9 |issue=1 |
|||
|pages=46{{ndash}}66 |year=2000 |pmid=11232349 }} {{closed access}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |author-mask=2 |ref=CITEREFMacmillan 2001 |
|||
|last1=Macmillan |first1=Malcolm B. |
|||
|title=John Martyn Harlow: Obscure Country Physician? |doi=10.1076/jhin.10.2.149.7254 |year=2001 |
|||
|journal=Journal of the History of the Neurosciences |volume=10 |issue=2 |pages=149{{ndash}}162 |pmid=11512426 |
|||
}} {{closed access}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |author-mask=2 |ref=CITEREFM8 |
|||
|url=https://elearning.unipd.it/scuolapsicologia/pluginfile.php/13618/mod_folder/content/0/Rehabilitating%20Phineas%20Gage.pdf |
|||
|last1=Macmillan |first1=Malcolm B. |last2=Lena |first2=M. L. |doi=10.1080/09602011003760527 |
|||
|title=Rehabilitating Phineas Gage |journal=Neuropsychological Rehabilitation |volume=20 |issue=5 |
|||
|pages=641{{ndash}}658 |year=2010 |pmid=20480430 |
|||
}} {{open access}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |ref=CITEREFRatiu 2004 |
|||
|last1=Ratiu |first1=P. |last2=Talos |first2=I. F. |last3=Haker |first3=S. |last4=Lieberman |pages=637{{ndash}}643 |
|||
|first4=D. |last5=Everett |first5=P. |title=The Tale of Phineas Gage, Digitally Remastered |pmid=15165371 |
|||
|doi=10.1089/089771504774129964 |journal=Journal of Neurotrauma |volume=21 |issue=5 |year=2004 |
|||
}} {{closed access}}<!--confusing ratiu cites and page #s need checking--> |
|||
*{{cite journal |ref=CITEREFR1 |
|||
|last1=Ratiu |first1=P. |last2=Talos |first2=I. F. |doi=10.1056/NEJMicm031024 |pmid=15575047 |
|||
|title=The Tale of Phineas Gage, Digitally Remastered |journal=New England Journal of Medicine |
|||
|volume=351 |issue=23 |pages=e21 |url=http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMicm031024 |year=2004 |
|||
}} {{open access}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |ref=CITEREFT1 |
|||
|last1=Tyler |first1=K.L. |last2=Tyler |first2=H.R. |year=1982 |volume=32 |page=A191 |
|||
|title=A 'Yankee Invention': the celebrated American crowbar case |work=Neurology |
|||
}} {{closed access}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |ref=CITEREFV |
|||
|last1=Van Horn |first1=J. D. |last2=Irimia |first2=A. |last3=Torgerson |first3=C. M. |
|||
|last4=Chambers |first4=M. C. |last5=Kikinis |first5=R. |last6=Toga |first6=A. W. |
|||
|title=Mapping Connectivity Damage in the Case of Phineas Gage |doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0037454 |
|||
|journal=PLoS ONE |volume=7 |issue=5 |pages=e37454 |year=2012 |pmid=22616011 |pmc=3353935 |
|||
}} {{open access}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |ref=CITEREFW |
|||
|last=Wilgus |first=B. & J. |year=2009 |title=Face to Face with Phineas Gage |
|||
|url=http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/09647040903018402#preview |pmid=20183215 |
|||
|journal=Journal of the History of the Neurosciences |volume=18 |issue=3 |pages=340{{ndash}}5 |doi=10.1080/09647040903018402 |
|||
}} {{closed access}} |
|||
*{{cite journal |author-mask=2 |ref=CITEREFW1 |
|||
|last=Wilgus |first=B. & J. |date=July{{ndash}}September 2009 |title=Phineas Gage{{snd}}Hiding in Plain Sight <!--derre.o/soc'y--> |
|||
|journal=The Daguerreian Society Newsletter |volume=21 |issue=3 |pages=6{{ndash}}9 |
|||
}} |
|||
*{{cite web |author-mask=2 |ref=CITEREFW2 |
|||
|last=Wilgus |first=B. & J. |year=2009 |title=Meet Phineas Gage |
|||
|url=http://www.brightbytes.com/phineasgage/index.html |accessdate=October 18, 2014 |
|||
}} {{open access}} |
|||
*{{cite web |author-mask=2 |ref=CITEREFW3 |
|||
|last=Wilgus |first=B. & J. |year=2010 |title=A New Image of Phineas Gage |
|||
|url=http://www.brightbytes.com/phineasgage/new_image.html |accessdate=March 10, 2010 |
|||
}} {{open access}} |
|||
{{refend}} |
|||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
| Line 1,187: | Line 1,166: | ||
| DATE OF BIRTH = July 9, 1823 |
| DATE OF BIRTH = July 9, 1823 |
||
| PLACE OF BIRTH = [[Grafton County, New Hampshire|Grafton Co.]], N.H. |
| PLACE OF BIRTH = [[Grafton County, New Hampshire|Grafton Co.]], N.H. |
||
| DATE OF DEATH = May 21, 1860<!--1860 is correct despite Harlow |
| DATE OF DEATH = May 21, 1860<!--1860 is correct despite Harlow 1868 reporting 1861; see Macmillan 2000 p108 --> |
||
| PLACE OF DEATH = In or near San Francisco |
| PLACE OF DEATH = In or near San Francisco |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Gage, Phineas}} |
{{DEFAULTSORT:Gage, Phineas}} |
||
[[Category:1823 births]] |
|||
[[Category:1860 deaths]] |
|||
[[Category:History of neuroscience]] |
|||
[[Category:American people in rail transportation]] |
|||
[[Category:American expatriates in Chile]] |
|||
[[Category:People from Grafton County, New Hampshire]] |
|||
[[Category:People from Windsor County, Vermont]] |
|||
[[Category:Burials in California]] |
|||
[[Category:People with brain injuries]] |
|||
Revision as of 23:41, 1 September 2015
Phineas P. Gage | |
|---|---|
 The first identified (2009) portrait of Gage, shown with his "constant companion during the remainder of his life"—his inscribed tamping iron.[a] | |
| Born | July 9, 1823 (date uncertain) |
| Died | May 21, 1860 (aged 36) In or near San Francisco |
| Cause of death | Status epilepticus |
| Resting place |
|
| Occupations |
|
| Known for | Personality change after brain injury |
| Spouse | None |
| Children | None[1]: 39, 319, 327 [2] |
Phineas P. Gage (1823 – May 21, 1860) was an American railroad construction foreman remembered for his improbable[3]: 19 survival of an accident in which a large iron rod was driven completely through his head, destroying much of his brain's left frontal lobe, and for that injury's reported effects on his personality and behavior over the remaining twelve years of his life—effects so profound (for a time at least) that friends saw him as "no longer Gage".

Long known as "the American Crowbar Case"—once termed "the case which more than all others is calculated to excite our wonder, impair the value of prognosis, and even to subvert our physiological doctrines" [5]—Phineas Gage influenced nineteenth-century discussion about the mind and brain, particularly debate on cerebral localization,[1]: ch7-9 [6] and was perhaps the first case to suggest that damage to specific parts of the brain might induce specific personality changes.[1]: 1 [7]: C
Gage is a fixture in the curricula of neurology, psychology, and related disciplines ,[8][9]: 149 "a living part of the medical folklore" [10]: 637 frequently mentioned in books and scientific papers;[1]: ch14 he even has a minor place in popular culture.[11] Despite this celebrity, the body of established fact about Gage and what he was like (before or after his injury) is small,[c] which has allowed "the fitting of almost any theory [desired] to the small number of facts we have" [1]: 290 —Gage acting as a "Rorschach inkblot" [12] in which proponents of various conflicting theories of the brain were able to find support for their views. Historically, published accounts (including scientific ones) have almost always severely distorted and exaggerated Gage's behavioral changes, frequently contradicting the known facts.
A report of Gage's physical and mental condition shortly before his death implies that his most serious mental changes were temporary, so that in later life, he was far more functional, and socially far better adapted, than in the years immediately following his accident. A social recovery hypothesis suggests that his employment as a stagecoach driver in Chile provided daily structure allowing him to regain lost social and personal skills.
Life
Background

Gage was the first of five children born to Jesse Eaton Gage and Hannah Trussell (Swetland) Gage, of Grafton County, New Hampshire.[b] Little is known about his upbringing and education beyond that he was literate.[1]: 17, 41, 90 [16]: 3
Town doctor John Martyn Harlow described Gage as "a perfectly healthy, strong and active young man, twenty-five years of age, nervo-bilious temperament, five feet six inches [1.68 m] in height, average weight one hundred and fifty pounds [68 kg], possessing an iron will as well as an iron frame; muscular system unusually well developed—having had scarcely a day's illness from his childhood to the date of [his] injury".[4]: 4 (In phrenology—then just ending its vogue[17]—nervo-bilious denoted an unusual combination of "excitable and active mental powers" with "energy and strength [of] mind and body [making] possible the endurance of great mental and physical labor".)[1]: 346–7 [18]: 6
Gage may have first worked with explosives during farmwork as a youth, or in nearby mines and quarries.[1]: 17–18 He is known to have worked on construction of the Hudson River Railroad near Cortlandt Town, New York,[19][16]: 3 and by the time of his accident he was a blasting foreman (possibly an independent contractor) on railway construction projects.[1]: 18–22, 32n9 His employers' "most efficient and capable foreman ... a shrewd, smart business man, very energetic and persistent in executing all his plans of operation",[4]: 13–14 he had even commissioned a custom-made tamping iron—a large iron rod—for use in setting explosive charges.[3]: 5 [1]: 25
Accident

| External videos | |
|---|---|
On September 13, 1848, Gage was directing a work gang blasting rock while preparing the roadbed for the Rutland & Burlington Railroad south of the town of Cavendish, Vermont. Setting a blast involved boring a hole deep into an outcropping of rock; adding blasting powder, a fuse, and sand; then compacting this charge into the hole using the tamping iron.[d] Gage was doing this around 4:30 p.m. when (possibly because the sand was omitted)[3]: 13–14 [4]: 5 [1]: 27 the iron sparked against the rock and the powder exploded. Rocketing from the hole, the tamping iron—three feet seven inches (1.1 m) long and 1+1⁄4 inches (3.2 cm) in diameter[4]: 5 [1]: 25 —"entered on the [left] side of [Gage's] face ... passing back of the left eye, and out at the top of the head".[e]
Despite nineteenth-century references to Gage as "the American Crowbar Case"[f] his tamping iron did not have the bend or claw sometimes associated with the term crowbar; rather, it was a pointed cylinder something like a javelin,[23] "round and rendered comparatively smooth by use":[4]: 5
The end which entered first is pointed; the taper being [eleven inches (27 cm) long, ending in a 1⁄4-inch (7 mm) point] [24]: 17 ... circumstances to which the patient perhaps owes his life. The iron is unlike any other, and was made by a neighbouring blacksmith to please the fancy of its owner.[3]: 14

Weighing 13+1⁄4 pounds (6.0 kg),[4]: 5 the tamping iron was found some 80 feet (25 m) away,[1]: 29 "smeared with blood and brain".[4]: 5
Gage "was thrown upon his back by the explosion, and gave a few convulsive motions of the extremities, but spoke in a few minutes", walked with little assistance, and sat upright in an oxcart for the 3⁄4-mile (1.2 km) ride to his lodgings in town.[4]: 5 About thirty minutes after the accident Dr. Edward H. Williams, finding Gage sitting in a chair outside the hotel, was greeted with "one of the great understatements of medical history":[26]: 244
When I drove up he said, "Doctor, here is business enough for you." I first noticed the wound upon the head before I alighted from my carriage, the pulsations of the brain being very distinct. The top of the head appeared somewhat like an inverted funnel, as if some wedge-shaped body had passed from below upward. Mr. Gage, during the time I was examining this wound, was relating the manner in which he was injured to the bystanders. I did not believe Mr. Gage's statement at that time, but thought he was deceived. Mr. Gage persisted in saying that the bar went through his head. Mr. G. got up and vomited; the effort of vomiting pressed out about half a teacupful of the brain, which fell upon the floor.[27]
Harlow took charge of the case around 6 p.m.:
You will excuse me for remarking here, that the picture presented was, to one unaccustomed to military surgery, truly terrific; but the patient bore his sufferings with the most heroic firmness. He recognized me at once, and said he hoped he was not much hurt. He seemed to be perfectly conscious, but was getting exhausted from the hemorrhage. His person, and the bed on which he was laid, were literally one gore of blood.[27]

Initial treatment
With Williams' assistance[g] Harlow shaved the scalp around the region of the tamping iron's exit, then removed coagulated blood, small bone fragments, and an ounce [30 g] of protruding brain. After probing for foreign bodies and replacing two large detached pieces of bone, Harlow closed the wound with adhesive straps, leaving it partially open for drainage;[1]: 60–1 the entrance wound in the cheek was bandaged only loosely, for the same reason. A wet compress was applied, then a nightcap, then further bandaging to secure these dressings. Harlow also dressed Gage's hands and forearms (which along with his face had been "deeply burned") and ordered that Gage's head be kept elevated.
Late that evening Harlow noted: "Mind clear. Constant agitation of his legs, being alternately retracted and extended like the shafts of a fulling mill. Says he 'does not care to see his friends, as he shall be at work in a few days.'" [27]
Convalescence
Despite his own optimism, Gage's convalescence was long, difficult, and uneven. Though recognizing his mother and uncle (summoned from Lebanon, New Hampshire, thirty miles away)[4]: 12 [1]: 30 on the morning after the accident, on the second day he "lost control of his mind, and became decidedly delirious". Two days later he was again "rational ... knows his friends", and after a week's further progress Harlow entertained, for the first time, the thought "that it was possible for Gage to recover ... This improvement, however, was of short duration." [27]

Beginning September 25[1]: 53 Gage was semi-comatose, "seldom speaking unless spoken to, and then answering only in monosyllables", and the next day Harlow noted, "Failing strength ... coma deepened; the globe of the left eye became more protuberant, with [granulation tissue][h] pushing out rapidly from the internal canthus [as well as] from the wounded brain, and coming out at the top of the head." After another day, "The exhalations from the mouth and head [are] horribly fetid. Comatose, but will answer in monosyllables if aroused. Will not take nourishment unless strongly urged. The friends and attendants are in hourly expectancy of his death, and have his coffin and clothes in readiness." [27]
Galvanized, Harlow "cut off the [granulation tissue] sprouting out from the top of the brain and filling the opening, and made free application of caustic [i.e. crystalline silver nitrate][1]: 54 to them. With a scalpel I laid open the [frontalis muscle,[31]: 392 from the exit wound to the top of the nose] and immediately there were discharged eight ounces [250 ml] of ill-conditioned pus, with blood, and excessively fetid." [27] ("Gage was lucky to encounter Dr. Harlow when he did," wrote Barker. "Few doctors in 1848 would have had the experience with cerebral abscess with which Harlow left [Jefferson Medical College] and which probably saved Gage's life." [6]: 679–80 See § Factors favoring Gage's survival, below.)
On October 7, Gage "succeeded in raising himself up, and took one step to his chair". One month later he was walking "up and down stairs, and about the house, into the piazza", and while Harlow was absent for a week, Gage was "in the street every day except Sunday", his desire to return to his family in New Hampshire being "uncontrollable by his friends ... got wet feet and a chill." He soon developed a fever, but by mid-November he was "feeling better in every respect ... walking about the house again". Harlow's prognosis at this point: Gage "appears to be in a way of recovering, if he can be controlled".[27]
Subsequent life and travels
By November 25, Gage was strong enough to return to his parents' home in Lebanon, New Hampshire, where by late December he was "riding out, improving both mentally and physically" [32] and (as recorded in the notes of a physician who spoke to Gage's mother) "abt. February he was able to do a little work abt. ye horses & barn, feedg. ye cattle &c; that as ye time for ploughing came he was able to do half a day's work after that & bore it well." [33][1]: ix, 93–4
Injuries

In April 1849 Gage returned to Cavendish and paid a visit to Harlow, who noted at that time loss of vision (and ptosis) of the left eye,[i] a large scar on the forehead (from Harlow's draining of the abscess)[31]: 392 and
upon the top of the head ... a deep depression, two inches by one and one-half inches [5 cm by 4 cm] wide, beneath which the pulsations of the brain can be perceived. Partial paralysis of the left side of the face. His physical health is good, and I am inclined to say he has recovered. Has no pain in head, but says it has a queer feeling which he is not able to describe.[4]: 12–13
Though a year later some physical weakness remained,[1]: 93 [35] Harlow later wrote that "physically, the recovery was quite complete during the four years immediately succeeding the injury".[4]: 19
New England and New York (1849–1852)
In November 1849 Henry Jacob Bigelow, the Professor of Surgery at Harvard Medical School, brought Gage to Boston "at very considerable expense [and after having] satisfied himself that the bar had actually passed through the man's head",[36]: 149 presented him to a meeting of the Boston Society for Medical Improvement and (possibly) to a Medical School class.[3]: 20 [1]: 43, 95 [37] (This may have been one of the earliest cases of a patient entering a hospital primarily to further medical research, rather than for treatment.)[38]
Unable to return to his railroad work () Gage appeared for a time, with his iron, at Barnum's American Museum in New York City (not the later Barnum's circus—there is no evidence Gage ever exhibited with a troupe or circus, or on a fairground).[39] Advertisements have also been found for public appearances by Gage—which he may have arranged and promoted himself—in New Hampshire and Vermont,[16]: 3–4 supporting Harlow's statement that Gage made public appearances in "most of the larger New England towns".[4]: 14 [40]: 829 (Years later Bigelow wrote that Gage had been "a shrewd and intelligent man and quite disposed to do anything of that sort to turn an honest penny", but had given up such efforts because "[that] sort of thing has not much interest for the general public".)[41][42]: 28 [16]: 3–4
For about eighteen months he worked for the owner of a livery and coach service in Hanover, New Hampshire.[4]: 14 [1]: 101
Chile and California (1852–1860)
In August 1852, Gage was invited to Chile to work as a long-distance stagecoach driver there, "caring for horses, and often driving a coach heavily laden and drawn by six horses" on the Valparaiso–Santiago route.[1]: 103–4 [4]: 14 After his health began to fail in mid-1859,[4]: 14–15 [j] Gage left Chile for San Francisco, arriving (in his mother's words) "in a feeble condition, having failed very much since he left New Hampshire ... Had many ill turns while in Valparaiso, especially during the last year, and suffered much from hardship and exposure." In San Francisco he recovered under the care of his mother and sister,[4]: 15 who had relocated there from New Hampshire around the time Gage went to Chile.[1]: 103–4 Then, "anxious to work", he found employment with a farmer in Santa Clara.[4]: 15
Death

In February 1860[j] Gage had several epileptic seizures.[1]: 14 [4]: 16 He lost his job, and (wrote Harlow) as the seizures increased in frequency and severity over the succeeding three months he "continued to work in various places [though he] could not do much".
On May 18 he "left Santa Clara and went home to his mother. At 5 o'clock, A.M., on the 20th, he had a severe convulsion. The family physician was called in, and bled him. The convulsions were repeated frequently during the succeeding day and night," [4]: 15 and he died during status epilepticus,[7]: E in or near[7]: B San Francisco, late on May 21, 1860, just under twelve years after his injury. He was buried in San Francisco's Lone Mountain Cemetery.[j]
Exhumation
In 1866, Harlow (who had "lost all trace of [Gage], and had well nigh abandoned all expectation of ever hearing from him again") somehow learned that Gage had died in California, and made contact with his family there. At Harlow's request Gage's grave was opened long enough to remove his skull, which the family then personally delivered to Harlow,[1]: 108–11 [4]: 15–16 [16]: 6 who was by now a prominent physician, businessman, and civic leader in Woburn, Massachusetts.[1]: 351–64 [9]
About a year after the accident, Gage had given his tamping iron to Harvard Medical School's Warren Anatomical Museum, but he later reclaimed it[3]: 22n [47][1]: 46–7 and made what he called "my iron bar" [16]: 4 [48] his "constant companion during the remainder of his life";[4]: 13 now it too was delivered by Gage's family to Harlow.[16]: 6 (Though some accounts assert that Gage's iron had been buried with him, there is no evidence for this.)[16]: 7 After studying them for a triumphal[6]: 679 1868 retrospective paper on Gage[4]: 3 Harlow redeposited the iron—this time with the skull—in the Warren Museum, where they remain on display today.[49]
The iron bears the following inscription, commissioned by Bigelow in conjunction with the iron's first deposit in the Museum[47] (though the date it gives for the accident is one day off, and Phinehas is not the way Gage spelled his name[40]: 839fig ):
This is the bar that was shot through the head of Mr Phinehas[sic] P. Gage at Cavendish, Vermont, Sept. 14,[sic] 1848. He fully recovered from the injury & deposited this bar in the Museum of the Medical College of Harvard University. Phinehas P. Gage Lebanon Grafton Cy N–H Jan 6 1850.[7]: D
The date Jan 6 1850 falls within the period during which Gage was in Boston under Bigelow's observation.[3]: 20 [4]: 4n [1]: 43
In 1940 Gage's headless remains were moved to Cypress Lawn Cemetery as part of a mandated relocation of San Francisco's dead to new resting places outside city limits.[1]: 119–20 [50]

Brain damage and mental changes

Extent of brain damage
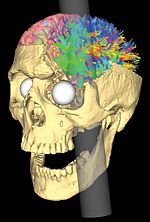

Debate about whether the trauma and subsequent infection had damaged both of Gage's frontal lobes (left and right), or only the left, began almost immediately after his accident.[k] The 1994 conclusion of Hanna Damasio et al., that both frontal lobes were damaged, was drawn not from Gage's skull but from a "Gage-like" one—a cadaver skull deformed to match the dimensions of Gage's.[40]: 829–30 [55]: 1103–4 Using CT scans of Gage's actual skull, Ratiu et al.[10]: 638 and Van Horn et al.[24]: 4–5 both rejected that conclusion, agreeing with Harlow's belief—based on probing Gage's wounds with his fingers[56]—that only the left frontal lobe had been damaged.[4]: 19
In addition, Ratiu et al. noted that the opening between the roof of the mouth and the base of the cranium (created as the iron passed through) has a diameter about half that of the iron itself; combining this with the hairline fracture running from behind the exit region down the front of the skull, they concluded that the skull "hinged" open as the iron entered from below, then (once the iron had exited at the top) was pulled closed by the resilience of soft tissues.[10]: 640 [40]: 830
Van Horn et al. concluded that damage to Gage's white matter (of which they made detailed estimates) was as or more significant to Gage's mental changes than cerebral cortex (gray matter) damage.[24]: abstr
First-hand reports of mental changes
Gage certainly displayed some kind of change in behavior after his injury,[16]: 12–15 but the nature, extent, and duration of this change have been difficult to establish. Only a handful of sources give direct information on what Gage was like (either before or after the accident),[c] the mental changes described after his death were much more dramatic than anything reported while he was alive,[1]: 375–6 and few sources are explicit about the period of Gage's life to which their various descriptions of him (which vary widely in their implied level of functional impairment) are meant to apply.[16]: 6–7
Early observations (1849–1852)
Harlow described the pre-accident Gage as hard-working, responsible, and "a great favorite" with the men in his charge, his employers having regarded him as "the most efficient and capable foreman in their employ". But these same employers, after Gage's accident, "considered the change in his mind so marked that they could not give him his place again":
The equilibrium or balance, so to speak, between his intellectual faculties and animal propensities, seems to have been destroyed. He is fitful, irreverent, indulging at times in the grossest profanity (which was not previously his custom), manifesting but little deference for his fellows, impatient of restraint or advice when it conflicts with his desires, at times pertinaciously obstinate, yet capricious and vacillating, devising many plans of future operations, which are no sooner arranged than they are abandoned in turn for others appearing more feasible. A child in his intellectual capacity and manifestations, he has the animal passions of a strong man. Previous to his injury, although untrained in the schools, he possessed a well-balanced mind, and was looked upon by those who knew him as a shrewd, smart business man, very energetic and persistent in executing all his plans of operation. In this regard his mind was radically changed, so decidedly that his friends and acquaintances said he was "no longer Gage".[4]: 13–14


This description ("now routinely quoted", says Kotowicz)[59]: 125 is from Harlow's observations set down soon after the accident,[1]: 90, 375 [16]: 6–9 but Harlow—perhaps hesitant to describe his patient negatively while he was still alive[1]: 375–6 —left these observations unpublished until 1868, after Gage had died and his family had supplied "what we so much desired to see" (as Harlow termed Gage's skull).[4]: 16
In the interim, Harlow's 1848 report, published just as Gage was emerging from his convalescence, only hinted at psychological symptoms:[1]: 169
The mental manifestations of the patient, I leave to a future communication. I think the case ... is exceedingly interesting to the enlightened physiologist and intellectual philosopher.[31]: 393
But after Bigelow termed Gage "quite recovered in faculties of body and mind", with only "inconsiderable disturbance of function",[3]: 13–14 a rejoinder in the American Phrenological Journal—
That there was no difference in his mental manifestations after the recovery is not true ... The man was gross, profane, coarse, and vulgar, to such a degree that his society was intolerable to decent people.[60]
—was apparently based on information anonymously supplied by Harlow.[1]: 350–1 Barker explains these contradictory evaluations (only six months apart) by differences in Bigelow's and Harlow's educational backgrounds:
Harlow's interest in phrenology prepared him to accept the change in character as a significant clue to cerebral function which merited publication. Bigelow had [been taught] that damage to the cerebral hemispheres had no intellectual effect, and he was unwilling to consider Gage's deficit significant ... The use of a single case [including Gage's] to prove opposing views on phrenology was not uncommon.[6]: 672, 678
Later observations (1852–1858)
In 1860, an American physician who had known Gage "well" in Chile reported that Gage remained "engaged in stage driving [and] in the enjoyment of good health, with no impairment whatever of his mental faculties".[61][16]: 8 Together with the fact that Gage was hired by his employer in advance, in New England, to be part of the new coaching enterprise in Chile,[4]: 15 [16]: 15 this implies that Gage's most serious mental changes had been temporary, so that the "fitful, irreverent ... capricious and vacillating" Gage described by Harlow immediately post-accident became, over time, far more functional and socially far better adapted.[40]: 831 [16]: 2, 15
This conclusion is reinforced (writes psychologist Malcolm Macmillan) by the responsibilities and challenges associated with stagecoach work such as that done by Gage in Chile, including the requirement that drivers "be reliable, resourceful, and possess great endurance. But above all, they had to have the kind of personality that enabled them to get on well with their passengers." [62][1]: 104–6 [16]: 4–5 A day's work for Gage meant "a 13-hour journey over 100 miles of poor roads, often in times of political instability or frank revolution. All this—in a land to whose language and customs Phineas arrived an utter stranger—militates as much against permanent disinhibition [i.e. an inability to plan and self-regulate] as do the extremely complex sensory-motor and cognitive skills required of a coach driver." [16]: 5 [40]: 831 (A visitor wrote: "The departure of the coach was always a great event at Valparaiso—a crowd of ever-astonished Chilenos assembling every day to witness the phenomenon of one man driving six horses.")[63]: 73
Social recovery
Macmillan writes that this contrast—between Gage's early, versus later, post-accident behavior—reflect Gage's "[gradual change] from the commonly portrayed impulsive and uninhibited person into one who made a reasonable 'social recovery'",[64] citing persons with similar injuries for whom "someone or something gave enough structure to their lives for them to relearn lost social and personal skills":[40]: 831
Phineas' survival and rehabilitation demonstrated a theory of recovery which has influenced the treatment of frontal lobe damage today. In modern treatment, adding structure to tasks by, for example, mentally visualising a written list, is considered a key method in coping with frontal lobe damage.[65]

According to a contemporary account by visitors to Chile,[40]: 831 Gage would have had to
rise early in the morning, prepare himself, and groom, feed, and harness the horses; he had to be at the departure point at a specified time, load the luggage, charge the fares and get the passengers settled; and then had to care for the passengers on the journey, unload their luggage at the destination, and look after the horses. The tasks formed a structure that required control of any impulsiveness he may have had.[67]
En route (Macmillan continues):
much foresight was required. Drivers had to plan for turns well in advance, and sometimes react quickly to manoeuvre around other coaches, wagons, and birlochos travelling at various speeds ... Adaptation had also to be made to the physical condition of the route: although some sections were well-made, others were dangerously steep and very rough.
Thus Gage's stagecoach work—"a highly structured environment in which clear sequences of tasks were required [but within which] contingencies requiring foresight and planning arose daily"—resembles rehabilitation regimens first developed by Soviet neuropsychologist Alexander Luria for the reestablishment of self-regulation in World War II soldiers suffering frontal lobe injuries.[16]: 5, 11–12, 15
A neurological basis for such recoveries may be found in emerging evidence "that damaged [neural] tracts may re-establish their original connections or build alternative pathways as the brain recovers" from injury.[64] Macmillan adds that if Gage made such a recovery—if he eventually "figured out how to live" (as Fleischman put it)[68]: 75 despite his injury—then it "would add to current evidence that rehabilitation can be effective even in difficult and long-standing cases";[40]: 831 and if Gage could achieve such improvement without medical supervision, "what are the limits for those in formal rehabilitation programs?" [67] As author Sam Kean put it, "If even Phineas Gage bounced back—that's a powerful message of hope." [23]
Exaggeration and distortion of mental changes
A moral man, Phineas Gage
Tamping powder down holes for his wage
Blew his special-made probe
Through his left frontal lobe
Now he drinks, swears, and flies in a rage.
— Anonymous[1]: 307
Macmillan's analysis of scientific and popular accounts of Gage found that they almost always distort and exaggerate his behavioral changes well beyond anything described by anyone who had contact with him.[c] In the words of Barker, "As years passed, the case took on a life of its own, accruing novel additions to Gage's story without any factual basis";[6]: 678 even today (writes historian Zbigniew Kotowicz) "Most commentators still rely on hearsay and accept what others have said about Gage, namely, that after the accident he became a psychopath." [59]: 125 and Grafman has written that "the details of [Gage's] social cognitive impairment have occasionally been inferred or even embellished to suit the enthusiasm of the story teller ..." [69]: 295
Behaviors ascribed to the post-accident Gage which are either unsupported by, or in contradiction to, the known facts include mistreatment of wife and children (of which Gage had neither);[70] inappropriate sexual behavior, promiscuity, or impaired sexuality;[71] lack of forethought, of concern for the future, or of capacity for embarrassment; parading his self-misery, and vainglory in showing his wounds;[72] inability[73] or refusal[74] to hold a job; irresponsibility and untrustworthiness;[75] aggressiveness and violence;[76] vagrancy and begging;[77] plus drifting,[78] drinking,[79] bragging,[80] lying,[81] brawling,[82] bullying,[83] psychopathy,[84] inability to make ethical decisions, loss of all respect for social conventions, acting "like an idiot",[85] and dying "due to a debauch".[86] None of these behaviors is mentioned by anyone who had met Gage or even his family;[c] as Kotowicz put it, "Harlow does not report a single act that Gage should have been ashamed of." [59]: 122–3 Gage is "a great story for illustrating the need to go back to original sources", writes Macmillan.[89]
For example, a passage by Harlow— "'... continued to work in various places;' could not do much, changing often, 'and always finding something that did not suit him in every place he tried'" [4]: 15 —has been misinterpreted[90] as meaning Gage could not hold a regular job after his accident,[91] "was prone to quit in a capricious fit or be let go because of poor discipline",[92]: 8–9 "never returned to a fully independent existence",[55]: 1102 and died "in careless dissipation"[93] in "the custody of his parents".[94] In fact, after his initial post-recovery months spent traveling and exhibiting, Gage supported himself—at a total of two jobs—from early 1851 until just before his death in 1860.[16]: 14–15 (Harlow's "changing often" refers only to Gage's final months, after convulsions had set in, and even then he remained "anxious to work".[1]: 107 [16]: 6 In Kotowicz's words, "What Harlow is telling us is clear and unambiguous: Gage returns from South America to his mother to recuperate. As soon as he is fit, he goes back to work with horses, which is what he has been doing for years.")[59]: 130n6
Theoretical use and misuse
Though Gage is considered the "index case for personality change due to frontal lobe damage" [6]: 672 [95][96][1]: 1 his scientific value is undermined by the uncertain extent of his brain damage[96] and the limited understanding of his behavioral changes.[c] Instead, Macmillan writes, "Phineas' story is [primarily] worth remembering because it illustrates how easily a small stock of facts becomes transformed into popular and scientific myth",[97] the paucity of evidence having allowed "the fitting of almost any theory [desired] to the small number of facts we have".[1]: 290 A similar concern was expressed as far back as 1877, when British neurologist David Ferrier (writing to Harvard's Henry Pickering Bowditch in an attempt "to have this case definitely settled") complained that
In investigating reports on diseases and injuries of the brain, I am constantly amazed at the inexactitude and distortion to which they are subject by men who have some pet theory to support. The facts suffer so frightfully ...[1]: 1, 75, 197–9, 464–5 [98]
More recently, neurologist Oliver Sacks refers to the "interpretations and misinterpretations [of Gage] from 1848 to the present".[99]
Cerebral localization
In the nineteenth-century controversy over whether the various mental functions are or are not localized in specific regions of the brain, both sides managed to enlist Gage in support of their theories.[6]: 678 [1]: ch9 For example, after Dupuy wrote that Gage proved that the brain is not localized (characterizing him as a "striking case of destruction of the so-called speech centre without consequent aphasia")[51] Ferrier made a "devastating reply" in his 1878 Goulstonian Lectures, "On the Localisation of Cerebral Disease", of which Gage (and the woodcuts of his skull and iron from Harlow's 1868 paper) were "an absolutely dominating feature".[52][26]: 198, 253
Phrenology

Throughout the nineteenth century, adherents of phrenology contended that Gage's mental changes (his profanity, for example)[60][1]: 151 stemmed from destruction of his mental "organ of Benevolence"—as phrenologists saw it, the part of the brain responsible for "goodness, benevolence, the gentle character ... [and] to dispose man to conduct himself in a manner conformed to the maintenance of social order"—and/or the adjacent "organ of Veneration"—related to religion and God, and respect for peers and those in authority.[1]: 150, 171n10 [100][2] (Phrenology held that the organs of the "grosser and more animal passions are near the base of the brain; literally the lowest and nearest the animal man [while] highest and farthest from the sensual are the moral and religions feelings, as if to be nearest heaven". Thus Veneration and Benevolence are at the apex of the skull—the region of exit of Gage's tamping iron.)[101]
Harlow wrote that Gage, during his convalescence, did not "estimate size or money accurately [and] would not take $1000 for a few pebbles";[31]: 392 by this he may have been implying damage to phrenology's "Organ of Comparison".[6]: 675–6
Psychosurgery and lobotomy
It is frequently said that what happened to Gage played a part in the later development of various forms of psychosurgery—particularly lobotomy[102]—or even that Gage's accident constituted "the first lobotomy".[103] Aside from the question of why the unpleasant changes usually (if hyperbolically) attributed to Gage would inspire surgical imitation, there is no such link, according to Macmillan:
There is simply no evidence that any of these operations were deliberately designed to produce the kinds of changes in Gage that were caused by his accident, nor that knowledge of Gage's fate formed part of the rationale for them[7]: F ... [W]hat his case did show came solely from his surviving his accident: major operations [such as for tumors] could be performed on the brain without the outcome necessarily being fatal.[1]: 250
Somatic marker hypothesis
A. Damasio, in support of his somatic marker hypothesis (relating decision-making to emotions and their biological underpinnings), draws parallels between behaviors he attributes to Gage and those of modern patients with damage to the orbitofrontal cortex and amygdala.[92]: ch3 [104] But A. Damasio's depiction of Gage has been criticized by Kotowicz as
grotesque fabrication ... ["perpetrating"] the myth of Gage the psychopath ... Damasio changes [Harlow's] narrative, omits facts, and adds freely ... It seems that the growing commitment to the frontal lobe doctrine of emotions brought Gage to the limelight and shapes how he is described." [l]
As Kihlstrom put it:
[M]any modern commentators exaggerate the extent of Gage's personality change, perhaps engaging in a kind of retrospective reconstruction based on what we now know, or think we do, about the role of the frontal cortex in self-regulation.[105]
Portraits


Two daguerreotype portraits of Gage, identified in 2009 and 2010,[a] are the only likenesses[107]: 343 [34][108]: 8 of him known other than a life mask taken for Bigelow in late 1849 (and now in the Warren Museum along with Gage's skull and iron).[3]: 22n [36]: 149 [1]: ii, 42 The first shows "a disfigured yet still-handsome" Gage[34] with one eye closed and scars clearly visible, "well dressed and confident, even proud" [107]: 343 and holding his iron, on which portions of its inscription can be made out.[106] (For decades the portrait's owners had imagined the subject was an injured whaler with his harpoon.)[106]
The second portrait, copies of which are in the possession of two different branches of the Gage family, shows Gage in a somewhat different pose, wearing a different shirt and different tie, but the same waistcoat and possibly the same jacket.[110]
Authenticity was confirmed in several ways (including photo-overlaying the inscription, as seen in the portraits, against that on the actual tamping iron, and matching the subject's injuries to those preserved in the life mask)[107]: 342–3 but about when, where, and by whom they were taken nothing is known, except that they were created no earlier than January 1850 (when the inscription was added to the tamping iron),[16]: 4 on different occasions, and are likely by different photographers.[108]: 8
The portraits add to the evidence that Gage's most serious mental changes were temporary .[67][111] "That [Gage] was any form of vagrant following his injury is belied by these remarkable images", wrote Van Horn et al.[24]: 13 "Although just one picture," Kean commented in reference to the first image discovered, "it exploded the common image of Gage as a dirty, disheveled misfit. This Phineas was proud, well-dressed, and disarmingly handsome." [23]
Early medical attitudes
A tone of amused wonderment was common in nineteenth-century medical writing about Gage (as well as about victims of other unlikely-sounding brain-injury accidents, including encounters with axes, bolts, low bridges, exploding firearms, a revolver shot to the nose, more tamping irons, and "even falling gum tree branches").[1]: 62–7 The Boston Medical & Surgical Journal, for example, termed Gage "the patient whose cerebral organism had been comparatively so little disturbed by its abrupt and intrusive visitor".[47]
Skepticism
Barker notes that Harlow's original 1848 report of Gage's recovery "was widely disbelieved, for obvious reasons" [6]: 676 and Harlow himself, in his 1868 retrospective, recalled this early skepticism:
The case occurred nearly twenty years ago, in an obscure country town ..., was attended and reported by an obscure country physician, and was received by the Metropolitan doctors with several grains of caution, insomuch that many utterly refused to believe that the man had risen, until they had thrust their fingers into the hole [in] his head, [see Doubting Thomas] and even then they required of the Country Doctor attested statements, from clergymen and lawyers, before they could or would believe—many eminent surgeons regarding such an occurrence as a physiological impossibility, the appearances presented by the subject being variously explained away.
"A distinguished Professor of Surgery in a distant city", Harlow said, had even dismissed Gage as a "Yankee invention".[4]: 3, 18
According to the Boston Medical and Surgical Journal, it was the 1850 report on Gage by Bigelow—Harvard's Professor of Surgery and "a majestic and authoritative figure on the medical scene of those times" [38]—that "finally succeeded in forcing [the case's] authenticity upon the credence of the profession ... as could hardly have been done by any one in whose sagacity and surgical knowledge his confrères had any less confidence".[47][citation needed] Noting that, "The leading feature of this case is its improbability ... This is the sort of accident that happens in the pantomime at the theater, not elsewhere", and calling the case "perhaps unparalleled in the annals of surgery", Bigelow emphasized that though "at first wholly skeptical, I have been personally convinced".[m]
Nonetheless (Bigelow wrote just before Harlow's 1868 presentation of Gage's skull) though "the nature of [Gage's] injury and its reality are now beyond doubt ... I have recd a letter within a month [purporting] to prove that ... the accident could not have happened ",[41] and two years later Jackson was still able to write that
The very small amount of attention that has been given to [the Gage case] can only be explained by the fact that it far transcends any case of recovery from injury of the head that can be found in the records of surgery. It was too monstrous for belief ... [36]: 149
Standard for other brain injuries

As the reality of Gage's accident and survival gained credence, it became "the standard against which other injuries to the brain were judged". After a miner survived traversal of his skull by a gas pipe (extracted "not without considerable difficulty and force, owing to a bend in the portion of the rod in his skull") his physician invoked Gage as the "only case comparable with this, in the amount of brain injury, that I have seen reported".[n]
Often these comparisons carried hints of competitiveness, humor, or both,[1]: 66 as when a Kentucky doctor, reporting a patient's survival of a gunshot to the nose, bragged:
If you Yankees can send a tamping bar through a fellow's brain and not kill him, I guess there are not many can shoot a bullet between a man's mouth and his brains, stopping just short of the medulla oblongata, and not touch either.[114]
Similarly, when a lumbermill foreman returned to work soon after a saw cut three inches (8 cm) into his skull from just between the eyes to behind the top of his head, his surgeon (who had removed from this wound "thirty-two pieces of bone, together with considerable sawdust") termed the case "second to none reported, save the famous tamping-iron case of Dr. Harlow", though apologizing that "I cannot well gratify the desire of my professional brethren to possess [the patient's] skull, until he has no further use for it himself." [115]
As these and other remarkable brain-injury survivals accumulated, the Boston Medical & Surgical Journal (1869) pretended to wonder whether the brain has any function at all: "Since the antics of iron bars, gas pipes, and the like skepticism is discomfitted, and dares not utter itself. Brains do not seem to be of much account now-a-days." [116] The Transactions of the Vermont Medical Society was similarly facetious: "'The times have been,' says Macbeth [Act III], 'that when the brains were out the man would die. But now they rise again.' Quite possibly we shall soon hear that some German professor is exsecting it." [21]: 53–4
Factors favoring Gage's survival

Harlow saw Gage's survival as demonstrating "the wonderful resources of the system in enduring the shock and in overcoming the effects of so frightful a lesion, and as a beautiful display of the recuperative powers of nature", and listed what he saw as the circumstances favoring it:
1st. The subject was the man for the case. His physique, will, and capacity of endurance, could scarcely be excelled.[4]: 18
2d. The shape of the missile—being pointed, round and comparatively smooth, not leaving behind it prolonged concussion or compression.[4]: 18
Despite its very large diameter and mass (compared to a weapon-fired projectile) the tamping iron's relatively low velocity drastically reduced the energy available to compressive and concussive "shock waves".[1]: 56, 68n3 [117][118] Ratiu et al.'s conclusion, that Gage's skull "hinged open" as the iron passed through,[10]: 639 implies a further reduction in such effects because of the increased volume available into which the brain could shift temporarily.[citation needed]
Harlow continued:
3d. The point of entrance outside of the superior maxillary bone—[the tamping iron] did little injury until it reached the floor of the cranium, when, at the same time that it did irreparable damage, it [created the] opening in the base of the skull, for drainage, [without which] recovery would have been impossible.[4]: 18
Barker writes that "[Head injuries] from falls, horse kicks, and gunfire, were well known in pre–Civil War America [and] every contemporary course of lectures on surgery described the diagnosis and treatment" of such injuries. But to Gage's benefit, surgeon Joseph Pancoast had performed "his most celebrated operation for head injury before Harlow's medical school class, [trephining] to drain the pus, resulting in temporary recovery. Unfortunately, symptoms recurred and the patient died. At autopsy, reaccumulated pus was found: granulation tissue had blocked the opening in the dura." By keeping the exit wound open and elevating Gage's head to encourage drainage from the cranium through the hole in the roof of the mouth, Harlow "had not repeated Professor Pancoast's mistake".[6]: 675 [1]: 58 [119]
Finally,
4th. The portion of the brain traversed was, for several reasons, the best fitted of any part of the cerebral substance to sustain the injury.[4]: 18
Precisely what Harlow's "several reasons" were is unclear, but he was likely referring, at least in part, to the understanding (slowly developing since ancient times) that injuries to the rear of the brain are especially dangerous, because they frequently interrupt vital functions such as breathing and circulation [1]: 126, 142 As British surgeon James Earle wrote in 1790, "[A] great part of the cerebrum may be taken away without destroying the animal, or even depriving it of its faculties, whereas the cerebellum will scarcely admit the smallest injury, without being followed by mortal symptoms." [1]: 128 [120]
Ratiu et al. and Van Horn et al. both concluded that the superior sagittal sinus must have remained intact, for otherwise Gage would almost certainly have suffered fatal blood loss or air embolism.[10]: 642 [24]: 17
As to his own role in Gage's survival, Harlow merely averred, "I can only say ... with good old Ambroise Paré, I dressed him, God healed him",[4]: 20 but Macmillan calls this self-assessment far too modest.[121] Noting that Harlow had been a "relatively inexperienced local physician ... graduated four and a half years earlier",[1]: 12 Macmillan's discussion of Harlow's "skillful and imaginative adaptation" of "conservative and progressive elements from the available therapies to the particular needs posed by Gage's injuries" emphasizes that he "did not apply rigidly what he had learned", for example foregoing an exhaustive search for bone fragments (which risked hemorrhage and further brain injury) and applying caustic silver nitrate to the granulation tissue instead of excising it (which risked hemorrhage) or forcing it into the wound (which risked compressing the brain).[1]: 58–62
See also
- Anatoli Bugorski—scientist whose head was struck by a particle-accelerator proton beam
- Eadweard Muybridge—another early case of head injury leading to mental changes
Notes
- ^ a b c The 2009-identified image is from the collection of Jack and Beverly Wilgus.[34][106][107][108] Like almost all daguerreotypes it shows its subject laterally (left-right) reversed, making it appear that Gage's right eye is injured.[107][108] However, all Gage's injuries, including to his eye, were on the left; therefore in presenting the image here a second, compensating reversal has been applied so as to show Gage as he appeared in life.[109][107]
The 2010-identified image is in the possession of Tara Gage Miller of Texas; an identical image belongs to Phyllis Gage Hartley of New Jersey.[109] (Both are descended from Gage's brother Roswell Rockwell Gage.)[16]: 4 Unlike the Wilgus portrait, which is itself a daguerreotype, the Miller and Hartley images are 19th-century photographic reproductions of a common original which remains undiscovered, itself a daguerreotype or other laterally reversing early-process photograph;[108] here again a compensating reversal has been applied.[109]
- ^ a b c Macmillan[1]: 14–17, 31n5, 490–1 discusses Gage's ancestry and early life. The birthdate July 9, 1823 is given by a Gage genealogy[13] without citation,[1]: 16 but is consistent with agreement among contemporary sources[14] that Gage was 25 years old on the date of his accident, and with his age (36 years) as given in undertaker's records after his death in May 1860.[1]: 108–9 Possible homes in childhood and youth are Lebanon or nearby East Lebanon, Enfield, and/or Grafton (all in Grafton County, New Hampshire), though Harlow refers to Lebanon in particular as Gage's "native place" [4]: 10 and "his home" [4]: 12 (likely that of his parents),[1]: 30 to which Gage returned ten weeks[7]: C after his accident.
There is nothing to indicate what Gage's middle initial P[15] stood for. His mother's first, middle, and maiden names are variously given as (respectively) Hannah or Hanna; Trussell, Trusel, or Trussel; and Swetland, Sweatland, or Sweetland.[1]: 490
- ^ a b c d e Macmillan[1]: 116–19, ch13-14 [7]: C [87] compares accounts of Gage to one another and against the known facts, as well as contrasting Gage's celebrity—he is mentioned in 91% of a sample of introductory psychology textbooks published 2012–2014[88]—with what was, until recently, the lack of any major study of him and dearth of papers solely or mainly about him.[1]: 1–2, 11
Until 2008[16]: 2–3 [40]: 830 the available sources offering significant information on Gage, and for which there is any evidence at all (even merely the source's own claim) of contact with him or with his family, were limited to Harlow (1848, 1849, 1868);[31][32][4] Bigelow 1850;[3] and Jackson (1849, 1870).[33][36] Macmillan notes that descriptions of Gage's behavior total just 300 words[1]: 90 and emphasizes the primacy of Harlow's three publications as sources.[1]: 94 (Harlow's original case notes have not been located.[1]: 90 A Warren Museum curator referred to the "stately elegance" of Harlow's writings on Gage.)[38] Macmillan & Lena[16]: 3–6, 8 present previously unknown sources found since 2008.
- ^ a b c Macmillan gives background on Cavendish (at the time called Duttonsville), the location and circumstances of the accident, and the steps in setting a blast.[1]: 13, 23–9 [9]: 151–2 [7]: A The blast hole, about 1+3⁄4 inches (4.5 cm) in diameter and up to 12 feet (4 m) deep, might require three men working as much as a day to bore using hand tools. The labor invested in setting each blast, the judgment involved in selecting its location and the quantity of powder to be used, and the often explosive nature of employer-employee relations on this type of job, all underscore the significance of Harlow's statements that Gage has been a "great favorite" with his men, and that his employers had considered him "the most efficient and capable foreman in their employ" prior to the accident.[1]: 13, 22–3, 25
- ^ a b [28] The Boston Post credits an earlier report (of unknown date) in the Ludlow (Vermont) Free Soil Union, which appears to have been the first report of Gage's accident;[1]: 11 although reprinted by several New England papers[1]: 35–36 it is itself no longer extant.[1]: 70n1 This report confuses the iron's circumference with its diameter,[1]: 12 and despite the reference to "shattering the upper jaw", that did not in fact happen.[29]
- ^ [21]: 54 [22] "Harlow always refers to the bar by its proper title, as a tamping iron. Bigelow's reference to a crowbar ... gave the case its nickname, which is still encountered today." [6]: 678
- ^ Williams family lore holds that Harlow did not appear until two days after Gage's accident, but nonetheless "sought eventually to take the whole glory of the successful outcome" of the case, even though Williams "was given full credit by all those who knew of his connection" to it. However, these stories conflict with every other account of Gage, including Williams' own.[1]: 279–84
- ^ In keeping with usage of the day[30]: 107 Harlow used the term fungus (a word possibly related to the Greek word for "sponge")[citation needed] in reference to the sponge-like granulation tissue.[1]: 53
- ^ Though "the globe of the left eye was protruded from its orbit by one-half its diameter" by the accident, Gage retained "indistinct" vision in it until the tenth day, when vision was permanently lost.[4]: 6, 8, 13 Ratiu et al. conclude that "the optic canal was spared ... [the vision loss] secondary to acute glaucoma or swelling of the optic nerve and compression against the rigid walls of the optic canal".[10]: 640 Harlow added that Gage could "adduct and depress the globe, but cannot move it in any other direction".
- ^ a b c d Gage's death and original burial are discussed by Macmillan.[1]: 108–9 [7]: D§corrections Harlow gives Gage's date of death as May 21, 1861,[4]: 15 but because bound, consecutive interment records[43] show that Gage was buried May 23, 1860,[1]: 122n17 Macmillan concludes that May 21, 1860 is the correct death date;[1]: 122n15 [16]: 6 this is confirmed by a contemporary obituary.[44] (Harlow's informant was Gage's mother;[4]: 15 [16]: 6 Macmillan[1]: 376 points out that, when combined with Gage's recorded age at death—36 years plus an unspecified number of months—the 1861 date obscures the fact that Gage had been conceived before his parents' April 27, 1823 marriage.) This implies that certain other dates Harlow gives for events late in Gage's life—his move from Chile to San Francisco and the onset of his convulsions—are also mistaken, presumably by the same one year; this article follows Macmillan[1]: 122n15 in correcting those dates (each of which carries this annotation). In 1867 Lone Mountain Cemetery was renamed Laurel Hill Cemetery.[45]
- ^ [1]: 3, 71 Early attempts to estimate the extent of damage include those by: Harlow;[31]: 389 Edward Elisha Phelps[33]; Bigelow;[3]: 21–2 Harlow;[4]: 17–19 Dupuy;[51] Ferrier;[52] Bramwell;[53] Cobb;[54] Tyler & Tyler.[22]
- ^ [59]: 125 Kotowicz continues, "Damasio's account of Gage's last months [is] such a grotesque fabrication that it leaves one baffled",[59]: 130n6 then quotes this passage from A. Damasio:[92]: 9–10
- In my mind is a picture of 1860s San Francisco as a bustling place, full of adventurous entrepreneurs engaged in mining, farming, and shipping. That is where we can find Gage's mother and sister, the latter married to a prosperous San Francisco merchant (D. D. Shattuck, Esquire), and that is where the old Phineas Gage might have belonged. But that is not where we would find him if we could travel back in time. We would probably find him drinking and brawling in a questionable district, not conversing with the captains of commerce, as astonished as anybody when the fault would slip and the earth would shake threateningly. He had joined the tableau of dispirited people who, as Nathanael West would put it decades later, and a few hundred miles to the south, "had come to California to die."
- ^ In addition to the "attested statements" mentioned by Harlow (which Harlow had gathered at Bigelow's request) and his own examination of Gage, Bigelow pointed out that the accident had occurred "in open day" with many witnesses, and that "in a thickly populated country neighbourhood, to which all the facts were matter of daily disucssion at the time of their occurrence, there is no difference of belief, nor has there been at any time doubt that the iron was actually driven through the brain. A considerable number of medical gentlemen also visited the case at various times to satisfy their incredulity." [3]: 13, 19–20 [1]: 42
- ^
[1]: 66 At the very meeting at which Harlow unveiled Gage's skull and iron, Bigelow ("in one of those coup dramatiques which were now and then incidents of his surgical communications [and] without giving notice that he intended to do so")[112]: 123 actually produced this patient, Joel Lenn, together with "the gas pipe which had pierced his head from the right forehead to left occiput, and the hat he had been wearing (with entrance and exit holes) ... This coup de théâtre must have been a painful coda for Harlow, eclipsing the pinnacle of his medical career." [6]: 679
A side effect of Lenn's post-accident medical treatment was to rid him of a 17-foot tapeworm. Months after the accident, his surgeon reported, "He seems to be perfectly rational, and will reply correctly in monosyllables to questions, but is entirely unable to connect words. He succeeds best, when excited, in swearing in French." [113]
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl bm bn bo bp bq br bs bt bu bv bw bx by bz ca cb Macmillan 2000.
- ^ a b Anonymous (November 6, 1848). "Alive from the Dead, Almost". North Star. Danville, Vermont. p. 1, col. 2. Transcribed in Macmillan 2000, pp. 39–40
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Bigelow 1850.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar Harlow 1868.
- ^ Campbell, H. F. (1851). "Injuries of the Cranium—Trepanning". Ohio Medical & Surgical Journal. 4 (1): 20–24.
{{cite journal}}: zero width joiner character in|title=at position 24 (help) (crediting the Southern Medical & Surgical Journal, unknown date). - ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Barker 1995.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Macmillan 2012.
- ^ Larner, Andrew; Leach, John Paul (July–August 2002). "Phineas Gage and the beginnings of neuropsychology" (PDF). Advances in Clinical Neuroscience and Rehabilitation. 2 (3): 26.

- ^ a b c Macmillan 2001.
- ^ a b c d e f Ratiu 2004.
- ^ Macmillan 2000, ch. 13; Macmillan 2008, p. 830.
- ^ Mazzoni, Giuliana; Nelson, Thomas O. (May 12, 2014). Metacognition and Cognitive Neuropsychology: Monitoring and Control Processes. Psychology Press. pp. 57–8. ISBN 978-1-317-77843-1.

- ^ Gage, Clyde Van Tassel (1964). John Gage of Ipswich, Mass. and his descendants: an historical, genealogical and biographical record, as developed from sources explained herein. Worcester, N.Y.: C.V. Gage.
- ^ "Incredible, But True Every Word". National Eagle. Claremont, New Hampshire. March 29, 1849. p. 2, col. 2. Reprinted: True Democrat and Granite State Whig (Lebanon, New Hampshire), April 6, 1849, p. 1, col. 7. Transcribed in Macmillan 2000, pp.40–1.
- Harlow 1848, p. 389; Bigelow 1850, p. 13; Harlow 1868, p. 4.
- ^ Harlow 1848, p. 389; Bigelow 1850, p. 13; Harlow 1868, p. 4; Macmillan 2000, p. 490; Macmillan 2008, p. 839 (fig.).
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y M8.
- ^ Roger Cooter (1984). The Cultural Meaning of Popular Science: Phrenology and the Organization of Consent in Nineteenth-century Britain. Cambridge University Press. p. 20. ISBN 978-0-521-22743-8.
- ^ Fowler, O. S. (1838). Synopsis of phrenology: and the phrenological developments: together with the character and talents of ________ as given by ________: with references to those pages of "Phrenology proved, illustrated and applied," in which will be found a full and correct delineation of the intellectual and moral character and manifestations of the above-named individual. New York: Fowler & Wells. p. 6.

- ^ Rutland Railroad Company (1897). "The Summit. (Letter of Edward H. Williams)". Heart of the Green mountains. Souvenir edition. Season of 1897. pp. 41–2.

- ^ a b R1.
- ^ a b Smith, William T. (1886). "Lesions of the Cerebral Hemispheres". Transactions of the Vermont Medical Society for the Year 1885. pp. 46–58.

- ^ a b T1.
- ^ a b c K.
- ^ a b c d e f g V.
- ^ Ratiu et al., p. 639; Van Horn et al., pp. 4–5, 17
- ^ a b M5.
- ^ a b c d e f g Excerpted from Williams' and Harlow's statements in: Harlow 1848, pp. 390–3; Bigelow 1850, p. 16; Harlow 1868, pp. 7–10.
- ^ "Horrible Accident". Boston Post. September 21, 1848.
- ^ Harlow 1848, p. 389; Bigelow 1850, p. 21; Harlow 1868, p. 16; Macmillan 2000, pp. 36–7.
- ^ Hooper, Robert (1809). "Injuries to the Brain from External Violence. Of the Consequences of Injuries to the Brain. Fungus and Hernia Cerebri". The surgeon's vade-mecum: containing the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of surgical diseases ... London: Printed for John Murray, Fleet Street; Adam Black, Edinburgh; and Wogan and Cumming, Dublin. p. 107.

- ^ a b c d e f H1.
- ^ a b H2.
- ^ a b c Jackson, J.B.S. (1849). Medical Cases 4'. Case 1777. Countway Library (Harvard Univ.) Mss., HMSb72.4.
- ^ a b c d T.
- ^ American Medical Association (1850). Report of the Standing Committee on Surgery. p. 345.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help)
- ^ a b c d e Jackson, J. B. S. (1870). "A Descriptive Catalog of the Warren Anatomical Museum". Frontis. and Nos. 949–51, 3106.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)
- ^ Boston Society for Medical Improvement (1849). Records 6. pp. 103–4.
- ^ a b c d Yakovlev, Paul I. (October 1958). "The "Crowbar Skull" and Mementoes of "Phrenological Hours"". Harvard Medical Alumni Bulletin. 33 (1): 19–24.

- ^ Bigelow 1868; Harlow 1868, p. 14; Macmillan 2000, pp. 14,98–9; Macmillan & Lena, pp. 3–4.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Macmillan 2008.
- ^ a b B2.
- ^ Bennett, W. (July–August 1987). "Dr. Warren's Possessions". Harvard Magazine. 89 (6): 24–31. PMID 11617033.
- ^ Volume 3: Lone Mountain register, 1850–1862, Halsted N. Gray – Carew & English Funeral Home Records (SFH 38), San Francisco History Center, San Francisco Public Library. p. 285.
- ^ "Deaths". New Hampshire Statesman. No. 2042. July 21, 1860. col. D.
- ^ "Laurel Hill Cemetery". Daily Alta California. April 12, 1867.
- ^ Harlow 1868, p.21; Macmillan 2000, pp.26,115, 479–80
- ^ a b c d "Bibliographical Notice". Boston Medical & Surgical Journal. 3 n.s. (7): 116–7. March 18, 1869.
- ^ G1.
- ^ "The Phineas Gage Case". Francis A. Countway Library (Harvard Medical School). Center for the History of Medicine. Warren Anatomical Museum. Retrieved 2013-01-10.

- ^ Proctor, William A. (1950), Location, regulation, and removal of cemeteries in the City and County of San Francisco, Department of City Planning, City and County of San Francisco

- ^ a b Dupuy, Eugene (1877). "A critical review of the prevailing theories concerning the physiology and the pathology of the brain: localisation of functions, and mode of production of symptoms. Part II". Med Times & Gaz. II: 356–8.

- ^ a b Ferrier, David (1878). "The Goulstonian lectures on the Localisation of Cerebral Disease. Lecture I (concluded)". Br Med J. 1 (900): 443–7. doi:10.1136/bmj.1.900.443. PMC 2220379. PMID 20748815.

- ^ Bramwell, B. (1888). "The Process of Compensation and some of its Bearings on Prognosis and Treatment". BMJ. 1 (1425): 835–40. doi:10.1136/bmj.1.1425.835. PMC 2197878. PMID 20752265.

- ^ Cobb, S. (1940). "Review of neuropsychiatry for 1940". Archives of Internal Medicine. 66: 1341–54. doi:10.1001/archinte.1940.00190180153011.
- Cobb, S. (1943). Borderlands of psychiatry. Harvard Univ. Press.
- ^ a b Damasio, H.; Grabowski, T.; Frank, R.; Galaburda, A. M.; Damasio, A. R. (1994). "The return of Phineas Gage: Clues about the brain from the skull of a famous patient". Science. 264 (5162): 1102–5. doi:10.1126/science.8178168. PMID 8178168.

- ^ Lena & Macmillan, p. 9; Harlow 1868, pp. 6,19; Bigelow 1850, p. 16–17; Harlow 1848, p. 390; Macmillan 2000, p. 86.
- ^ Eliot, Samuel Atkins, ed. (1911). "John M. Harlow". Biographical History of Massachusetts: Biographies and Autobiographies of the Leading Men in the State. Vol. 1. Massachusetts Biographical Society.

- ^ Harlow 1868, p. 20; Barker 1995, p. 672
- ^ a b c d e f K2.
- ^ a b "A most remarkable case". American Phrenological Journal and Repository of Science, Literature, and General Intelligence. 13 (4). Fowler & Wells. p. 89, col. 3. April 1851.

- ^ Cite error: The named reference
hamiltonwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Austin, K. A. (1977). A Pictorial History of Cobb and Co.: The Coaching Age in Australia, 1854–1924. Sydney: Rigby. ISBN 0-7270-0316-X.
- ^ Merwin, Mrs. George B. (1863). Three Years in Chili. New York: Follett, Foster and Company.

- ^ a b Jarrett, Christian (May 2012). "Neuroscience still haunted by Phineas Gage". BPS Research Digest – British Psychological Society.

- ^ M4.
- ^ Macmillan 2000, pp. 104, 121 n13; Macmillan & Lena, p.5
- ^ a b c M2.
- ^ F.
- ^ G.
- ^
Moffat, Gregory K. (2012). Browne-Miller, Angela (ed.). Fundamentals of Aggression. ABC-CLIO. p. 44. ISBN 978-0-313-38276-5.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|work=ignored (help)
- Nye, Robert Nason, ed. (1942). C. C. Thomas. pp. 366–7 http://books.google.com/books?id=sRmgAAAAMAAJ.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|work=ignored (help); Missing or empty|title=(help)
- Anonymous (1848); Macmillan 2000, p. 39.
- Nye, Robert Nason, ed. (1942). C. C. Thomas. pp. 366–7 http://books.google.com/books?id=sRmgAAAAMAAJ.
- ^
Beaumont, Graham; Kenealy, Pamela; Rogers, Marcus (1991). The Blackwell Dictionary of Neuropsychology. Wiley.

- Crider, A. B.; Goethals, G. R.; Kavanagh, R. D.; Solomon, P. R. (1983). Psychology. Scott, Foresman.
- Myers, David G. (1995). Psychology. Worth Publishers. ISBN 978-0-87901-644-9.

- Macmillan 2000, pp. 319, 327–8
- ^ Damasio 1994, pp. 11, 51; Macmillan 2000, pp. 119, 331.
- ^
Groves, Philip M.; Schlesinger, K. (1982). Introduction to Biological Psychology (2nd ed.). Dubuque, Iowa: Brown.
- Kalat, James W. (1981). Biological Psychology. Belmont, California: Wadsworth.
- Lahey, B. B. (1992). Psychology: An Introduction (4th ed.). Dubuque, Iowa: Brown. p. 63.
- Smith, A. (1985). The Body. Harmondsworth, England: Penguin.
- Macmillan 2000, p. 323.
- ^
Altrocchi, John (1980). Abnormal Behavior. Harcourt, Brace, Jovanovich. ISBN 978-0-15-500370-5.
- Morris, C. G. (1996). Psychology: An Introduction (9th ed.). Prentice-Hall.
- Macmillan 2000, pp. 107, 323.
- ^
Blakeslee, Sandra (May 24, 1994). "Old Accident Points to Brain's Moral Center". New York times. p. C1.
- Damasio et al. 1994, p. 1102; Macmillan 2000, p. 116.
- ^
Dimond, Stuart J. (1980). Neuropsychology: A Textbook of Systems and Psychological Functions of the Human Brain. London: Butterworths.
- Macmillan 2000, pp. 321, 331.
- ^
Restak, Richard M. (1984). The Brain. Bantam Books.
- Tow, Peter Macdonald (1955). Personality changes following frontal leucotomy: a clinical and experimental study of the functions of the frontal lobes in man. With a foreword by Sir Russell Brain. London, New York: Oxford University Press.
- Macmillan 2000, p. 323.
- ^
Blakemore, Colin (1977). Mechanics of the mind. Cambridge University Press.
- Brown, H. (1976). Brain and Behavior: A Textbook of Physiological Psychology. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Hart, Leslie A. (1975). How the Brain Works: A New Understanding of Human Learning, Emotion, and Thinking. Basic Books.
- Macmillan 2000, pp. 316, 323.
- ^
Hughes, C. D. (1897). "Neurological progress in America". Journal of the American Medical Association. 29 (7): 315–23.

- Smith, A. (1984). The Mind. London: Hodder and Stoughton.
- Wilson, Andrew (January 1879). The old phrenology and the new. Vol. CCXLIV. pp. 68 85.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help)
- Macmillan 2000, pp. 118, 316, 321.
- ^ Nye 1942, pp. 366–7
- ^ Blakeslee 1994; Macmillan 2000, pp. 119, 321.
- ^ Damasio 1994, p. 9; Macmillan 2000, p. 119.
- ^
Sdorow, Lester (1990). Psychology. Dubuque, Iowa: Brown.
- Macmillan 2008, p. 830; Macmillan 2000, p. 321.
- ^
Changeux, Jean-Pierre (1985). Neuronal Man: The Biology of the Mind. Tr. by Laurence Garey (1st American ed. ed.). Pantheon Books. pp. 158–9.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help)- Macmillan 2000, 321.
- ^ Blakeslee 1994; Macmillan 2000, p. 39.
- ^ Wood, Thomas F., ed. (July 1882). "Notes. Lodgement of Foreign Bodies in the Brain". North Carolina Medical Journal. 1 (1). Wilmington: 60–2.
- ^ M6.
- ^ Griggs, Richard A. (2015). "Coverage of the Phineas Gage Story in Introductory Psychology Textbooks: Was Gage No Longer Gage?". Teaching of Psychology. 42: 195–202. doi:10.1177/0098628315587614.
- ^ Benderly, Beryl Lieff (September 2012). "Psychology's tall tales". gradPSYCH. American Psychological Association: 20.

- ^ Macmillan 2000, pp. 119,316,323; Macmillan 2008, p. 830; Kotowicz, p. 130 n6.
- ^ Hockenbury, Don H.; Hockenbury, Sandra (1997). Psychology. Worth Publishers. ISBN 978-1-57259-396-1.

- ^ a b c Damasio, Antonio R. (1994). Descartes' error: emotion, reason, and the human brain. Quill. ISBN 978-0-380-72647-9.

- ^ Damasio, A. R.; Van Hoesen, G. W. (1983). Paul Satz; Kenneth M. Heilman (eds.). Emotional disturbances associated with focal lesions of the limbic frontal lobe. New York: Guilford Press. pp. 85–110. ISBN 978-0-89862-200-3.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help)
- ^ Bower, B. "The Social Brain: New Clues from Old Skull". JSTOR 3978044.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)
- ^ Stuss, D. T.; Gow, C. A.; Hetherington, C. R. (1992). "'No longer Gage': Frontal lobe dysfunction and emotional changes". Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 60 (3): 349–359. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.60.3.349. PMID 1619089.

- Hockenbury, Don H.; Hockenbury, Sandra E. (2008). Psychology. p. 74. ISBN 978-1-429-20143-8.

- Hockenbury, Don H.; Hockenbury, Sandra E. (2008). Psychology. p. 74. ISBN 978-1-429-20143-8.
- ^ a b F1.
- ^ Macmillan 2008, p. 831; Macmillan 2000, chs. 5–6, 9–14; Macmillan 1996, pp. 251–9.
- ^ Ferrier, David (1877–79). "Correspondence with Henry Pickering Bowditch". Countway Library (Harvard Univ.) Mss. HMS c5.2. Transcribed in Macmillan 2000, pp. 464–5.
- ^ Sacks, Oliver (1995). An Anthropologist on Mars. pp. 59–61. ISBN 0-679-43785-1. OCLC 30810706.

- ^ Gall, Franz Joseph (1835). Capen, Nahum (ed.). On the functions of the brain and of each of its parts: with observations on the possibility of determining the instincts, propensities, and talents, or the moral and intellectual dispositions of men and animals, by the configuration of the brain and head. The phrenological library. Translated from the French by Winslow Lewis, Jr. Boston: Marsh, Capen & Lyon.

- Sizer, Nelson (1888). Forty years in phrenology; embracing recollections of history, anecdote, and experience. New York: Fowler & Wells. p. 194.

- Sizer, Nelson (1888). Forty years in phrenology; embracing recollections of history, anecdote, and experience. New York: Fowler & Wells. p. 194.
- ^
Burton, Warren (1842). Uncle Sam's recommendation of phrenology to his millions of friends in the United States: In a series of not very dull letters. New York: Harper and Brothers. p. 217.

- Davidson, James Wood (July 1866). How We Read Each Other. Phrenology. Vol. 2. Atlanta: J.J. Toon. pp. 557–62, 559.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help)
- Phrenology for "Tim Bobbin". Vol. XXIV. February 13, 1897. p. 302.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help)
- Davidson, James Wood (July 1866). How We Read Each Other. Phrenology. Vol. 2. Atlanta: J.J. Toon. pp. 557–62, 559.
- ^
Carlson, N. R. (1994). Physiology of Behavior. p. 341. ISBN 0-205-07264-X.
- Macmillan 2000, pp. 246; 252–3 n9,10.
- ^ William G. Van der Kloot (1974). Readings in Behavior. Ardent Media. p. 289. ISBN 978-0-03-084077-7.

- ^ Damasio, Antonio R.; Everitt, B. J.; Bishop, D. (October 29, 1996). "The Somatic Marker Hypothesis and the Possible Functions of the Prefrontal Cortex [and Discussion]". Philosophical Transactions: Biological Sciences. Executive and Cognitive Functions of the Prefrontal Cortex. 351 (1346): 1413–1420. doi:10.1098/rstb.1996.0125.

- ^ K1.
- ^ a b c W2.
- ^ a b c d e f W.
- ^ a b c d e W1.
- ^ a b c L.
- ^ W3.
- ^ Smith, Stephen (July 22, 2009). "Icon, revealed: Newly discovered image offers fresh insights about medical miracle". Boston Globe.

- Carey, Benedict (Jul 22, 2009). "The Curious Case of Phineas Gage, Refocused". New York Times.

- Carey, Benedict (Jul 22, 2009). "The Curious Case of Phineas Gage, Refocused". New York Times.
- ^ A Memoir of Henry Jacob Bigelow. Boston: Little, Brown. 1894.

- ^ Jewett, M. (1868). "Extraordinary Recovery after Severe Injury to the Head". Western Journal of Medicine. 43: 241. Reprinted: Boston Medical and Surgical Journal. Vol. 78. Boston: David Clapp & Sons. April 23, 1868. pp. 188–9.

- ^ Sutton, W. L. (1850). "A Centre Shot". Boston Medical & Surgical Journal. 3: 151–2.

- ^ Folsom, A. C. (May 1869). "Extraordinary Recovery from Extensive Saw-Wound of the Skull". Pacific Medical and Surgical Journal. pp. 550–555.
- ^ "Medical Intelligence. Extraordinary Recovery". Boston Medical & Surgical Journal. 3 n.s. (13): 230–1. April 29, 1869.
- ^ Ordia, J. I. (1989). "Neurologic function seven years after crowbar impalement of the brain". Surgical Neurology. 32: 152–155. doi:10.1016/0090-3019(89)90204-8.
- ^ Mitchell, B.D.; Fox, B.D.; Humphries, W.E.; Jalali, A.; Gopinath, S. (2012). "Phineas Gage revisited: Modern management of large-calibre penetrating brain injury". Trauma. 14 (3): 263–269. doi:10.1177/1460408612442462.

- ^ Pancoast, Joseph (1852). A Treatise on Operative Surgery: Comprising a Description of the Various Processes of the Art, Including All the New Operations; Exhibiting the State of Surgical Science in Its Present Advanced Condition (3rd ed.). Philadelphia: A. Hart. p. 106.

- ^ Pott, Percivall (1790). James Earle (ed.). The chirurgical works : of Percivall Pott, F.R.S. Surgeon to St. Bartholomew’s Hospital. A new edition, with his last corrections. To which are added a short account of the life of the author ... London : printed for J. Johnson, G.G.J. and J. Robinson, T. Cadell, J. Murray, W. Fox, J. Bew, S. Hayes, and W. Lowndes. p. 184.

- ^ Macmillan 2000, p. 12, ch. 4, pp. 355–9; Macmillan 2008, pp. 28–9; Macmillan 2001, pp. 151–3.
Sources
- For general readers
- Harlow, John Martyn (1868). "Recovery from the Passage of an Iron Bar through the Head" (PDF). Publications of the Massachusetts Medical Society. 2: 327–47. Reprinted as Recovery from the Passage of an Iron Bar through the Head (David Clapp & Son, 1869). 22 pages.

- Kean, Sam (May 6, 2014). "Phineas Gage, Neuroscience's Most Famous Patient". Slate.

- Macmillan, Malcolm B. (2000). An Odd Kind of Fame: Stories of Phineas Gage. MIT Press. ISBN 0-262-13363-6 (hbk, 2000) ISBN 0-262-63259-4 (pbk, 2002).
 • See also "An Odd Kind of Fame §Corrections".
• See also "An Odd Kind of Fame §Corrections". 
- —— (September 2008). "Phineas Gage—Unravelling the myth". The Psychologist. 21 (9). British Psychological Society: 828–31.
{{cite journal}}: zero width joiner character in|title=at position 13 (help)
- —— (July 2009). "More About Phineas Gage, Especially After the Accident". Retrieved July 27, 2013.

- —— (2012). "The Phineas Gage Information Page". The University of Akron. Retrieved July 22, 2013. Includes:
- Macmillan, Malcolm B.; Aggleton, John (March 6, 2011). "Phineas Gage: The man with a hole in his head" (Audio interview). Interviewed by Claudia Hammond; Dave Lee.
{{cite interview}}: Unknown parameter|callsign=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|program=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: interviewers list (link)
- Twomey, S. (January 2010). "Finding Phineas". Smithsonian. 40 (10): 8–10.

- For young readers
- Fleischman, J. (2002). Phineas Gage: A Gruesome but True Story About Brain Science. ISBN 0-618-05252-6.

- For researchers and specialists
- Barker, F. G. II (1995). "Phineas among the phrenologists: the American crowbar case and nineteenth-century theories of cerebral localization" (PDF). Journal of Neurosurgery. 82 (4): 672–82. doi:10.3171/jns.1995.82.4.0672. PMID 7897537.

- Bigelow, Henry Jacob (July 1850). "Dr. Harlow's Case of Recovery from the Passage of an Iron Bar through the Head". American Journal of the Medical Sciences. 20: 13–22.

- —— (May 12, 1868). "Your favor of April 29th is before me" (manuscript). Letter to M. Jewett. Records of the Warren Anatomical Museum, 1828–1892 (inclusive) (AA 192.5), Harvard Medical Library in the Francis A. Countway Library of Medicine.
- Fuster, Joaquin M. (2008). The prefrontal cortex. Elsevier/Academic Press. p. 172. ISBN 0-12-373644-7.

- Grafman, J. (2002). "The Structured Event Complex and the Human Prefrontal Cortex". Principles of Frontal Lobe Function. pp. 292–310. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780195134971.003.0019. ISBN 978-0-195-13497-1.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|editors=ignored (|editor=suggested) (help)
- Gage, P.P. (185[4?]). "Please give my iron bar to the bearer" (Note to unknown recipient). Records of the Warren Anatomical Museum, 1828–1892 (inclusive) (AA 192.5), Harvard Medical Library in the Francis A. Countway Library of Medicine, Box 1.
- Harlow, John Martyn (December 13, 1848). "Passage of an Iron Rod Through the Head" (PDF). Boston Medical & Surgical Journal. 39 (20): 389–93. doi:10.1056/nejm184812130392001.
 (Transcription.)
(Transcription.)
- —— (January 3, 1849). "Medical Miscellany (letter)". Boston Medical & Surgical Journal. 39: 507. Reproduced in Macmillan 2000, p. 389.
- Kihlstrom, J. F. (2010). "Social neuroscience: The footprints of Phineas Gage". Social Cognition. 28 (6): 757–82. doi:10.1521/soco.2010.28.6.757.

- Lena, M. L.; Macmillan, Malcolm B. (March 2010). "Picturing Phineas Gage (Invited comment)". Smithsonian. p. 4.

- Kotowicz, Z. (2007). "The strange case of Phineas Gage". History of the Human Sciences. 20 (1): 115–31. doi:10.1177/0952695106075178.

- Macmillan, Malcolm B. (1996). Code, C.; Wallesch, C. W.; Lecours, A. R.; Joanette, U. (eds.). "Phineas Gage: A Case for All Reasons". Classic Cases in Neuropsychology. London: Erlbaum. pp. 243–62.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|displayeditors=ignored (|display-editors=suggested) (help)
- —— (2000). "Restoring Phineas Gage: A 150th Retrospective". Journal of the History of the Neurosciences. 9 (1): 46–66. doi:10.1076/0964-704X(200004)9:1;1-2;FT046. PMID 11232349.

- —— (2001). "John Martyn Harlow: Obscure Country Physician?". Journal of the History of the Neurosciences. 10 (2): 149–162. doi:10.1076/jhin.10.2.149.7254. PMID 11512426.

- ——; Lena, M. L. (2010). "Rehabilitating Phineas Gage" (PDF). Neuropsychological Rehabilitation. 20 (5): 641–658. doi:10.1080/09602011003760527. PMID 20480430.

- Ratiu, P.; Talos, I. F.; Haker, S.; Lieberman, D.; Everett, P. (2004). "The Tale of Phineas Gage, Digitally Remastered". Journal of Neurotrauma. 21 (5): 637–643. doi:10.1089/089771504774129964. PMID 15165371.

- Ratiu, P.; Talos, I. F. (2004). "The Tale of Phineas Gage, Digitally Remastered". New England Journal of Medicine. 351 (23): e21. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm031024. PMID 15575047.

- Tyler, K.L.; Tyler, H.R. (1982). "A 'Yankee Invention': the celebrated American crowbar case". Neurology. 32: A191.

- Van Horn, J. D.; Irimia, A.; Torgerson, C. M.; Chambers, M. C.; Kikinis, R.; Toga, A. W. (2012). "Mapping Connectivity Damage in the Case of Phineas Gage". PLoS ONE. 7 (5): e37454. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0037454. PMC 3353935. PMID 22616011.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link)
- Wilgus, B. & J. (2009). "Face to Face with Phineas Gage". Journal of the History of the Neurosciences. 18 (3): 340–5. doi:10.1080/09647040903018402. PMID 20183215.

- —— (July–September 2009). "Phineas Gage – Hiding in Plain Sight". The Daguerreian Society Newsletter. 21 (3): 6–9.
- —— (2009). "Meet Phineas Gage". Retrieved October 18, 2014.

- —— (2010). "A New Image of Phineas Gage". Retrieved March 10, 2010.

External links
[[:s:|]]
- Warren Anatomical Museum, Center for the History of Medicine, Francis A. Countway Library of Medicine (Harvard Medical School) – Home of Gage's skull and iron.
- Meet Phineas Gage – How the owners of the 2009-identified daguerreotype learned it depicted Gage.
- Phineas Gage roadside memorial, Cavendish, Vermont.
